Physical layer security algorithm combining subcarrier grouping and exclusive-OR operation
A physical layer security, subcarrier technology, applied in security devices, shaping networks in transmitters/receivers, baseband systems, etc., can solve problems such as unfavorable security, algorithm parameter leakage, difficulty in guaranteeing, etc., to enhance information security. Ease of performance, computational processing, and the effect of increasing complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
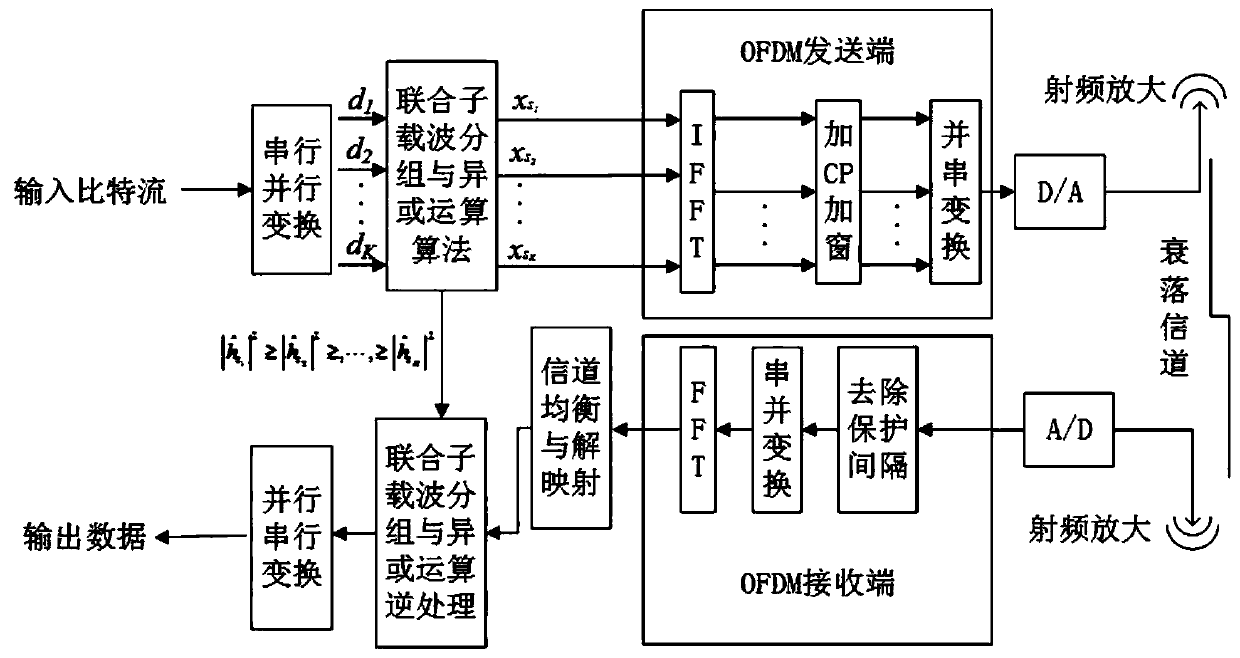
[0026] A physical layer security algorithm combining subcarrier grouping and XOR operation, which is suitable for multi-carrier communication networks combined with OFDM systems. OFDM systems use K subcarriers for transmission, such as figure 1 Shown is a block diagram of the OFDM system embedded in the security encoding and decoding module provided by this embodiment. A physical layer security algorithm of joint subcarrier grouping and XOR operation provided by this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0027] S1. Channel estimation. Before information transmission, the legal receiver first sends the pilot sequence uplink, the sender estimates the uplink main channel, and then the sender sends the pilot sequence downlink, and the legal receiver estimates the downlink main channel, using channel reciprocity , assuming that the uplink main channel and the downlink main channel have the same information, and their frequency channel quality coefficient vectors are all H b , ...
