Application of alpha-L-rhamnosidase derived from bacteria in efficient production of hesperetin-7-O-glucoside
A technology of rhamnosidase and glucoside, applied in the application, glycosylase, enzyme and other directions, can solve the problem of non-specific hydrolysis bond type of rhamnosidase, achieve broad application prospects, simple separation and simple steps Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
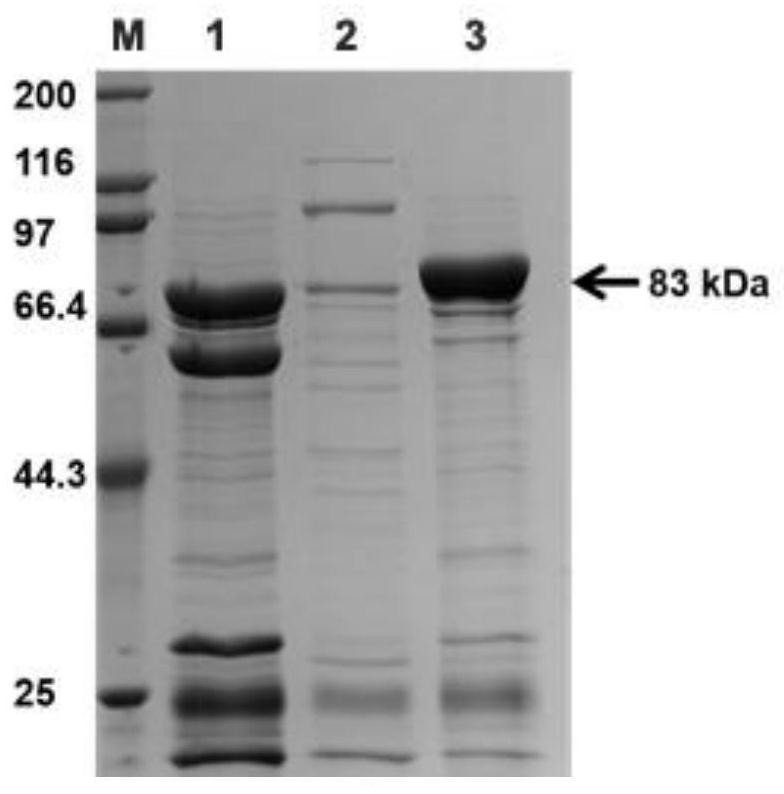
[0028] Embodiment 1: Cloning, expression and purification of α-L-rhamnosidase FjRha gene
[0029] Using the genomic DNA of Flavobacter johnii (CGMCC No.1.8922) from the China General Microorganism Culture Collection Center (http: / / www.cgmcc.net / ) as a template, according to the genome of Flavobacter johnii in the NCBI database The gene sequence of the predicted rhamnosidase (GenBank accession No.ABQ07113.1) was designed with upstream and downstream primers P1 and P2 for PCR amplification. The PCR amplification product was detected and purified by 0.8% agarose gel electrophoresis, and passed The PCR recovery kit is recovered to obtain the gene fragment of Flavobacterium johnsonii α-L-rhamnosidase FjRha;
[0030] Wherein, the sequences of the upstream and downstream primers P1 and P2 are as follows:
[0031] P1: 5'-AATT GCTAGC AATTGTTCCAGAGTTTGTTTT-3', the underline indicates the NheI restriction site,
[0032] P2: 5'-GCCG GAATTC CTAAACCGCTTTTCCATTT-3', the underline indicate...
