Preparation method and application of aloe emodin azole compounds
A technology of emodin azoles and compounds, applied in organic chemistry, resistance to vector-borne diseases, antibacterial drugs, etc., can solve the problems of different molecular states, different solubility, patient tolerance and unsatisfactory curative effect, etc., to achieve Short synthetic route, simple preparation of raw materials, and the effect of solving drug resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
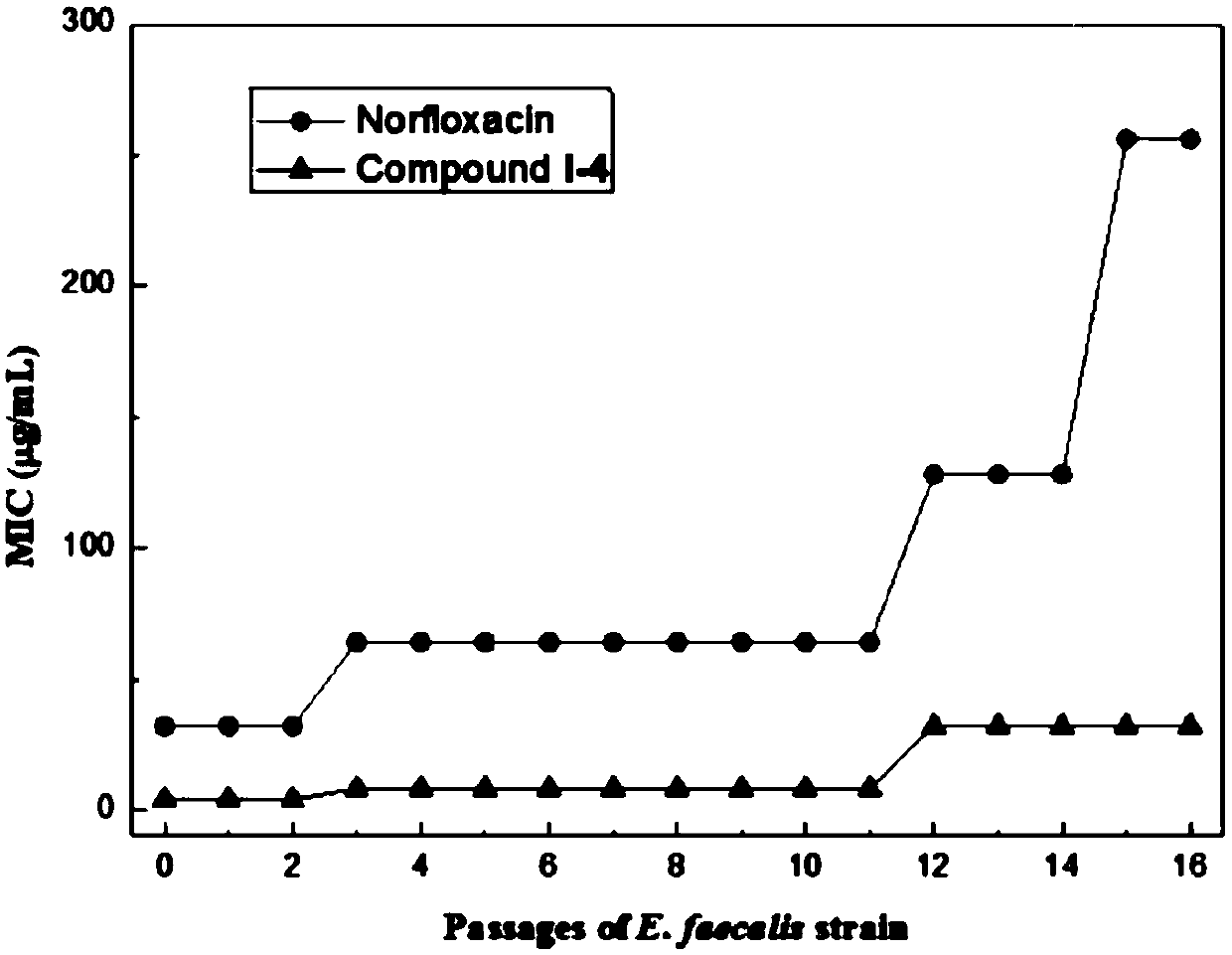
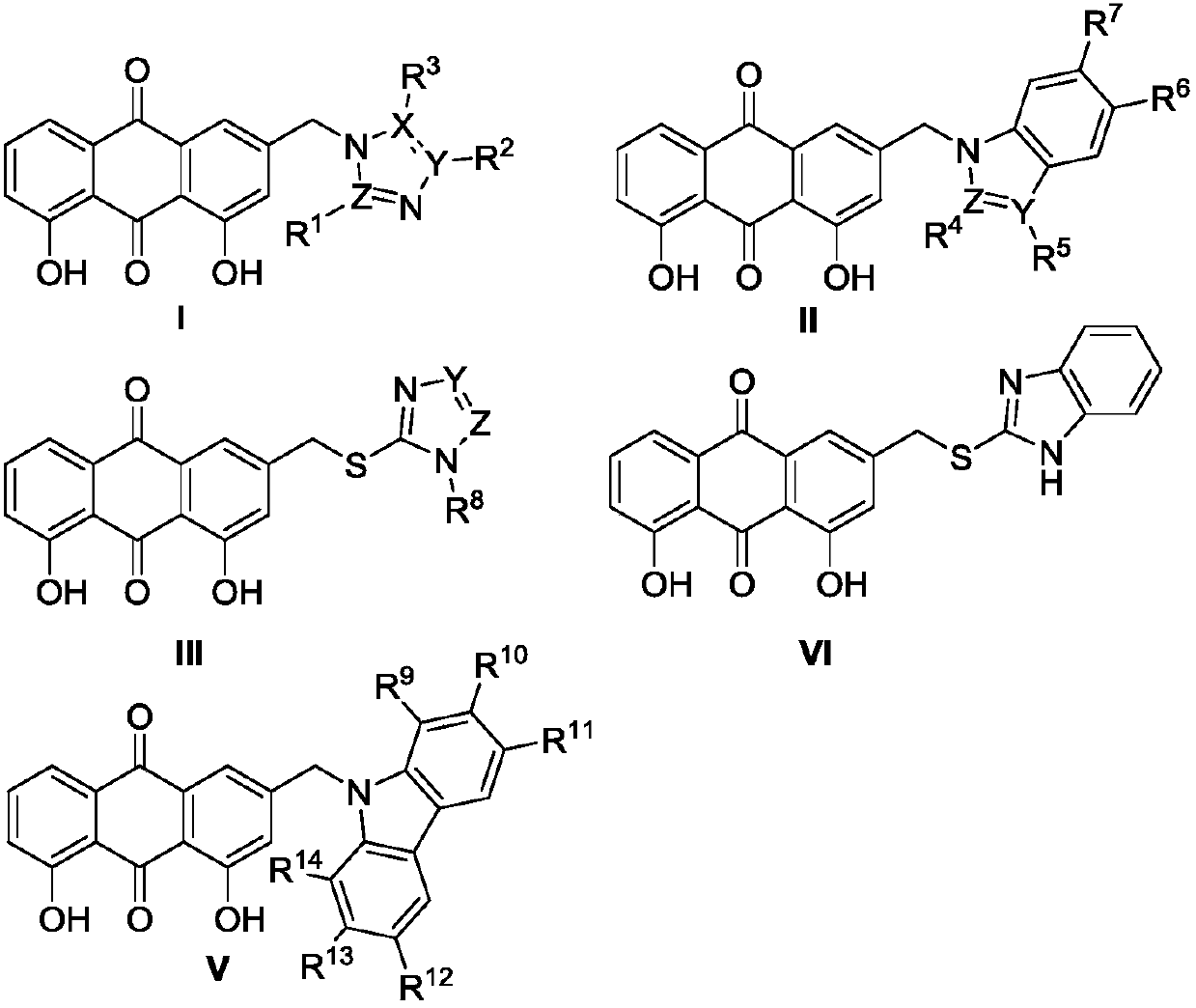
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
[0038] Experimental example 1, the preparation of intermediate VI
[0039]
[0040] Add 1,8-dihydroxy-3-hydroxymethylanthraquinone (2.7g, 10mmol) and thionyl chloride (20mL, 275mmol) into a 150mL round-bottomed flask, add N,N-dimethylformamide (200mL ) as a solvent, added at room temperature and stirred to react, followed by TLC until the end of the reaction. Quenched with ice water, filtered, washed, and recrystallized to obtain compound VI (1.76 g), with a yield of 61.0%.
experiment example 2
[0041] Experimental example 2, the preparation of compound I-1
[0042]
[0043] Add 2-nitroimidazole (84.81mg, 0.75mmol), potassium carbonate (138.21mg, 1.00mmol) and acetonitrile (10mL) into a 100mL round bottom flask, heat up to 65°C under stirring, and stir until most of the raw materials are dissolved for one hour After cooling to room