Carbon-based material of graphene-similar three-dimensional porous composite iron oxide, and preparation method
A three-dimensional porous, carbon-based material technology, used in electrical components, battery electrodes, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of poor cycle performance, low sulfur utilization, and low sulfur loading, and achieve buffer volume expansion, large pores and ratios Surface area, the effect of increasing sulfur loading
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
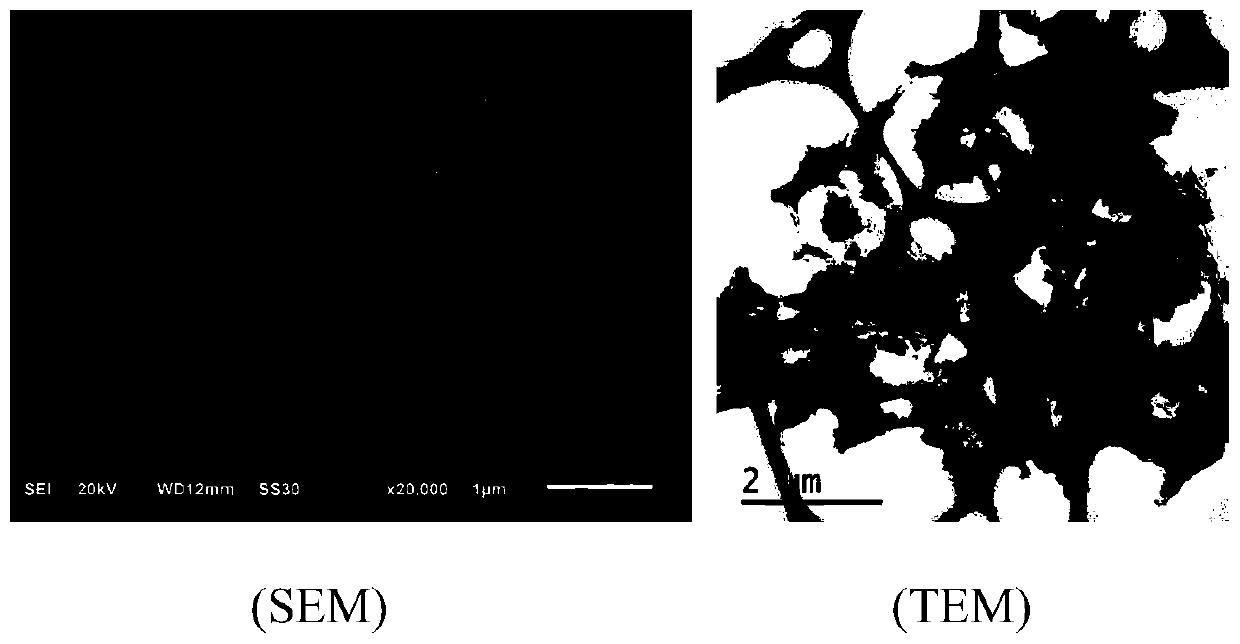
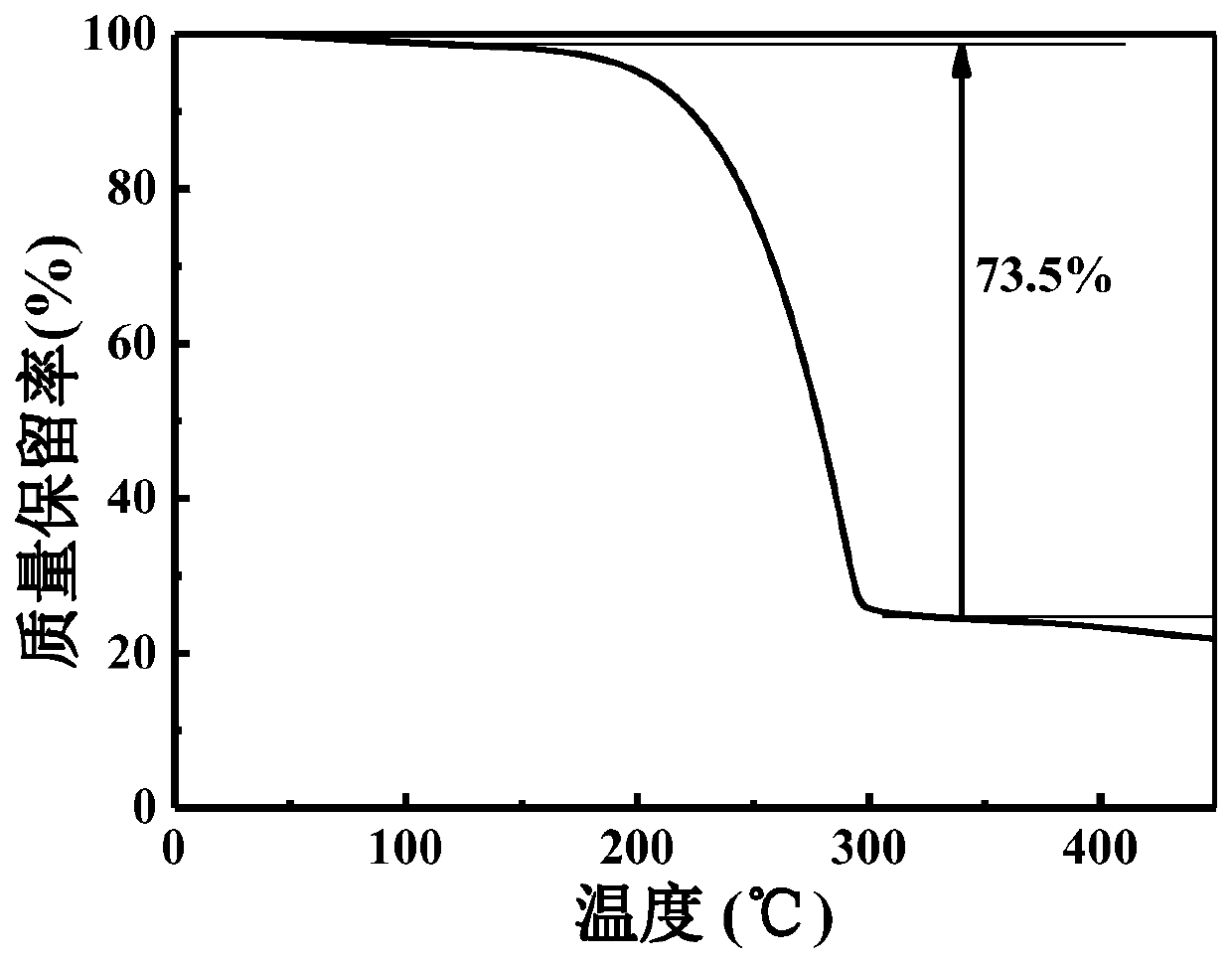
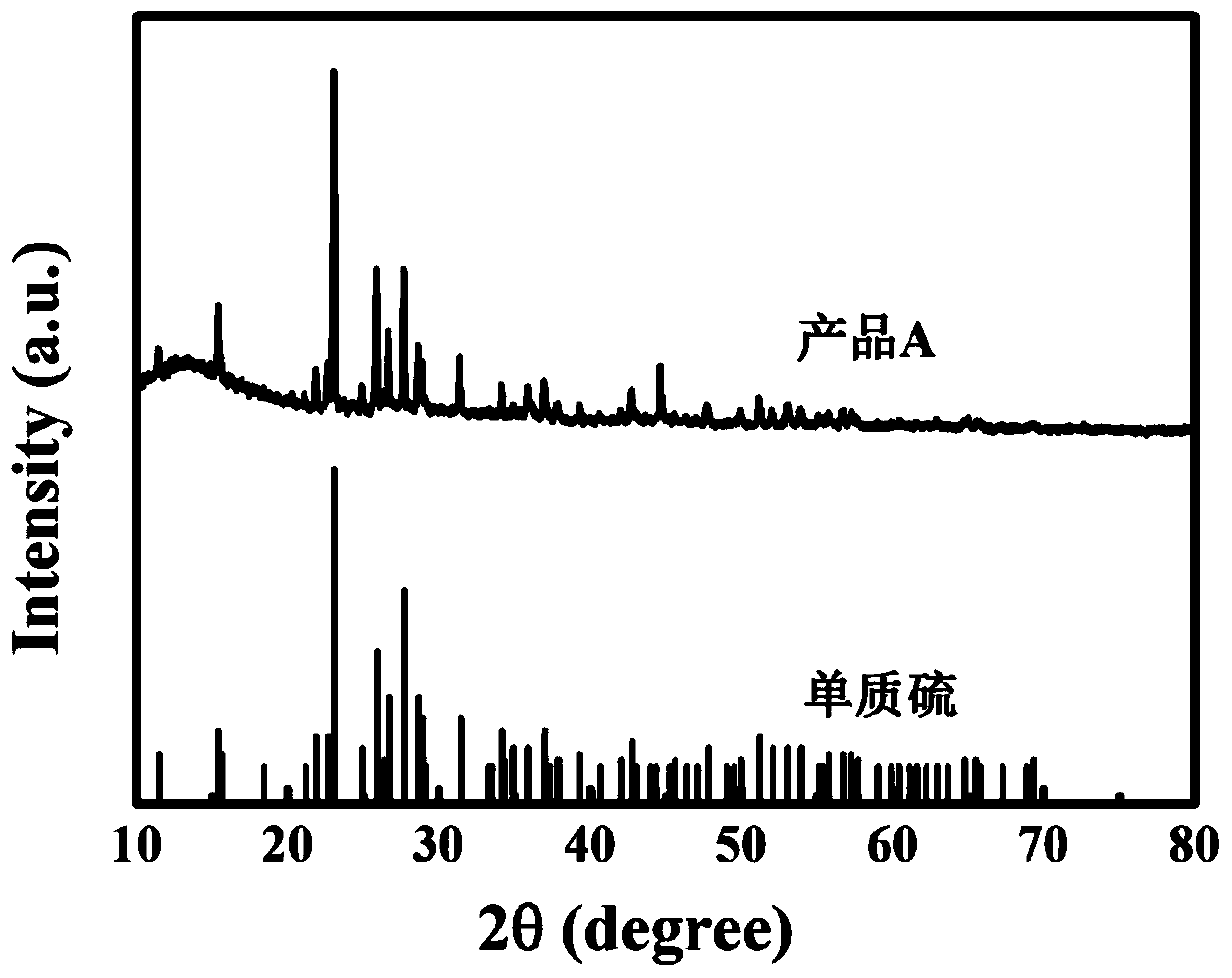
[0030] refer to figure 1 —6, a carbon-based material and preparation method of graphene-like three-dimensional porous composite iron oxide, comprising the following steps:
[0031] (1) Add sodium chloride, carbon source, surfactant and catalyst iron salt into deionized water at room temperature, and stir thoroughly for 2-3 hours to form a uniform and transparent orange solution. A certain amount of catalyst iron salt is put into the deionized water, and 7-8g of sodium chloride, 1-3g of citric acid and 0.2-0.3g of polyvinylpyrrolidone are added to each 40ml of deionized water.
