A production method of austenitic stainless steel for controlling cobalt content
A technology of austenitic stainless steel and a production method, which is applied in the production field of austenitic stainless steel for controlling cobalt content and can solve problems such as the inability to meet the use requirements of austenitic stainless steel for nuclear
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
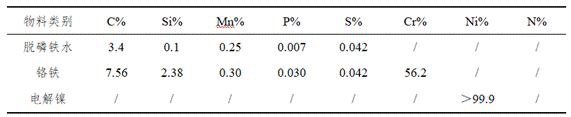
[0049] Step 1, raw material preparation: 114t of nuclear austenitic stainless steel molten steel smelted in this embodiment requires 70t of dephosphorized molten iron, 38t of ferrochrome, and 9.1t of electrolytic nickel, wherein the chemical compositions of dephosphorized molten iron, ferrochrome and electrolytic nickel are as follows Table 1 shows.
[0050] Table 1 Chemical composition of dephosphorized hot metal, ferrochrome and electrolytic nickel in Example 1
[0051]
[0052] Step 2. AOD process control: smelting in a furnace with a furnace age of 50, AOD reduction slag alkalinity 2.0, desulfurization stage alkalinity 3.0, slag dumping after reduction, ladle slag amount 250mm.
[0053] Step 3, LF treatment process: After the slag is pulled into the station, the temperature is measured at 1578°C, and after 5 minutes of power transmission, 85kg of electrolytic nickel and 210kg of ferrochrome are added, and the temperature is measured again at 1582°C. Blow for 12 minutes...
Embodiment 2
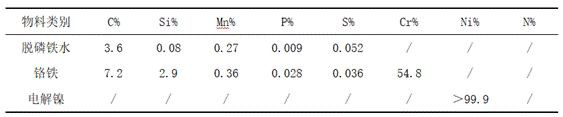
[0056] Step 1, raw material preparation: 110t of nuclear austenitic stainless steel molten steel smelted in this embodiment requires 68t of dephosphorized molten iron, 37t of ferrochrome, and 8.9t of electrolytic nickel, wherein the chemical compositions of dephosphorized molten iron, ferrochrome and electrolytic nickel are as follows Table 2 shows.
[0057] Chemical composition of dephosphorized hot metal, ferrochrome and electrolytic nickel in Table 2 Example 2
[0058]
[0059] Step 2, AOD process control: smelting with a furnace age of 20 furnaces, AOD reduction slag alkalinity 1.9, desulfurization stage alkalinity 2.5, slag dumping after reduction, ladle with slag 200mm.
[0060] Step 3, LF treatment process: After removing slag, enter the station to measure the temperature at 1568°C, add 108kg of electrolytic nickel after 8 minutes of power transmission and temperature rise, measure the temperature again at 1586°C, start weak blowing for 15 minutes, and calm down for ...
Embodiment 3
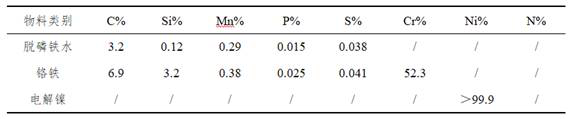
[0063]Step 1. Raw material preparation: 112t of nuclear austenitic stainless steel molten steel smelted in this embodiment requires 67t of dephosphorized molten iron, 42t of ferrochrome, and 9.25t of electrolytic nickel, wherein the chemical compositions of dephosphorized molten iron, ferrochrome and electrolytic nickel are as follows Table 3 shows.
[0064] Chemical composition of dephosphorized hot metal, ferrochrome and electrolytic nickel in Table 3 Example 3
[0065]
[0066] Step 2, AOD process control: smelting with a furnace age of 80, AOD reduction slag alkalinity 1.8, desulfurization stage alkalinity 2.0, slag pouring after reduction, ladle slag amount 150mm.
[0067] Step 3, LF treatment process: After the slag is pulled into the station, the temperature is measured at 1583°C, and after 3 minutes of power transmission, 72kg of electrolytic nickel and 164kg of ferrochrome are added, and the temperature is measured again at 1582°C. Blow for 12 minutes, and cool do...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com