Method and device for preparing ethylene glycol by hydrogenating dimethyl oxalate
A technology of dimethyl oxalate and ethylene glycol, which is applied in the preparation of carboxylate, chemical instruments and methods, preparation of hydroxyl compounds, etc., can solve the problems of easy deactivation of catalyst, high manufacturing cost, complex structure of isothermal reactor, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
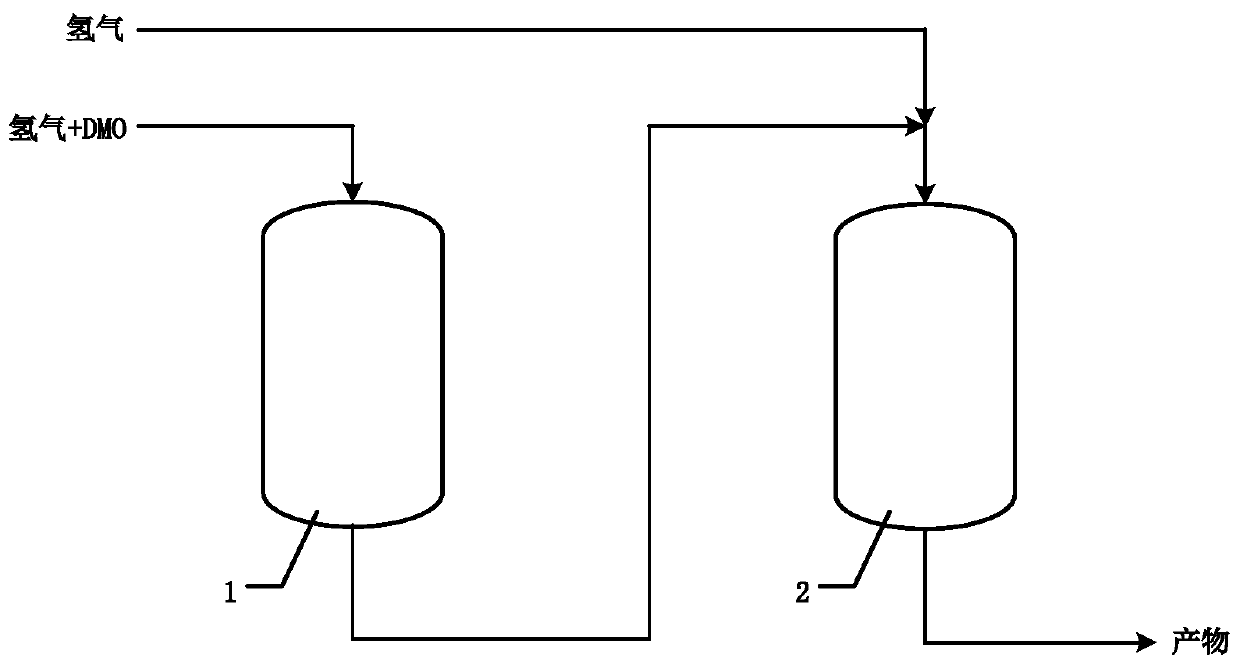
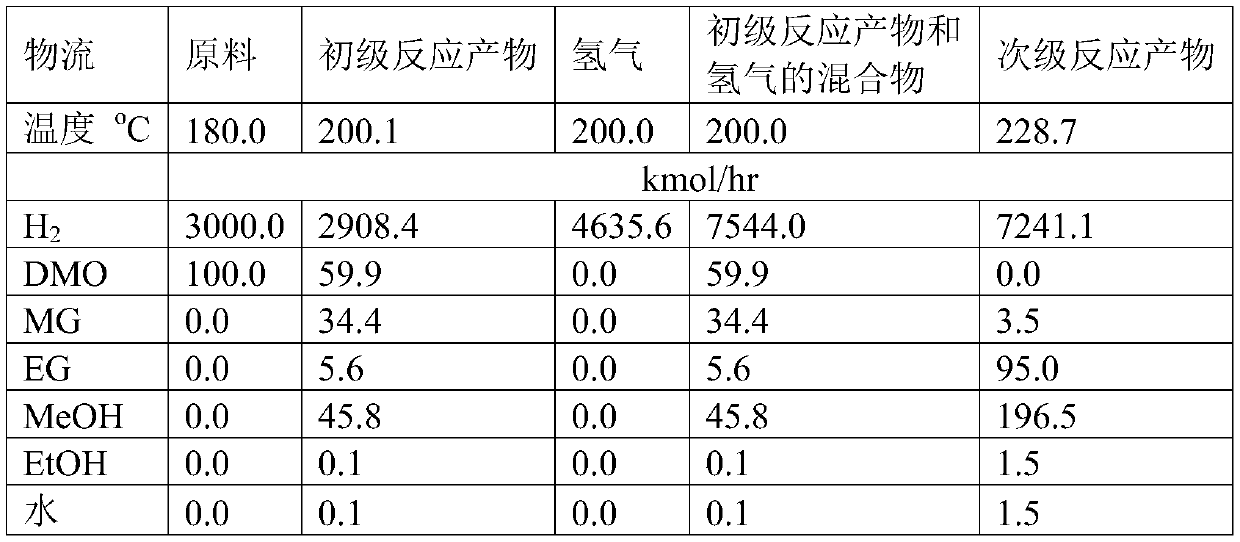
[0073] Example 1 in such as figure 1 carried out in the described device. The hydrogenation reaction of dimethyl oxalate was carried out using two adiabatic reactors. In the first stage of reaction, a low hydrogen ester ratio (H 2 : DMO=30), carry out at low temperature (180°C), reduce the reaction depth, and control the overall reaction heat release. About 40% of the dimethyl oxalate reacts in primary reactor 1 to form methyl glycolate (primary) and ethylene glycol (secondary). The adiabatic temperature rise in the primary reactor 1 is 20.1°C, and the outlet temperature of the primary reactor 1 is 200.1°C, which is the same as the optimum hydrogenation reaction temperature in the mainstream process. The primary reaction product is mixed with hydrogen to form a mixture with a hydrogen-to-ester ratio of 80, and then enters the secondary reactor 2 to hydrogenate the remaining dimethyl oxalate and the methyl glycolate generated in the primary reactor 1 to obtain Secondary re...
