Novel self-filtering narrow spectral response organic light detector
A photodetector and narrow spectrum technology, applied in the field of new self-filtering narrow spectrum response organic photodetectors, can solve the problem of low photon and charge utilization, not paying attention to the band gap relationship between P-type layer and N-type layer materials, Problems such as poor controllability of light field and charge
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
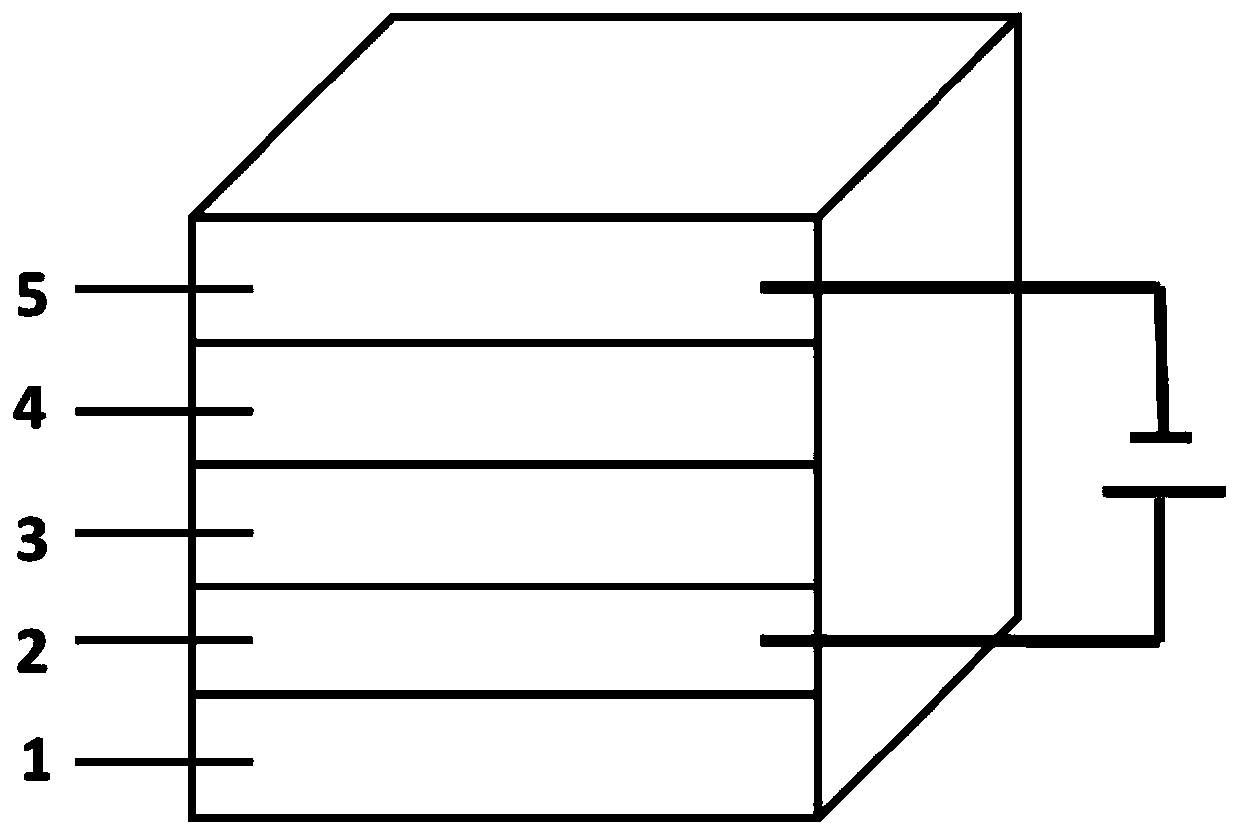
[0115] Such as figure 1 As shown, the novel self-filtering narrow spectral response organic photodetector has a device structure including a substrate 1 , a positive electrode 2 , a P-type layer 3 , an N-type layer 4 and a negative electrode 5 .
[0116] The substrate 1 is glass; the positive electrode 2 is indium tin oxide (ITO); the P-type layer 3 is a single-layer P-type layer structure, and the material of the P-type layer is naphthothiadiazole material NT812, and the film thickness is 1200nm; the material of the N-type layer 4 is a non-fullerene electron acceptor material IEICO-4F, with a film thickness of 150nm; the negative electrode 5 is silver. The band gap of the P-type layer material NT812 is wider than that of the N-type layer material IEICO-4F.
[0117] The preparation method of the above-mentioned organic photodetector comprises the following steps:
[0118] Step 1: Clean the glass substrate sequentially with acetone, special detergent for micron-sized semicond...
