Loading structure for adsorbing heavy metal pollutants and preparation method and application thereof
A load structure, heavy metal technology, applied in the direction of water pollutants, alkali metal compounds, metal processing equipment, etc., can solve the problems of reducing adsorption efficiency, limiting adsorption efficiency, low adsorption selectivity, etc., to achieve fast and simple manufacturing process, avoid secondary Secondary pollution, high adsorption selectivity effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0032] The present invention also provides a method for preparing the load structure as described above, comprising the following steps:
[0033] Step 1. Use 3D drawing software to design a load structure of specific shape and size;
[0034] Step 2, uniformly doping heavy metal adsorption nanomaterials into 3D printing materials;
[0035] Step 3, printing the 3D printing nanocomposite material obtained in step 2 into the loading structure designed in step 1 by 3D printing technology;
[0036] Step 4, repeatedly cleaning the loading structure printed in step 3 to remove the 3D printing material remaining on the surface, and drying it.
[0037] Wherein, in step 1, the load structure includes a grid, a filter membrane, a filter ball or a pipe-type structure; in step 2, in some embodiments, the heavy metal adsorption nanomaterial can be mixed into the 3D printing material by stirring , in other embodiments, other suitable doping methods can be selected according to actual needs;...
Embodiment 1
[0042] Preparation of grid structure loaded with heavy metal adsorption nanomaterials:
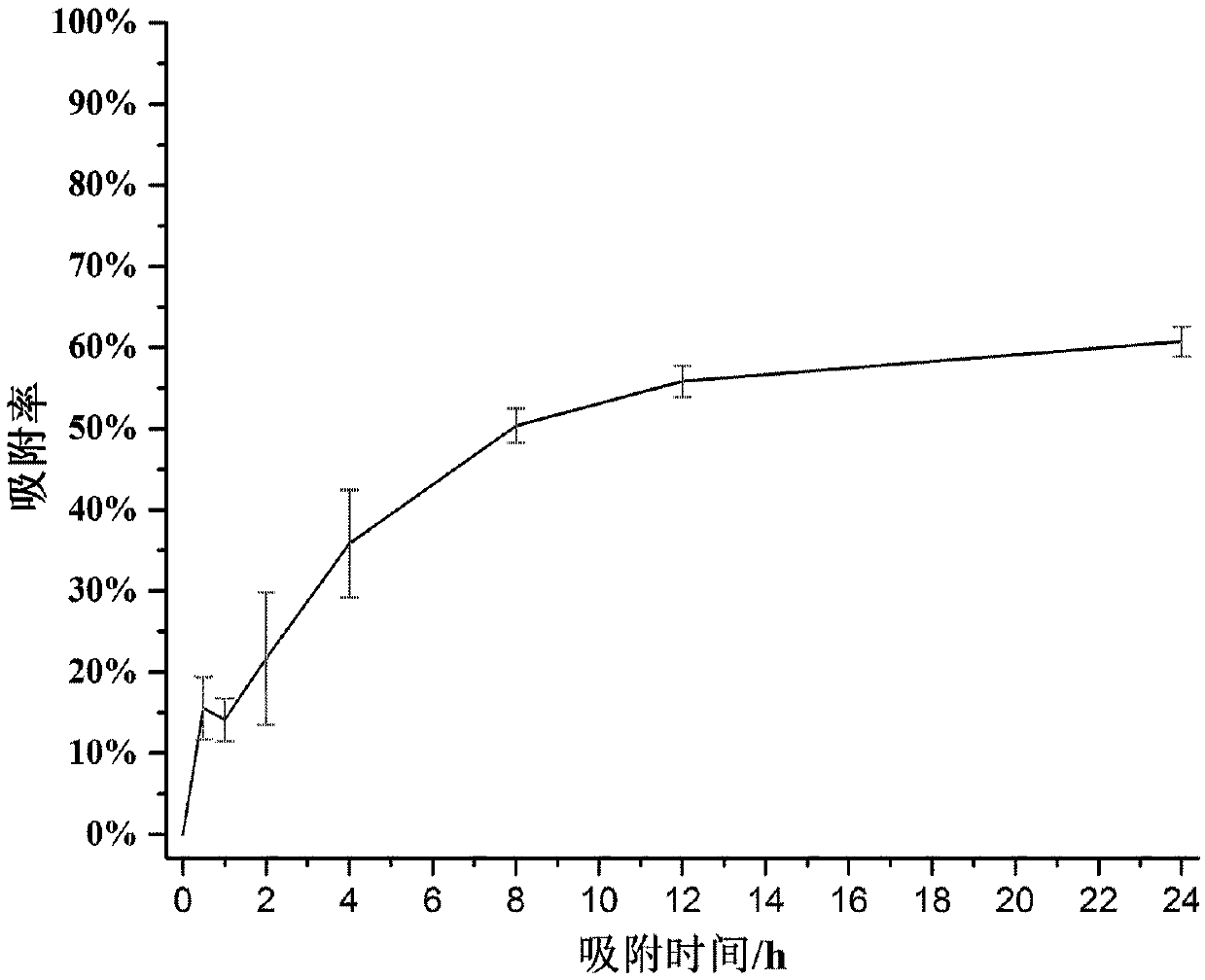
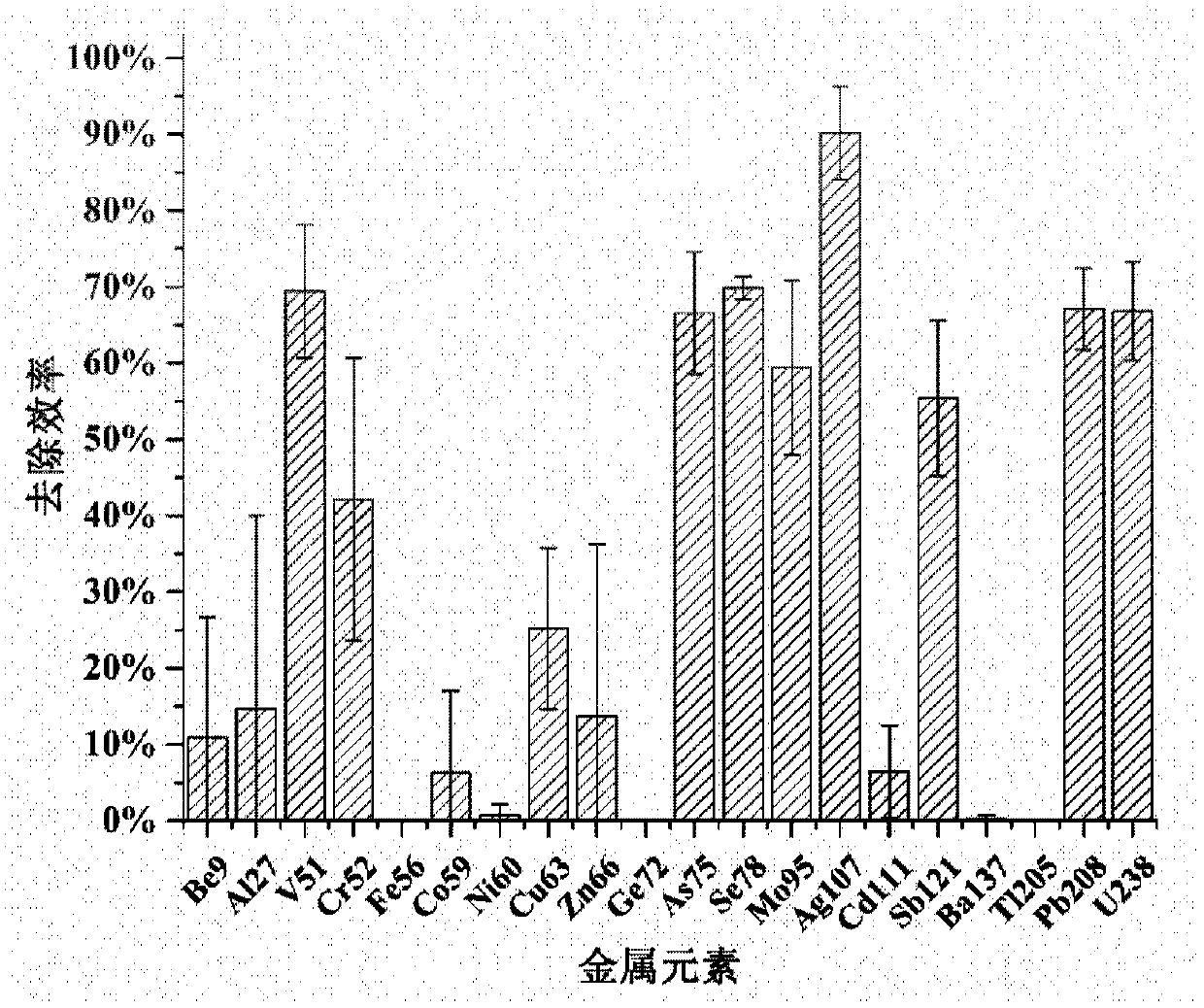