Embodiment 2
[0079] The hydrogenation reaction of dimethyl oxalate in Example 2 was carried out using two adiabatic reactors. The first stage reaction was carried out in primary reactor 1 at 200° C. with a hydrogen-to-ester ratio of 50. The adiabatic temperature rise in the primary reactor is 25.3°C, and the primary reaction product at the outlet of the primary reactor passes through a heat exchanger for heat exchange and cooling, and the temperature after cooling is 200°C. The cooled primary reaction product is mixed with hydrogen, the hydrogen-ester ratio is adjusted to an appropriate ratio, and then the hydrogenation reaction is carried out in the secondary reactor to obtain a secondary reaction product containing ethylene glycol.
[0080] Example 2 utilizes two different catalysts to hydrogenate dimethyl oxalate. The catalyst InNi / Ni used in the first step of hydrogenation mainly hydrogenates dimethyl oxalate to generate methyl glycolate. The catalyst used in the second step of hydroge...
Embodiment 3
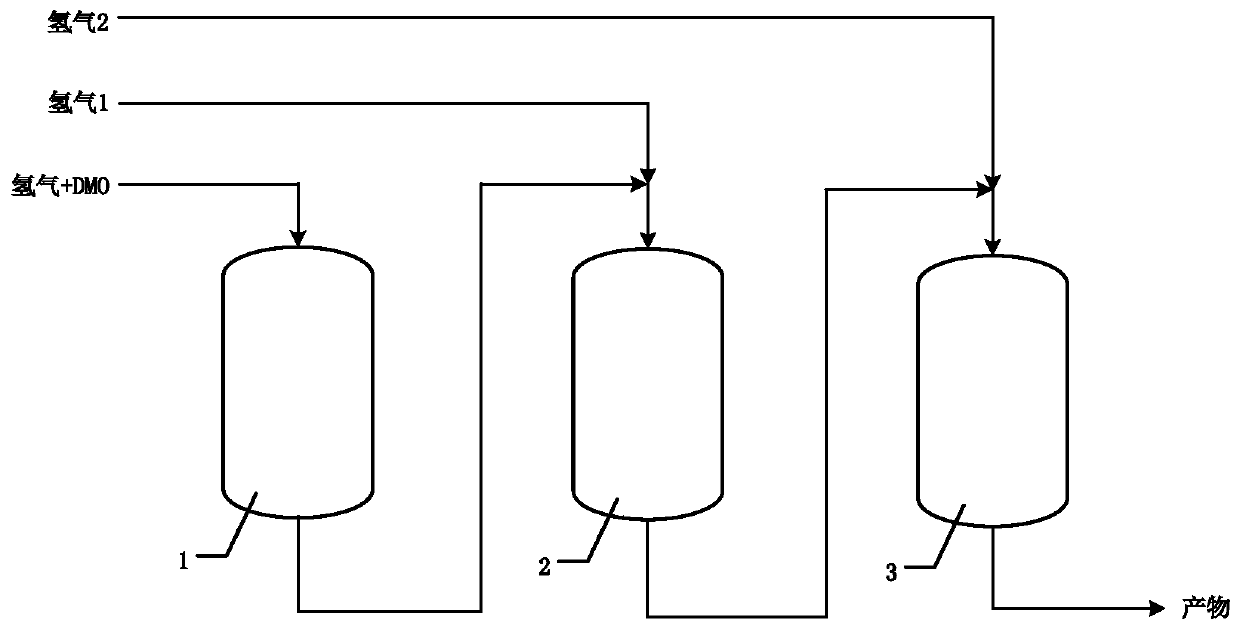
[0085] The dimethyl oxalate hydrogenation reaction of embodiment 3 utilizes three adiabatic reactors to carry out, and reaction device is as figure 2As shown, the three reactors all use the same catalyst InNiC0.5 / Ni. The first stage of reaction was carried out in the primary reactor 1 at 180° C. with a hydrogen-to-ester ratio of 30 to obtain primary reaction products. Then, the primary reaction product is mixed with hydrogen 1, and after adjusting the ratio of hydrogen to ester to an appropriate ratio, hydrogenation reaction is carried out in the secondary reactor 2 to obtain the first secondary reaction product. The first secondary reaction product continues to be mixed with hydrogen 2, and after adjusting the hydrogen-ester ratio to an appropriate ratio, hydrogenation reaction is carried out in the secondary reactor 3 to obtain a second secondary reaction product containing ethylene glycol.
[0086] By controlling the reaction conditions, the adiabatic temperature rise is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com