Method for controlling fermentation of macrolide antibiotics
A technology of macrolides and macrolides, which is applied in the field of fermentation regulation of macrolide antibiotics based on culture temperature regulation, can solve the problem of rising, difficulty in controlling the fermentation process, and inability to continuously meet the needs of product synthesis, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of reducing consumption, improving equipment utilization, and easy control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Bacteria: Streptomyces avermitilis Streptomyces avermitilis SIIA-1502
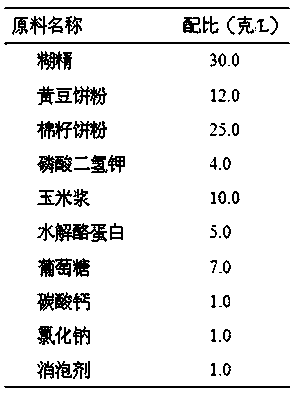
[0022] Proportion of fermentation medium:
[0023]
[0024] Accurately weigh the starch according to the specified ratio and put it into the fermentation batching tank (add appropriate amount of water in advance), start stirring, add amylase (0.5% of the weight of starch) and steam to heat, gradually raise the temperature to 85°C, keep stirring for 60 minutes, so that the starch is fully liquefaction. Put the above ingredients into the batching tank and add water to a constant volume, stir for 15 minutes and measure the pH, the pH should be 6.9, heat up, and when the temperature reaches 121°C, start to sterilize for 30 minutes.
[0025] Fermentation volume: 6000L;
[0026] Inoculation amount: 10 eggplant bottles;
[0027] Stirring speed: 80-220rpm;
[0028] Air flow: 1:0.5-0.8vvm;
[0029] Culture cycle: 315 hours.
[0030] In the early 80 hours of the fermentation of the abamectin-produc...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Strains: Actinomycetes mobilis SIIA-1602 ( Actinoplanes SIIA-1602)
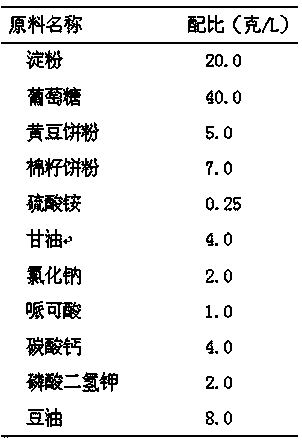
[0050] Proportion of fermentation medium:
[0051]
[0052] Accurately weigh the starch according to the specified ratio and put it into the fermentation batching tank (add appropriate amount of water in advance), start stirring, steam heating, gradually raise the temperature to 70°C, keep stirring for 10 minutes, so that the starch is fully gelatinized. Put the above ingredients into the batching tank and add water to a constant volume, stir for 15 minutes, then measure the pH, the pH should be 6.9, heat up, and when the temperature reaches 121°C, start to sterilize for 30 minutes.
[0053] Fermentation volume: 6000L;
[0054] Inoculation amount: 8%;
[0055] Stirring speed: 80-220rpm;
[0056] Air flow: 1:0.5-0.8vvm;
[0057] Culture cycle: 220 hours.
[0058] In the early stage of 0-60 hours of fermentation of the sirolimus-producing bacteria, the mycelium is rapidly grown through the basal...
Embodiment 3
[0075] Strain: New species of Streptomyces thousand Buddha SIIA-9818 ( Streptomyces qianfoensis sp.nov. SIIA-9818)
[0076] Proportion of fermentation medium:
[0077]
[0078] Accurately weigh the starch according to the specified ratio and put it into the fermentation batching tank (add appropriate amount of water in advance), start stirring, steam heating, gradually raise the temperature to 70°C, keep stirring for 10 minutes, so that the starch is fully gelatinized. Put the above ingredients into the batching tank and add water to a constant volume, stir for 15 minutes and measure the pH, the pH should be 6.9, heat up, and when the temperature reaches 121°C, start to sterilize for 30 minutes.
[0079] Fermentation volume: 6000L;
[0080] Inoculation amount: 8%;
[0081] Stirring speed: 80-220rpm;
[0082] Air flow: 1:0.8-1.0vvm;
[0083] Culture cycle: 220 hours.
[0084] In the early stage of fermentation of tacrolimus-producing bacteria for 0-48 hours, the myce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com