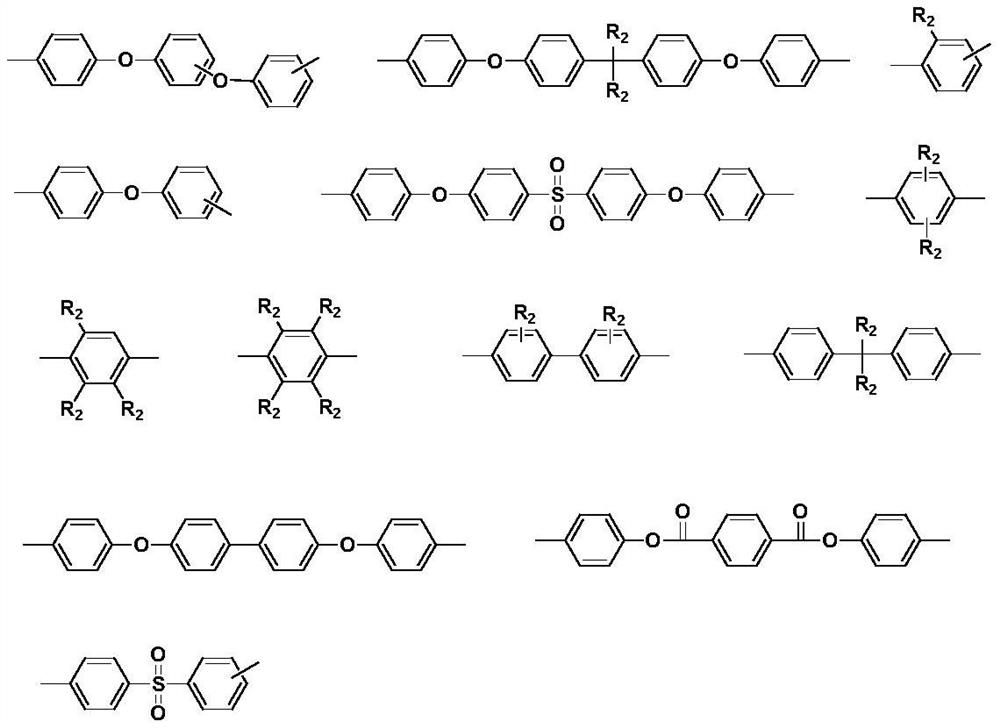
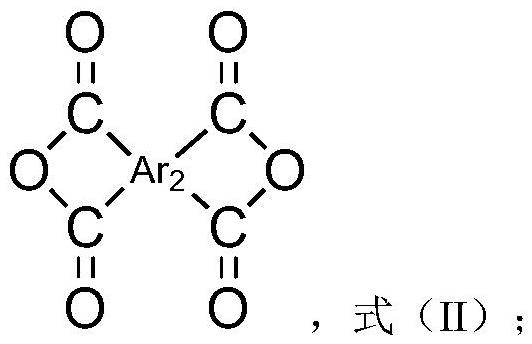
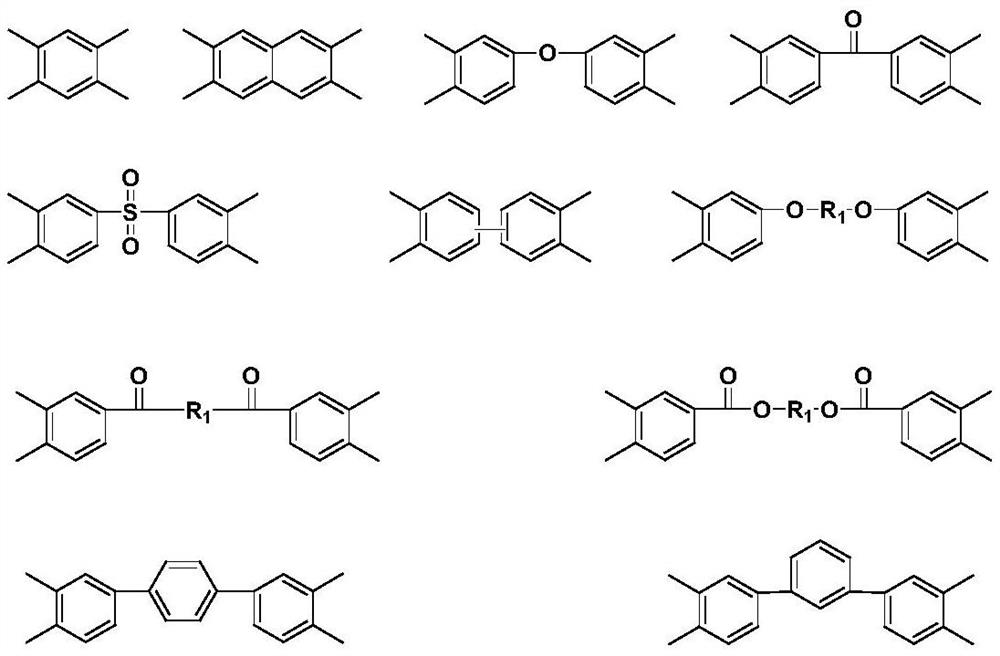
Preparation method of polyamic acid solution
A polyamic acid and solution technology, which is applied in the field of polyamic acid solution preparation, can solve problems such as viscosity changes, affecting processing and molding, quality of polyimide products, and difficulty in mass transfer of dianhydride monomers.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Dissolve 23.38g (116.77mmol) of diphenyl ether diamine (ODA) in 273.94g of N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMAc), stir at 25°C, after complete dissolution, add 24.96g (114.43mmol) Perphthalic dianhydride (PMDA), fully reacted to obtain A solution (dianhydride, diamine molar ratio 0.98, solid content 15%, the same below). Using the same method, 19.41 g (96.92 mmol) ODA, 289.68 g DMAc, and 31.71 g (145.38 mmol) PMDA were used to prepare B solution (molar ratio 1.50, solid content 15%). Add 11.36g of solution B into solution A and stir thoroughly at 25°C to obtain a final polyamic acid solution (molar ratio 0.994, solid content 15%). The above experiment was repeated three times, and the final solution was measured at a shear rate of 1s -1 The apparent viscosities under the conditions are 288Pa·s, 293Pa·s and 290Pa·s respectively. After passing the solution through a 2 μm glass fiber filter membrane, the filter screen was irradiated by ultraviolet fluorescent lamps without any fo...
Embodiment 2
