Method for treating radioactive element-containing wastewater by using zeolitic material
A technology for the treatment of radioactive elements and materials, applied in the fields of radioactive pollutants, non-metallic elements, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of limited adsorption effect and high cost of radioactive elements, and achieve high use value, fast reaction speed, and efficient adsorption. effect of ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
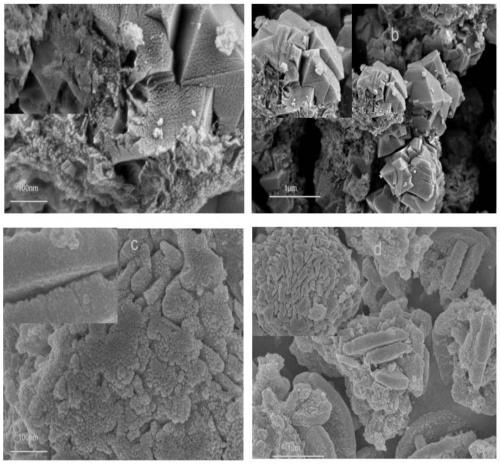
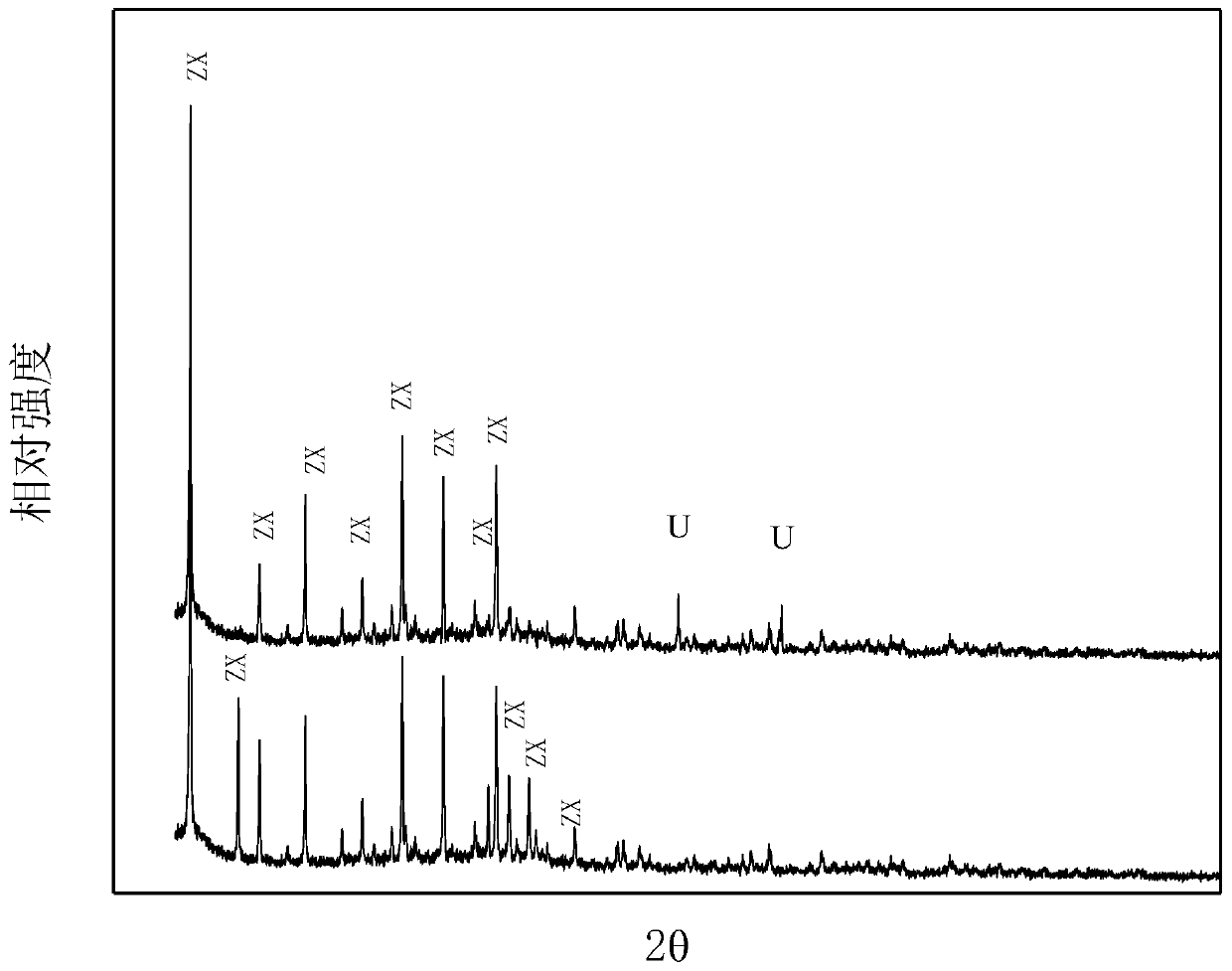
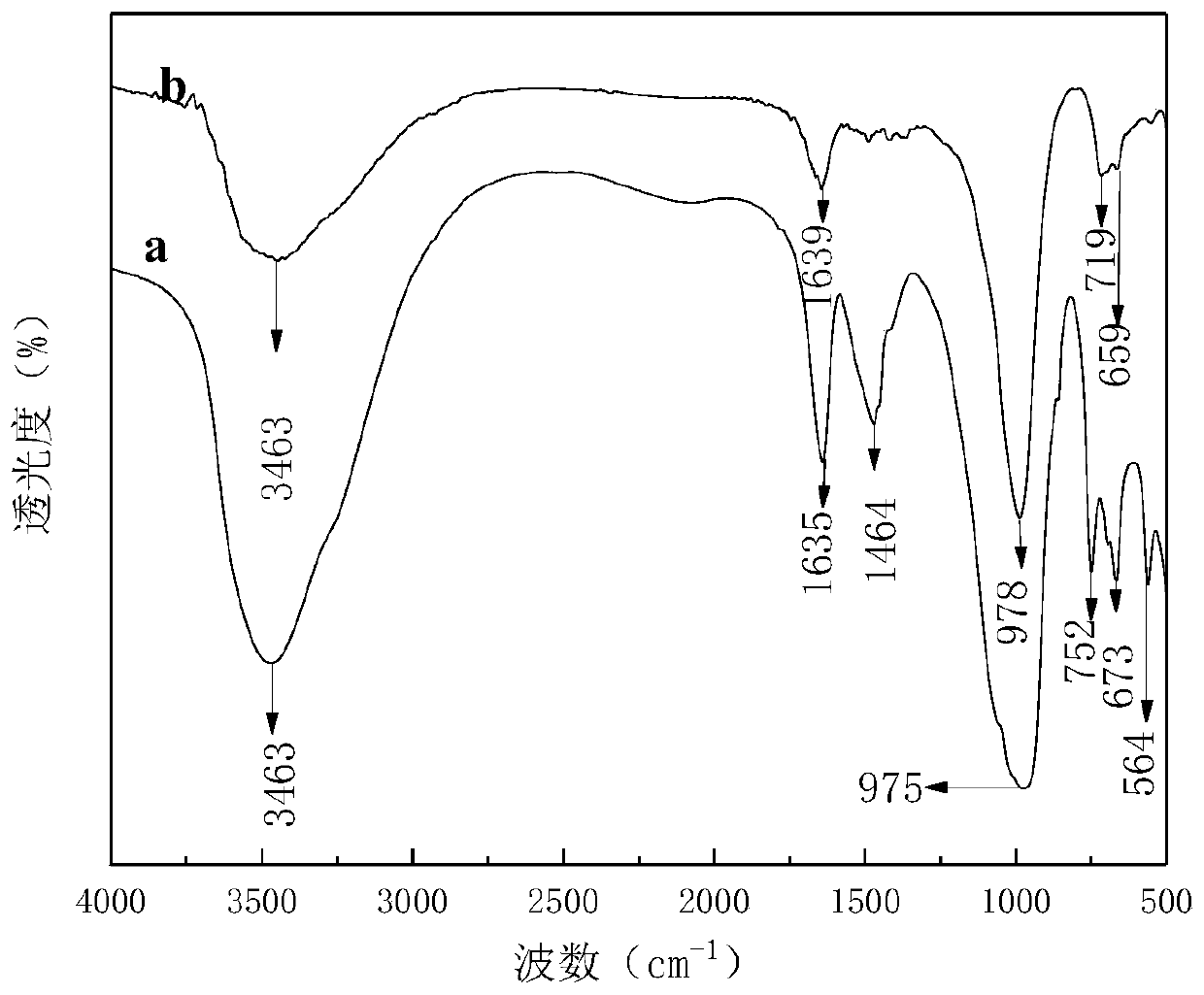
[0044] According to m (basalt material): m (hydrochloric acid) = 10: 1, m (basalt material after pickling): m (sodium hydroxide) = 1: 1, weigh 40g of basalt material and dissolve in 50ml of hydrochloric acid solution ; 10g of pickled, washed and dried basalt material and 10g of sodium hydroxide particles were evenly mixed and placed in a crucible, and roasted at 650°C for 3h in a muffle furnace. Then take out the roasted solid, add 50ml of deionized water, age for 10h under the condition of magnetic stirring at 150r / min, transfer the mixture to a polytetrafluoroethylene autoclave, put it in an