Non-metal heating plate for cooking, preparation method thereof and heating device
A heating device, non-metallic technology, applied in the field of heating device, non-metallic heating plate for cooking and its preparation, to achieve the effect of smooth surface, easy operation and high surface density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0095] Correspondingly, the present invention also provides a method for preparing a non-metal heating plate for cooking, including:
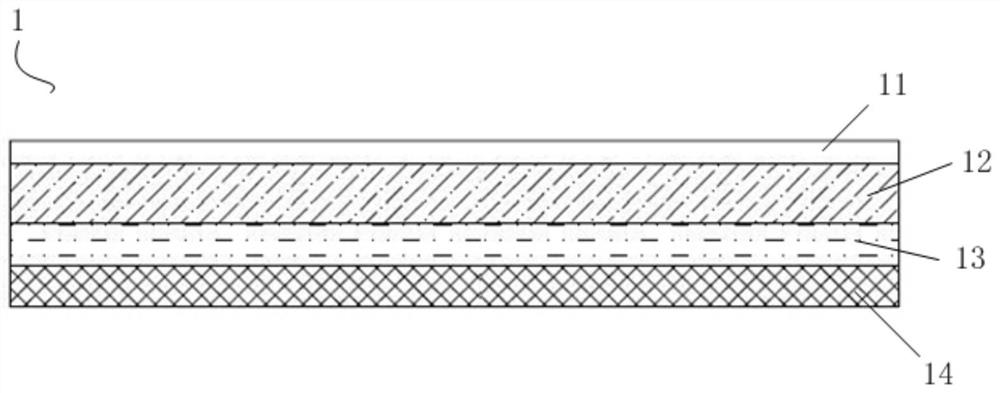
[0096] 1. Select expansion coefficient -6 K -1 The ceramic substrate, its surface is polished;
[0097] It should be noted that the technical details of the ceramic substrate are the same as those described above, and will not be repeated here.
[0098] 2. Select expansion coefficient -6 K -1 A glass sheet whose thermal expansion coefficient differs from that of the ceramic substrate by -6 K -1 ;
[0099] It should be noted that the technical details of the glass sheet are the same as those described above, and will not be repeated here.
[0100] 3. The ceramic substrate and the glass sheet are bonded together and sintered to form an integrated structure to obtain a ceramic substrate covered with a glass sheet.
[0101] It should be noted that, after the ceramic substrate and the glass sheet are bonded together, they are preferably put int...
Embodiment approach
[0128] The grounding method of the present invention has multiple implementations, including:
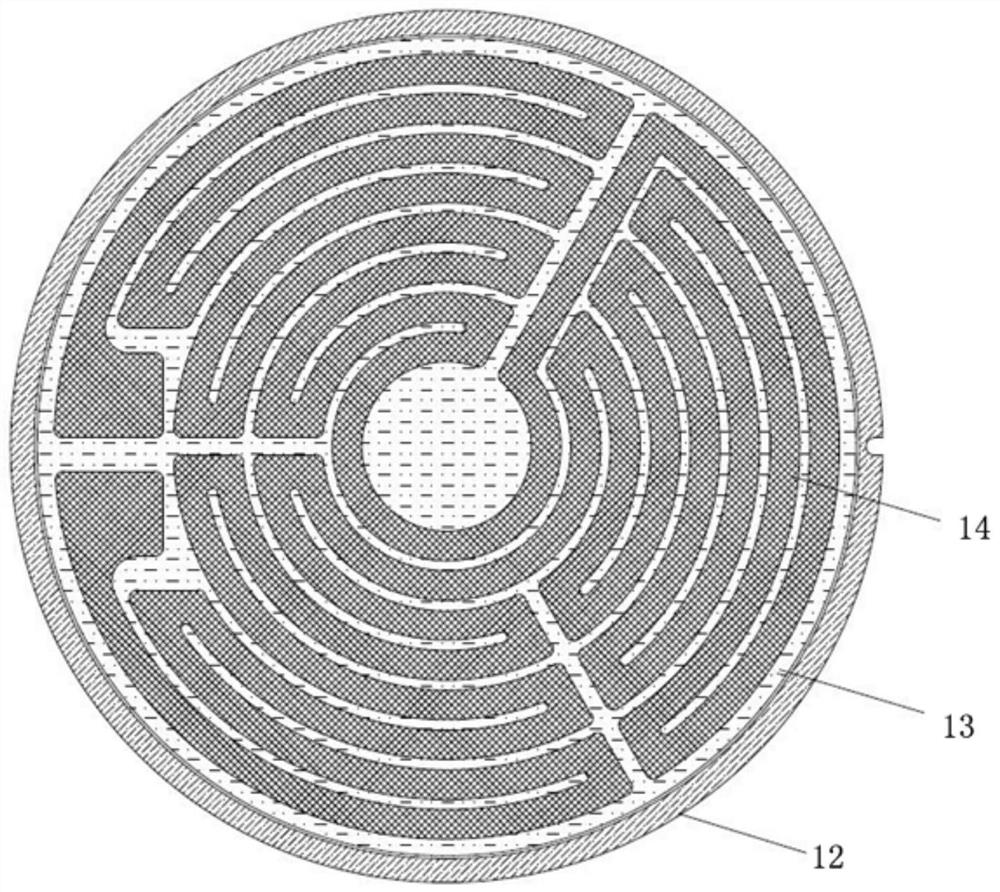
[0129] Such as Figure 5 with Figure 7 As shown, as the first embodiment of the grounding method of the present invention, the conductor is directly the conductive glass sheet 11 or the conductive ceramic substrate 12, and the grounding member 162 is against the conductive glass sheet 11 or the conductive ceramic substrate 12. catch.
[0130] Conductive glass sheets can be realized in this way. You can choose conductive glass sheets, or you can sinter glass paste containing gold, silver, platinum, palladium, ruthenium, nickel, copper and other metals through high temperature sintering to obtain conductive glass sheets. pieces of glass.
[0131] Specifically, the conductive ceramic substrate can be realized in this way. During the preparation process of the ceramic substrate, conductive materials are added to finally produce a ceramic substrate with certain conductivity.
[0132...
Embodiment 1
[0146] 1. Choose a 2.0mm thick silicon carbide ceramic substrate (the thermal expansion coefficient is about 4.5×10 -6 K -1 ) and 0.1mm thick silica-alumina glass sheet (thermal expansion coefficient is about 3.7×10 -6 K -1 ), bond the ceramic substrate and the glass sheet, and sinter at 950° C. for 10 minutes to obtain a composite substrate. Then screen-print SiO on the backside of the SiC ceramic substrate 2 -Al 2 o 3 -B 2 o 3 The insulating dielectric slurry is sintered at 850° C. for 10 minutes to form a film to form an insulating glaze layer to obtain a composite ceramic substrate.
[0147] 2. The performance test results of the above composite ceramic substrate are as follows:
[0148]
[0149] The composite ceramic substrate has excellent comprehensive performance and is suitable for use as a heating disk substrate of a glass jug.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com