[0032] (2) Put the solution obtained in step (1) in the refrigerator to freeze into ice, then put it into a freeze dryer, take it out after 60-70 hours, and obtain a yellow sample.
[0033] (3) The yellow sample obtained by freeze-drying in step (2) was carbonized at an annealing temperature of 600-700° C. for 3-4 hours under the protection of an inert gas to obtain a black solid powder. The inert gas...
Embodiment example 1
[0037](1) In this example, 7.35g of sodium chloride, 1.25g of citric acid, 0.25g of polyvinylpyrrolidone and 0.32g of ferric chloride hexahydrate were added to 40ml of deionized water at room temperature, and polyvinylpyrrolidone was used as a surfactant and Nitrogen source, stirred well for 2 hours to form a homogeneous transparent orange solution.
[0038] (2) Put the solution obtained in step (1) into ice, put it into a freeze dryer, take it out after 72 hours, and obtain a yellow sample.
[0039] (3) Under the protection of argon, the yellow sample obtained by freeze-drying in step (2) was heated to 650°C at a heating rate of 2°C per minute and carbonized for 3 hours to obtain a black solid powder.
[0040] (4) Disperse the carbonized black powder obtained in step (3) in 100ml of deionized water, filter the sample with a vacuum filtration device, and continuously inject 1000ml of deionized water during the suction filtration process to remove the sodium chloride template, ...
Embodiment 2
[0043] (1) Add 7.35g of sodium chloride, 1.25g of citric acid, 0.25g of polyvinylpyrrolidone and 0.47g of cobalt chloride hexahydrate into 40ml of deionized water at room temperature, with polyvinylpyrrolidone as a surfactant and nitrogen source, and stir well A homogeneous clear pink solution formed in 2 hours.
[0044] (2) Put the solution obtained in step (1) in the refrigerator to freeze into ice, then put it into a freeze dryer, take it out after 72 hours, and obtain a pink sample.
[0045] (3) Under the protection of argon, the yellow sample obtained by freeze-drying in step (2) was heated to 650°C at a heating rate of 2°C per minute and carbonized for 3 hours to obtain a black solid powder.
[0046] (4) Disperse the carbonized black powder obtained in step (3) in 100ml of deionized water, filter the sample with a vacuum filtration device, and continuously inject 1000ml of deionized water during the suction filtration process to remove the sodium chloride template, and t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com