Embodiment 2
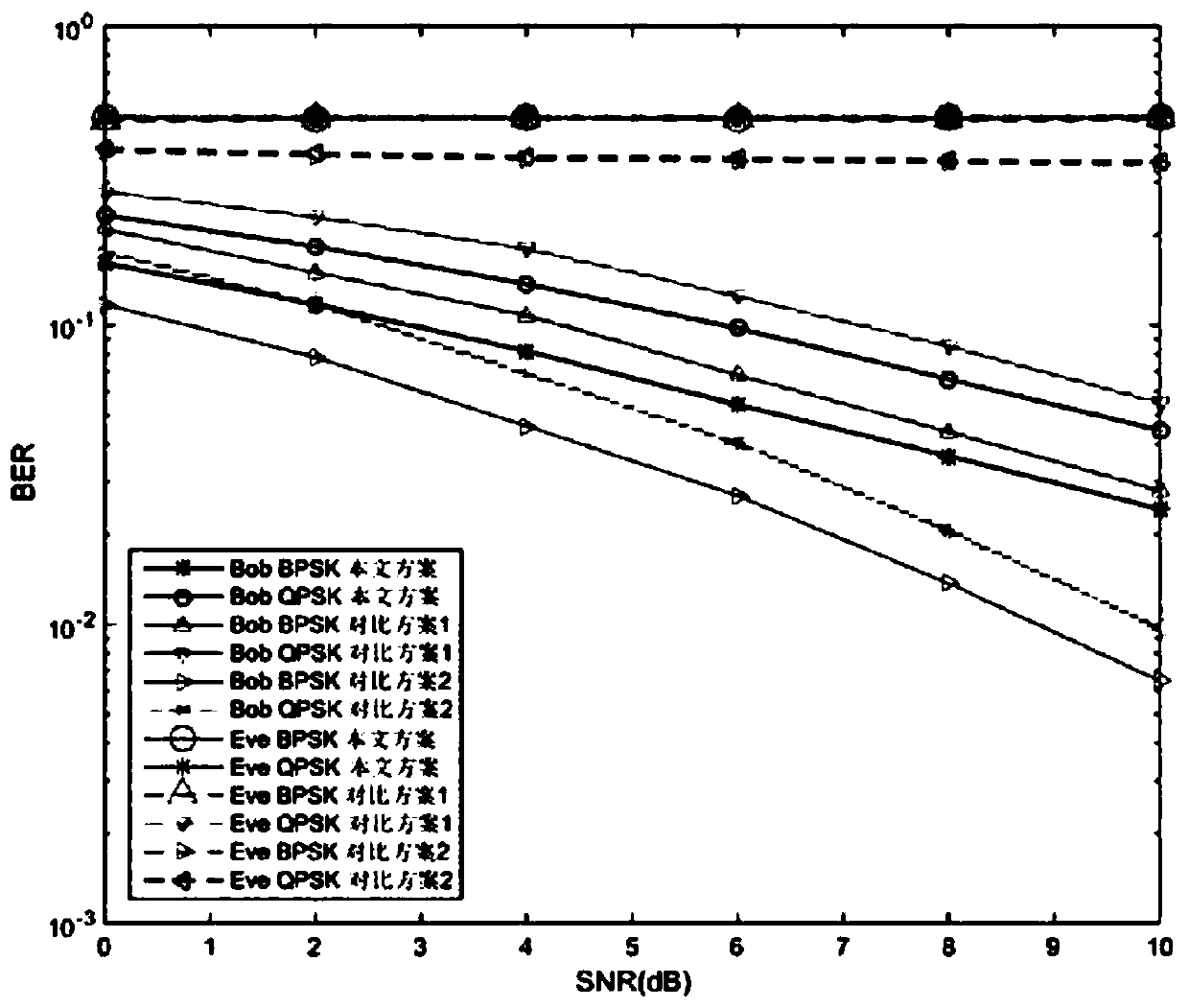
[0045]Since the reception situation at the eavesdropping end cannot be fully known, it is difficult to accurately calculate the confidentiality capacity of the system. The security performance of the algorithm is obtained by analyzing the bit error rate of the legal receiver and the eavesdropper. In this embodiment, the channel modeling in the OFDM system is a multipath channel model, each path adopts a Rayleigh fading channel model independent of each other, the noise model is additive white Gaussian noise, and the modulation methods used are BPSK modulation and QPSK modulation. The number K of carriers is 64, and the length of the cyclic prefix is 16. It is assumed that time synchronization has been completed and ISI has been completely eliminated. Through the MATLAB simulation platform, simulate the OFDM symbols sent by the sender under different SNR conditions, conduct 1e5 independent experiments respectively, and count the bit error rate (BER, Bit Error Rate) of the leg...
