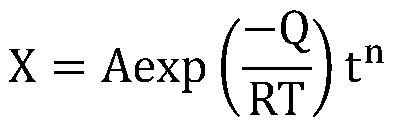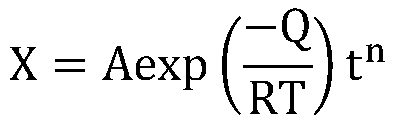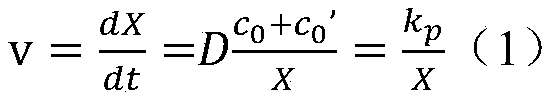Method for calculating thickness of oxide film of martensite heat-resistant steel under supercritical high-temperature steam
A technology of high-temperature steam and calculation methods, applied in chemical statistics, computational theoretical chemistry, computer material science, etc., can solve problems such as accelerated oxidation corrosion, need to cut pipes, and different growth rates of scale, so as to save costs and guarantee The effect of safe operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] The calculation method involved in the present invention is compared with the T91 oxidation experiment results.
[0058] In 2013, Ma Yunhai et al. reported the oxidation of T91 steel at 26MPa, 600°C / 650°C / 700°C, respectively substituted the experimental conditions into the formula proposed by the present invention, and used the present invention to calculate the oxide film thickness and its experimental The measured thicknesses were compared and the results are shown in Table 2. It can be seen that the calculated thickness is very close to the experimentally measured thickness.
[0059] Table 2 The present invention calculates the comparison of thickness and measured thickness
[0060] temperature / ℃ time / h Measuring thickness / μm Calculate thickness / μm Absolute error / μm Error percentage / % 600 1100 75 80.2 5.2 6.9 650 500 106 109.8 3.8 3.6 700 1000 238 258.2 20.2 8.5
Embodiment 2
[0062] The calculation method involved in the present invention is compared with the T / P92 experimental results.
[0063] Zhu Zhongliang et al. reported in 2013 the experiment of P92 steel oxidized at 550 °C and 25 MPa for 600 h. According to the SEM image of its cross-section, the thickness of the oxide film was about 28 μm. Substituting the above experimental conditions into the fitting formula obtained in the present invention, the calculated oxide film thickness is 28.8 μm, which is very close to the measurement result, and the error percentage is only 2.8%.
Embodiment 3
[0065] The calculation method involved in the present invention is applied in the actual power plant environment.
[0066] According to the steam scale thickness data of boiler pipes operating in power plants recorded in the "Design Guidelines for Preventing Steam Oxidation, Flue Gas Corrosion and Erosion of Heating Surface Tubes of Pulverized Coal Boilers in Large Power Plants", the oxidation of T92 pipes after 22981 hours of operation at 600 ° C and 25 MPa The skin thickness was 376 μm. Substituting the above conditional parameters into the fitting formula obtained in the present invention, the calculated thickness of the oxide film is 367.14 μm, and the error is only 2.4% compared with the measurement result, which shows that the fitting formula obtained in the present invention performs well in practical applications.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com