oven, and crystallize at a constant temperature of 120°C for 12h Afterwards, the reactor was taken out and cooled to room temperature. The obtained precipitate was washed with deionized water until neutral, and the solid and liquid were centrifuged, and the upper layer solid was taken in a thermostat, and dried at 60° C. for 12 hours to obtain the product. Wherein the upper white solid ...
Embodiment 2
[0055] This example is to investigate the adsorption of basalt-based X-type zeolite materials to uranium-containing wastewater with different pH values. Image 6 The initial concentration of uranium-containing wastewater in the tests shown was 35 mg.L -1 , the adsorption time is 8h, the wastewater temperature is 30°C, the volume of the uranium-containing wastewater used in the test is 340mL, the amount of adsorbent in the wastewater is 0.005g, and the pH value of the wastewater is 3-10.
[0056] Depend on Image 6 It can be seen that the pH value of the wastewater is in the range of 5-7, and the composite material has a high adsorption capacity for uranium in the uranium-containing wastewater. from Image 6 It can be seen that the uranium-containing wastewater to be treated has a pH of 6 and is the result of adsorption of UO by basalt-based X-type zeolite materials. 2 2+ The optimal pH value, and the adsorption effect of this pH value data point is significantly better tha...
Embodiment 3
[0058] This example is to investigate the variation of the adsorption of basalt-based X-type zeolite material to uranium-containing wastewater with temperature. Figure 7 The initial concentration of uranium-containing wastewater in the tests shown was 35 mg.L -1 , the adsorption temperature is 25-45°C, the pH of the wastewater is 6, the volume of the uranium-containing wastewater used in the test is 340mL, the amount of adsorbent in the wastewater is 0.005g, and the adsorption time of the wastewater is 12h.
[0059] Depend on Figure 7 It can be seen that at a temperature of 30°C, the basalt-based X-type zeolite material has the maximum adsorption capacity of uranium in uranium-containing wastewater (adsorption capacity is 2268mg / g, adsorption rate is 95.33%). from Figure 7 It can be seen that when the adsorption temperature is 30°C, it is the best adsorption temperature. Additionally, from Figure 7 It can be seen that when the temperature of wastewater adsorption is 30...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com