Embodiment 2
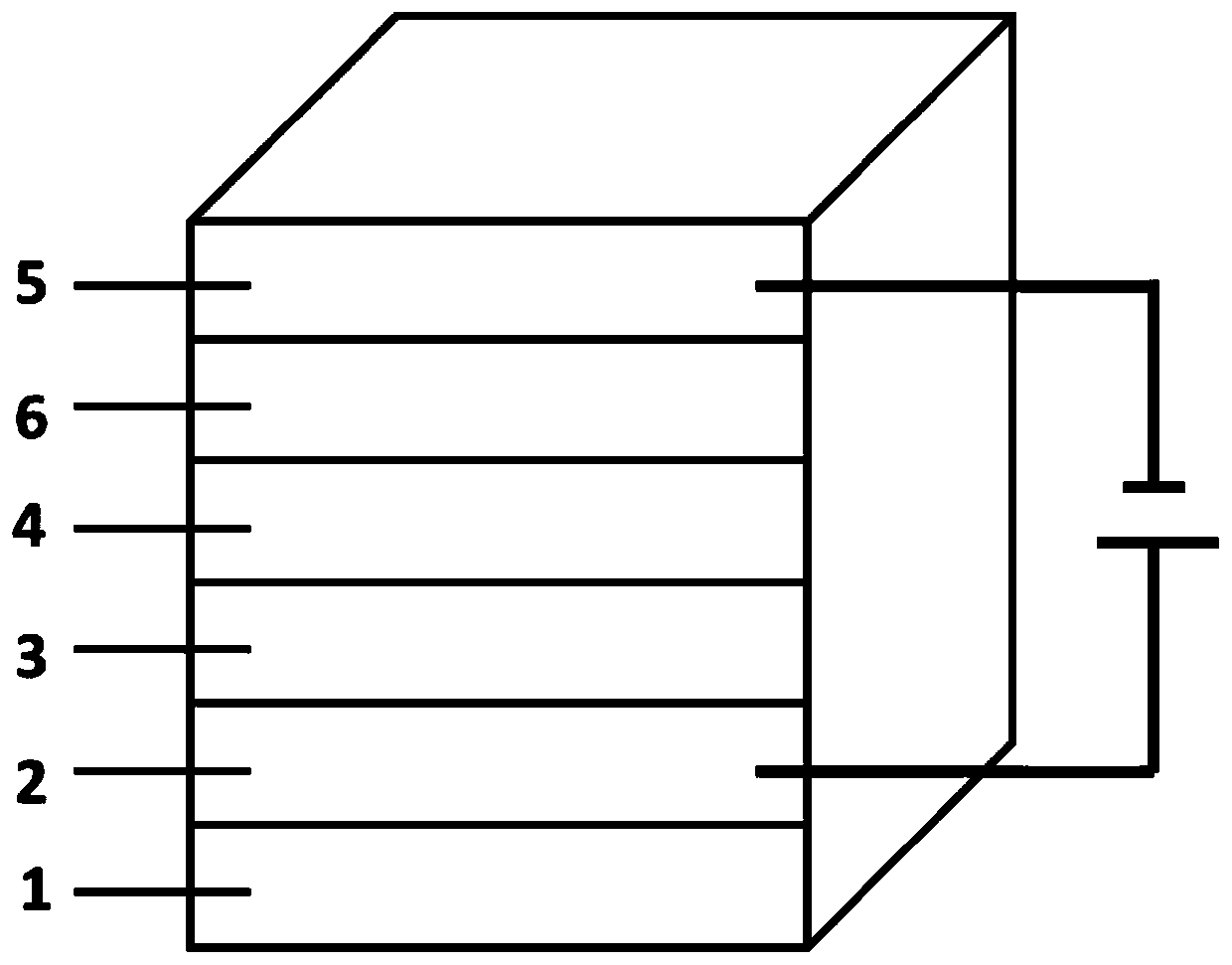
[0124] Repeat embodiment 1, increase buffer layer 6 between its N-type layer 4 and negative electrode 5, specifically as follows: figure 2 As shown, the novel self-filtering narrow spectral response organic photodetector has a device structure including a substrate 1 , a positive electrode 2 , a P-type layer 3 , an N-type layer 4 , a buffer layer 6 and a negative electrode 5 .
[0125] The substrate 1 is glass; the positive electrode 2 is indium tin oxide (ITO); the P-type layer 3 is a single-layer P-type layer structure, and the material of the P-type layer is naphthothiadiazole material NT812; The material of N-type layer 4 is non-fullerene electron acceptor material IEICO-4F, and the film thickness is 150nm; the negative electrode 5 is silver; the buffer layer 6 material is water-alcohol-soluble polymer material [9,9- Dioctylfluorene-9,9-bis(N,N-dimethylaminopropyl)fluorene] (PFN), with a film thickness of 8nm; the bandgap of the P-type layer material NT812 is wider than t...
Embodiment 3
[0135] Repeat embodiment 2, add one deck P-type layer in addition, form multilayer P-type layer structure, specifically as follows: figure 2 As shown, the novel self-filtering narrow spectral response organic photodetector has a device structure including a substrate 1 , a positive electrode 2 , a P-type layer 3 , an N-type layer 4 , a buffer layer 6 and a negative electrode 5 .
[0136] The substrate 1 is glass; the positive electrode 2 is indium tin oxide (ITO); the P-type layer (3) is a multi-layer P-type layer structure, and the first P-type layer material is polythiophene and its derivatives The material is poly(3-hexylthiophene) (P3HT), the film thickness is 150nm, the second P-type layer material is naphthothiadiazole material NT812, the film thickness is 800nm, wherein the second P-type layer is in direct contact with the N-type layer, and the second P-type layer is in direct contact with the N-type layer. A P-type layer is not in direct contact with the N-type layer;...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com