[0043] Such as figure 1As shown, in this embodiment, a grid for adsorbing trivalent arsenic ions in water is manufactured by using the method of the present invention. In this embodiment, firstly, a grid with a face-centered cubic structure is designed by using three-dimensional drawing software. This structure has a high space utilization rate, a large specific surface area, and a stable structure. The grid thickness is 0.3mm, the length, width, and height of a single grid are 2.5mm, and the three-dimensional dimensions of the entire grid are 1.53cm, 1.53cm, and 1.375cm. Then, in order to adsorb and remove trivalent arsenic ions in water, we selected nano-zero-valent iron with a particle size of 50nm as the heavy metal adsorption nanomaterial, and doped nano-zero-valent iron powder with a particle size of 50nm at a mass fraction of 2% into the 3D printing light. In the cured resin, us...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Preparation of grid structure loaded with heavy metal adsorption nanomaterials:
[0054] Such as Figure 4 As shown, in this embodiment, a grid for adsorbing trivalent arsenic ions in water with the same size and shape as that in Embodiment 1 is fabricated by using the method of the present invention. The grid is also firstly designed using 3D drawing software. The thickness of the grid is 0.3mm, and the length, width and height of each grid are 2.5mm. The three-dimensional dimensions of the entire grid are 1.53cm, 1.53cm, and 1.375cm. But the difference is that in this example, we choose 5-10nm hydrophilic and lipophilic anatase nano-titanium dioxide as heavy metal adsorption nanomaterials, and 5-10nm hydrophilic and lipophilic anatase nano-titanium dioxide powder as 2% mass fraction is doped into the 3D printing photocurable resin, and then fully stirred evenly using a magnetic stirrer to obtain a 3D printing nanocomposite material. Afterwards, the grid is process...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com