A marine sediment-derived lignin-degrading bacteria and its application in degrading lignin
A technology for lignin degrading bacteria and marine sediments, which is applied in the field of applied microorganisms to achieve the effects of strong lignin degradation ability, increased separation efficiency and strong application value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Example 1 Acquisition of lignin-degrading bacteria DBX666
[0020] (1) Enrichment culture of lignin-degrading bacteria
[0021] Add 5 g of sediment to a conical flask containing 100 mL of enrichment medium, and cultivate at 8°C at 150 rpm for 15 days to obtain the first-generation enriched culture; 1% of the inoculum was inoculated into an Erlenmeyer flask with fresh enrichment medium, and cultured at 8°C at 150 rpm for 14 days to obtain a second-generation enriched culture; The % inoculum was inoculated into a conical flask with enriched medium, and cultured at 8°C at 150 rpm for 14 days to obtain the third-generation enriched culture. The sediments were from a station in the East Pacific. Sediment samples, the enriched medium formula is (g / L): K 2 HPO 4 , 0.1g; KH 2 PO 4 , 0.4g; (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 , 0.7125g; KNO 3 , 0.63125g; yeast extract, 0.1g; dealkalized lignin, 1g. Adjust the pH of the medium to 7.0.
[0022] (2) Screening and purification of lignin-degrad...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Example 2 Molecular identification and naming preservation of lignin-degrading bacteria DBX666 strain
[0025] (1) Molecular identification of strains
[0026]The conventional molecular cloning method was used to amplify and determine the 16S rDNA gene of the strain DBX666. The operation steps were as follows: ① DNA template preparation: pick a single colony with an inoculation loop into a 0.2 mL PCR tube containing 100 μl sterile water, boil at 98 °C for 15 min, Obtain a DNA template for PCR amplification. ②PCR amplification: The 16S rDNA amplification system (50ul) of the strain includes 0.5 μl of high-fidelity Taq enzyme, 5 μl of 10×Buffer, 4 μl of dNTP, 1 μl of upstream primer (1492R), 1 μl of downstream primer (27F), 1 μl of DNA template, deionized 37.5 μl of water; PCP reaction conditions are: pre-denaturation at 94 °C for 5 min, denaturation at 94 °C for 30 s, annealing at 56 °C for 30 s, extension at 72 °C for 2 min, after 30 cycles, final extension at 72 °C fo...
Embodiment 3
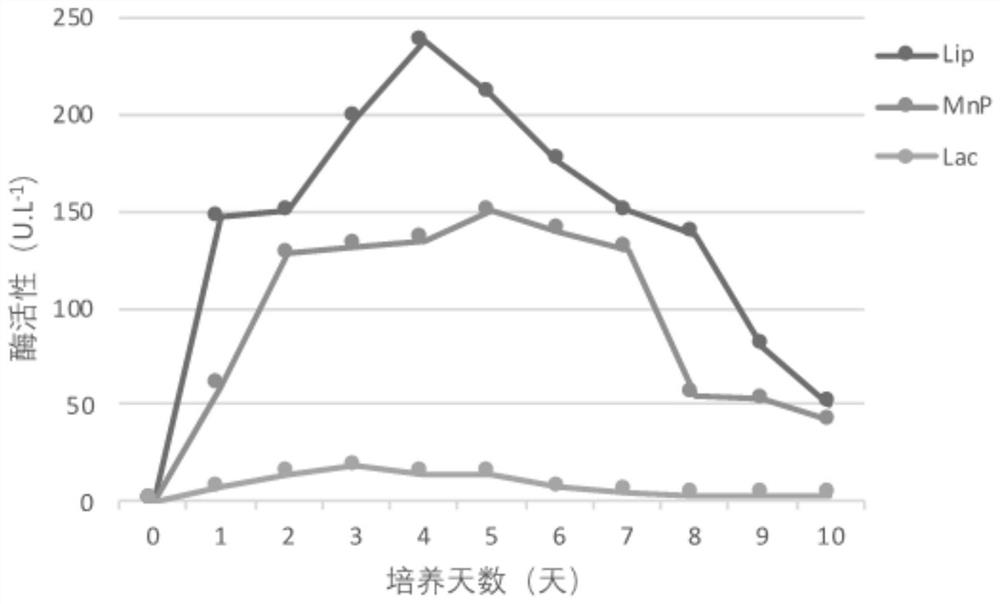
[0029] Example 3: Application of strain DBX666 in lignin degradation
[0030] (1) Determination of lignin degradation efficiency of strain DBX666
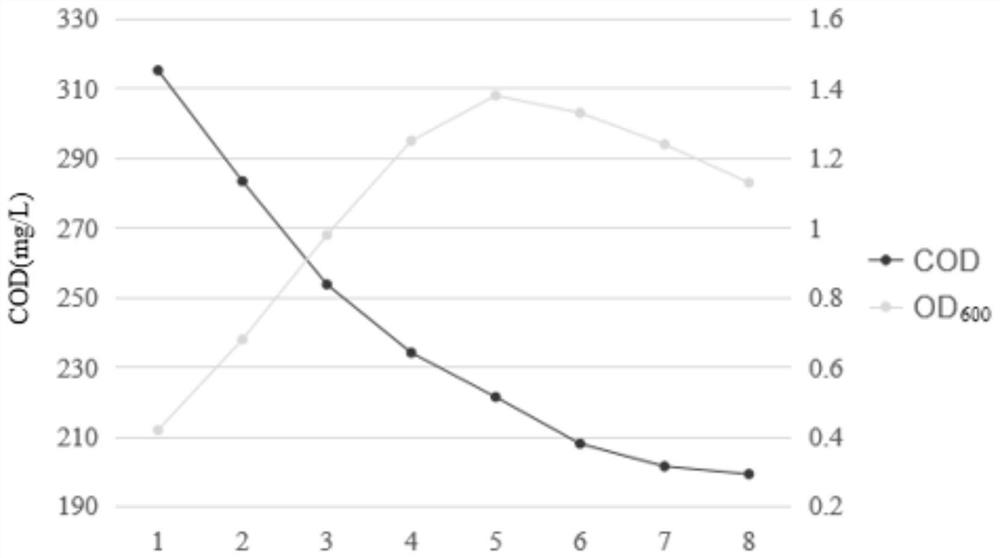
[0031] The strain DBX666 was inoculated into an enzyme-producing medium and cultivated to a logarithmic growth phase (OD600=0.6-0.8). Enzyme medium formulation includes: K 2 HPO 4 , 0.1g; KH 2 PO 4 , 0.4g; (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 , 0.7125g; KNO 3 , 0.63125g; yeast extract, 0.1g; dealkalized lignin, 1-5g, adjust the pH of the medium to 7.0. The bacterial solution was inoculated into the enzyme-producing medium at a ratio of 1:100, and cultured with shaking at 20°C at 150 rpm, and the bacterial solution was taken every 24 hours to determine the lignin degradation rate of the strain. In the enzyme-producing medium, lignin, as the only carbon source, contributed to the total COD load, so the removal of COD was used to characterize the degradation rate of lignin. The determination of COD adopts the chromate method in the national stand...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com