Embodiment 3
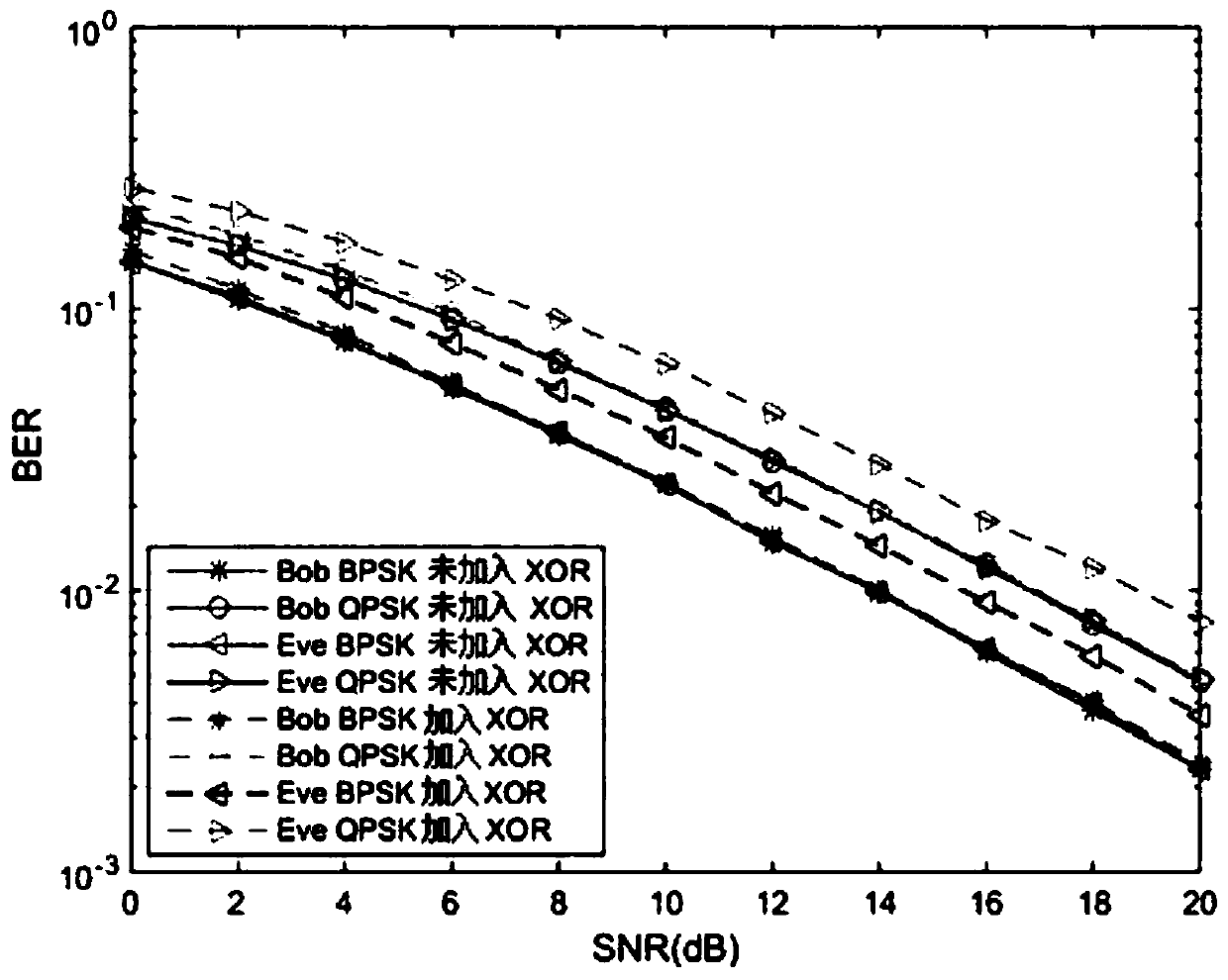
[0049] This embodiment considers an FDD system, assuming that the simulated environment is that the legitimate receiver feeds back the subcarrier sorting result to the sender, and an eavesdropper can eavesdrop on the complete sorting result. Such as image 3 Shown is a comparison of the BER performance of the scheme with and without the XOR operation. Therefore, an eavesdropper can correctly perform the subcarrier ordering decoding process during demodulation. It can be seen that since the eavesdropper obtains the sorting sequence, the performance of the eavesdropper without XOR operation is almost the same as that of the legitimate receiver. However, the scheme of adding XOR operation only loses a small amount of BER performance to the legal receiver, and the BER performance will decrease obviously to the eavesdropper. This is because from the perspective of the main channel, we let the better subcarriers transmit the original bits, and the poorer subcarriers transmit the X...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com