Hard alloy with surface-layer binding-phase-rich gradient structure and preparation method thereof
A cemented carbide and gradient structure technology, applied in the field of powder metallurgy, can solve the problems of low binder content in the surface layer, toughening effect, chipping, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
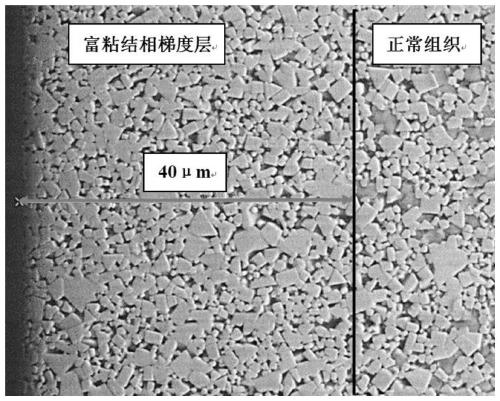
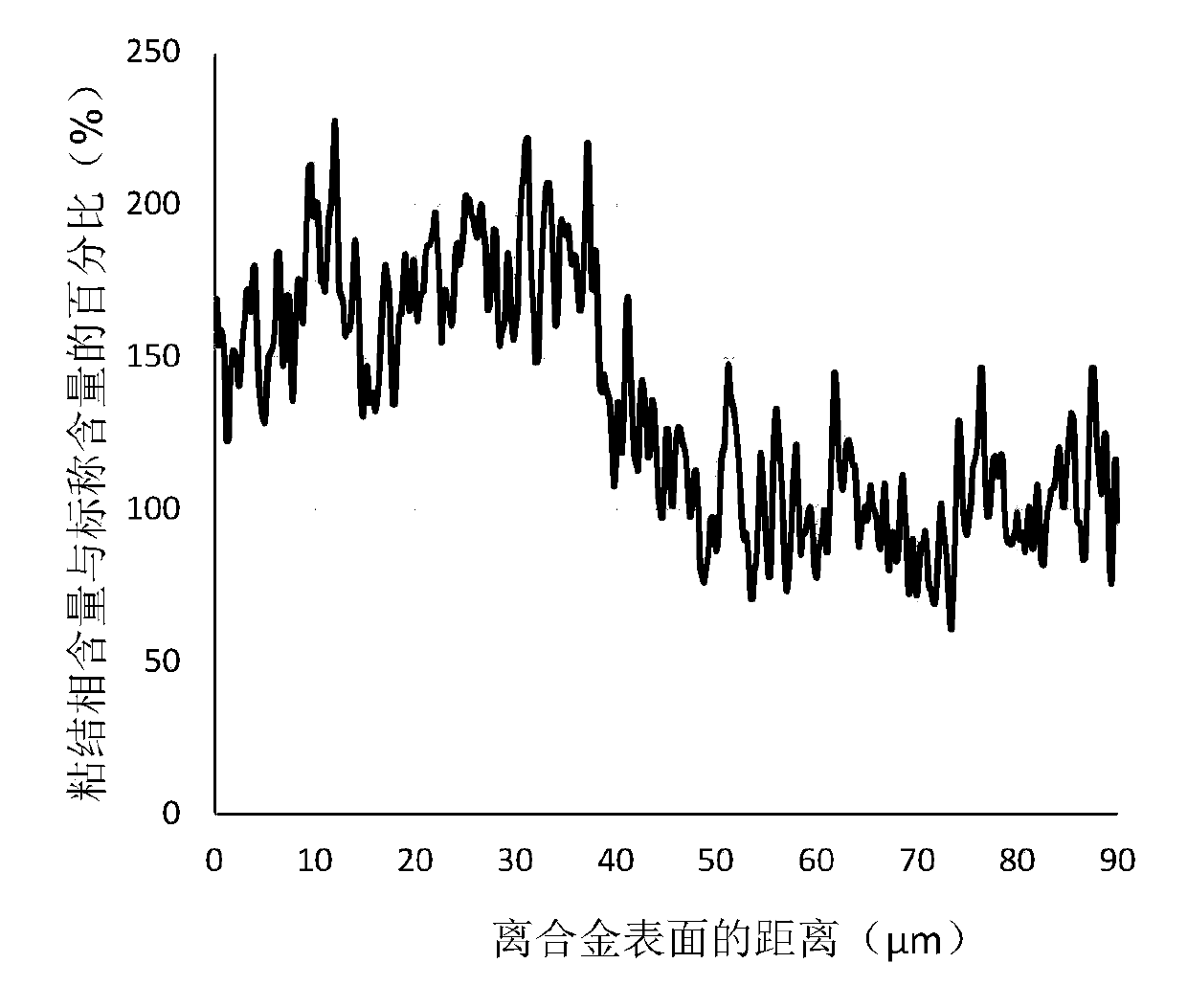
[0045] A kind of cemented carbide of the present invention has surface layer rich binder phase gradient structure, described cemented carbide is made of WC, Co, Re, TaC, NbC, TiC, TiC 0.5 N 0.5 composition. The mass percentage of each substance in the cemented carbide is: WC 79.5%, Co 8%, Re 0.5%, TaC 5%, NbC 3%, TiC 2%, TiC 0.5 N 0.5 2%. The thickness of the binder-rich gradient structure is 40 μm, and the content of the binder phase at 0-20 μm away from the alloy surface is evenly distributed, about 11%, which is 137.5% of the nominal content of 8%. The binder phase at 20-32 μm away from the alloy surface The junction phase content is evenly distributed, about 15%, which is 188% of the nominal content of 8%. Lower, here the transition layer between the gradient layer and the core tissue (normal tissue). Such as figure 1 Shown is the binder phase distribution map (EPMA) in the 100 μm region of the cemented carbide surface of the embodiment of the present invention. Suc...
Embodiment 2
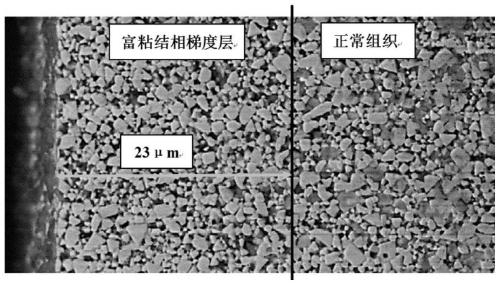
[0053] A kind of cemented carbide of the present invention has surface layer rich binder phase gradient structure, described cemented carbide is made of WC, Co, TaC, NbC, TiC, TiC 0.5 N 0.5 composition. The mass percentage of each substance in the cemented carbide is: WC 83%, Co 7%, TaC 