A carbonyl reductase resistant to high concentration of alcohol solution and its application
A carbonyl reductase and alcohol solution technology, applied in the field of biological enzyme catalysis, can solve the problems of affecting conversion rate, poor fluidity of conversion system, limiting substrate concentration and dosage, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
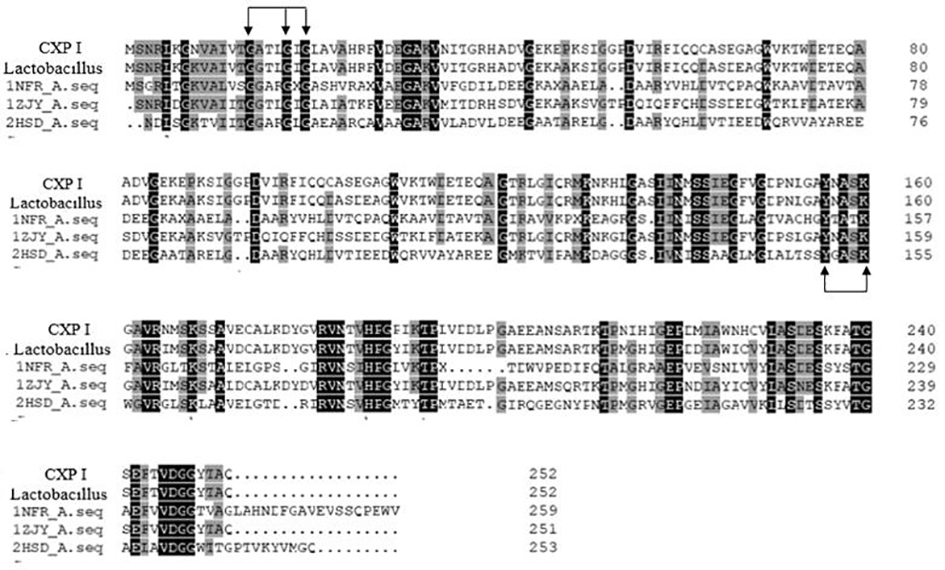
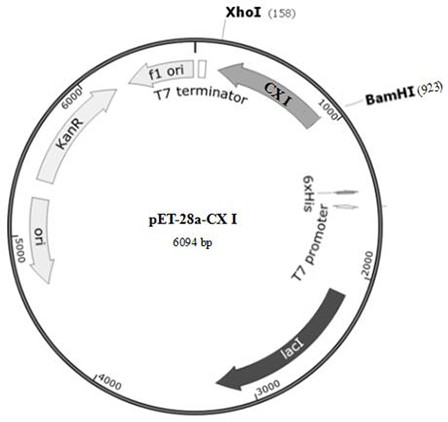
[0041] Carbonyl reductase CXP I, whose amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.1, contains a polypeptide chain consisting of 253 amino acids, and is obtained by performing site-directed mutation on the gene of CX-LAC II strain.
[0042] The CX-LAC II strain was deposited in the China Type Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on February 24, 2020. The preservation address is: No. 3, No. 1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, No. 19432, and it was identified as Lactobacillus furfur ( Lactobacillus farraginis ), facultative anaerobic, in the MRS solid medium, the colony is raised, slightly white, moist, with neat edges, and the colony is round, with a diameter of 3.0 mm±1.0 mm. Microscopically, Gram-positive, generally short rods arranged in chains, usually immobile. CX-LAC II contains the gene sequence CX II as shown in SEQ ID No.3.
[0043] Conduct site-directed mutation design on the gene sequence of CX II, mutate the 24th base A to T, the 519th base T to A, the ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] This embodiment also provides two amino acid sequences, SEQ ID NO.8 and SEQ ID NO.9, which have no less than 90% homology with the sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1, which are based on the CX II gene of CX-LAC II For site-directed mutation, the mutation rules should at least include the mutation of K at position 8 to N, the mutation of D at position 173 to E, the mutation of Y at position 190 to P, and the mutation of I at position 226 to N. At the same time, the coenzyme binding domain conservative sequence GATLGIG (position 14-20 in the amino acid sequence of CXP II) and the catalytic conservative sequence YNASK (position 156-160 in the amino acid sequence of CXP II) should be retained during mutation. At the same time, amino acid residues 190-220 need to be reserved. This region forms a loop structure in the protein structure and can be used to bind the loop with the substrate.
Embodiment 3
[0051] With (3S)-3-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino-1-chloro-4-phenyl-2-butanone as the substrate, the six carbonyl reductase crude enzyme solutions obtained in Example 1 were used for enzyme activity experiments . The names, nucleotide sequences and corresponding mutation sites of the six carbonyl reductases are shown in Table 1:
[0052]
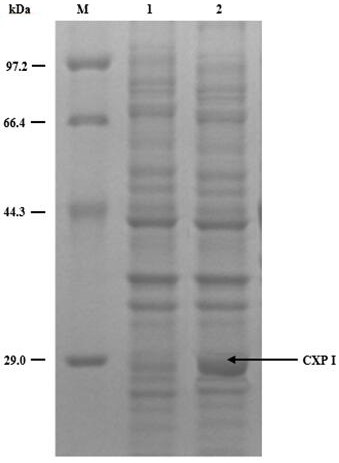
[0053] Prepare the reaction system as follows: 50 mL system: add 1g (3S)-3-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino-1-chloro-4-phenyl-2-butanone, add different concentrations of isopropanol, stir at 40°C, Add 2.4 g magnesium sulfate, 130 mg NAD + , use potassium phosphate or sodium buffer solution (100 mmol / L, pH8.0) to make up to 50 mL, and add 1 g of crude enzyme solution. After reacting for 24 h, the conversion rate and de value were detected by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The results are shown in Table 2. It can be seen that CXP I can be normally converted to almost exhausted substrate under 60% (m / V) isopropanol concentration, an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com