Embodiment 2
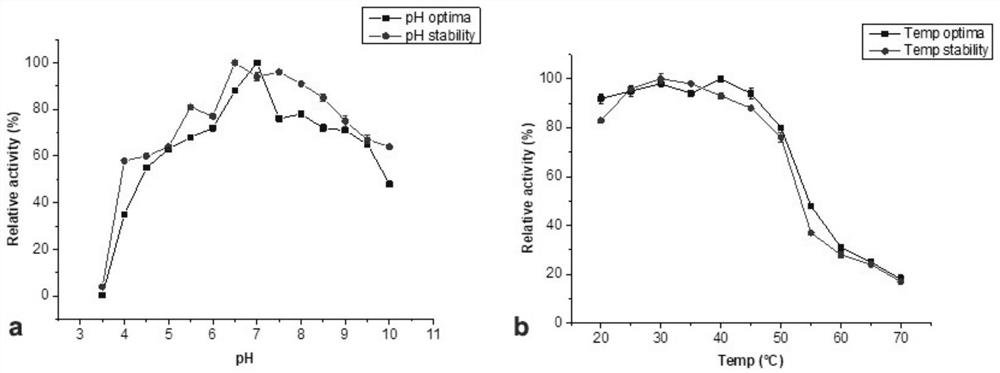
[0041] Example 2: Enzymatic properties of recombinant α-L-rhamnosidase FjRha
[0042] 2.1 Enzyme activity assay
[0043] Take 20 μL of enzyme solution, add 60 μL of 2 mM pNP-Rha solution (pH 6.5, prepared in 50 mM sodium phosphate buffer), react at 37°C for 10 min, add 120 μL of 5 mM sodium carbonate solution to terminate the reaction, OD 405 nm detects absorbance. The measured enzyme activity of the recombinant α-L-rhamnosidase FjRha enzyme solution was 1U / mg enzyme protein.
[0044] Enzyme activity is defined as: 1 μmol of p-nitrophenol is released by hydrolyzing pNP-Rha per minute, which is 1 enzyme activity unit (U).
[0045] 2.2 Determination of specificity of enzyme hydrolysis substrate
[0046] Using pNP-Rha, hesperidin, naringin and rutin as substrates to detect the hydrolysis activity of recombinant α-L-rhamnosidase FjRha on artificial substrate pNP-Rha and natural substrates containing different rhamnosidic bonds .
[0047] The specific reaction of substrate hyd...
Embodiment 3
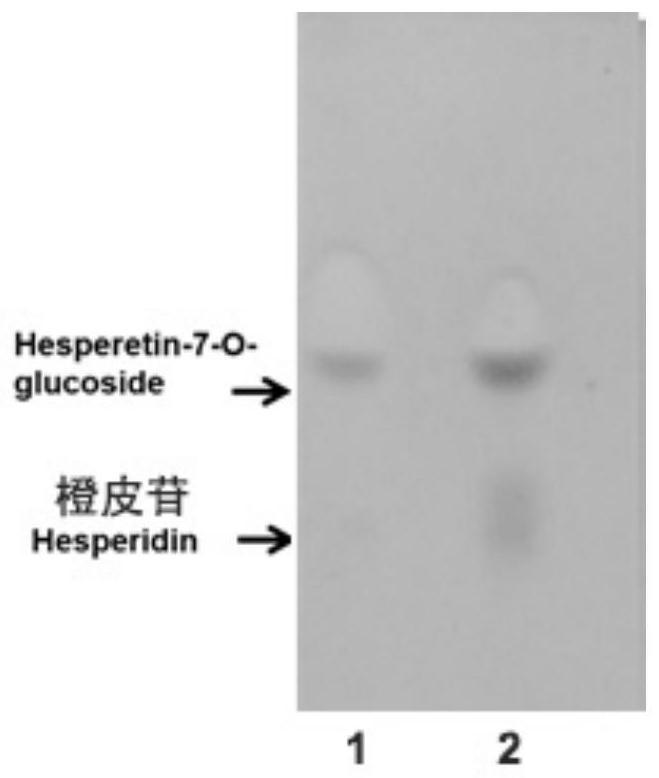
[0060] Example 3: Recombinant α-L-rhamnosidase FjRha catalyzes hesperidin to generate hesperetin-7-O-glucoside
[0061] In 10mL, 50mM Tris-HCl buffer, hesperidin final concentration 5mM (3g / L), 8U / mL recombinant α-L-rhamnosidase FjRha, pH 7.0, react at 37°C, shake 100rpm for 20h , to get the reaction solution.
[0062] 3.1 TLC analysis of hesperetin 7-O-glucoside
[0063] Take 1 μL of the above reaction solution, spot the sample at the origin of the TLC silica gel plate, develop the layer system (chloroform: ethyl acetate: methanol: water = 3:3:1:0.2, volume ratio) to perform chromatography on the sample on the silica gel , blow dry after chromatography, the color developer is anisaldehyde-sulfuric acid solution, blow dry after dyeing, and heat the alcohol lamp to develop color. TLC analysis results such as image 3 As shown, a product point consistent with the mobility and color reaction of hesperetin 7-O-glucoside appeared in the reaction solution, and it was preliminaril...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com