4%, NbC 2%, TiC 3%, TiC 0.5 N 0.5 1%. The thickness of the binder-rich gradient structure is 25 μm, and the content of the binder phase at 0-15 μm from the alloy surface is evenly distributed, about 10%, which is 143% of the nominal content of 7%. The binder phase at 15-25 μm from the alloy surface The content of the binding phase is evenly distributed, about 12.5%, which is 178.5% of the nominal content of 7%, and the content of the binding phase decreases rapidly at a distance of 25-30 μm from the alloy surface, which is between the gradient layer and the core tissue (normal tissue) transition layer. Such as image 3 Shown is the binder phase distribution map (EPMA) in the 100 μm region...
Embodiment 3
[0060] A kind of cemented carbide of the present invention has surface rich binder phase gradient structure, described cemented carbide is made of WC, Co, Ni 3 Al, B, TaC, TiC, TiC 0.5 N 0.5 composition. The mass percentage of each substance in cemented carbide is: WC accounts for 84.95%, Co accounts for 8%, Ni 3 Al accounted for 1%, B accounted for 0.05%, TaC accounted for 2%, TiC accounted for 3.5%, TiC 0.5 N 0.5 0.5%. The thickness of the gradient structure rich in binder phase is 47 μm, and the content of binder phase at 0-20 μm away from the alloy surface gradually increases from 9.6% to 13%, which is 120-162% of the nominal content of 8%, and 20% away from the alloy surface The binder phase content at -47μm is evenly distributed, about 14.0%, which is 175% of the nominal content of 8%, and the binder phase content decreases rapidly at 47-50μm from the alloy surface, where the gradient layer and the core structure ( transition layer between normal tissues). Such as...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com