[0040]Dissolve 2002.4g (10mol) ODA in 23089.0g DMAc, stir at 25°C, after complete dissolution, add 2072.1g (9.5mol) PMDA, and obtain A solution (molar ratio 0.95, solid content 15%) after full reaction. Using the same method, 1001.2g (5mol) ODA, 14944.0g DMAc, and 1635.9g (7.5mol) PMDA were used to prepare solution B (molar ratio 1.50, solid content 15%). Add 2757.5g of solution B into solution A and stir thoroughly at 25°C to obtain a final polyamic acid solution (molar ratio 0.99, solid content 15%). The above experiment was repeated three times, and the final solution was measured at a shear rate of 1s -1 The apparent viscosities under the conditions are 248Pa·s, 244Pa·s and 252Pa·s respectively. After passing the solution through a 2 μm glass fiber filter membrane, the filter screen was irradiated by ultraviolet fluorescent lamps without any foreign matter.
Embodiment 3
[0042] Dissolve 2002.4g (10mol) ODA in 27837.0g NMP, stir at 0°C, after complete dissolution, add 1090.6g (5mol) PMDA, fully react to obtain A solution (molar ratio 0.5, solid content 10%). Using the same method, 1001.2g (5mol) ODA, 28641.6g NMP, and 2181.2g (10mol) PMDA were used to prepare solution B (molar ratio 2.0, solid content 10%). The two solutions A and B were mixed and stirred thoroughly at 0° C. to obtain the final polyamic acid solution (molar ratio 1, solid content 10%). The final solution was measured at a shear rate of 1s -1 The apparent viscosity under the condition is 168Pa·s. After passing the solution through a 2 μm glass fiber filter membrane, the filter screen was irradiated by ultraviolet fluorescent lamps without any foreign matter.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com