temperature, compound VI (144.34mg, 0.50mmol) was added, refluxed at 80°C, and traced by TLC until the reaction was completed. Cool to room temperature, add glacial acetic acid to neutralize until the pH is neutral. Suction filtration, the filtrate was extracted with dichloromethane solution, concentrated, separated by column chromatography, recrystallized, dried and other post-treatments to obtain compound I-1 (40 mg), yield 22.4%; yellow powder; melting point: >250 ° C; 1 H NMR (600MHz, DMSO-d 6 )δ11.97(s,2H,anthraquinone-1,8-2OH),10.13(s,1H,imidazole-4-H),8.15(s,1H,imidazole-5-H),7.86(d,J= 7.7Hz,1H,anthraquinone-5-H),7.84(s,1H,anth...
experiment example 3
[0044] Experimental example 3, the preparation of compound 1-2
[0045]
[0046]Add 4-nitroimidazole (84mg, 0.75mmol), potassium carbonate (138mg, 1.00mmol) and acetonitrile (10mL) into a 100mL round bottom flask, heat up to 65°C under stirring, stir until most of the raw materials are dissolved for one hour and then cool After reaching room temperature, compound VI (144mg, 0.50mmol) was added, refluxed at 80°C, followed by TLC until the reaction was completed. Cool to room temperature, add glacial acetic acid to neutralize until the pH is neutral. Suction filtration, the filtrate was extracted with dichloromethane solution, concentrated, separated by column chromatography, recrystallized, dried and other post-treatments to obtain compound I-2 (110mg), yield 60.4%; yellow powder; melting point: >250°C; 1 H NMR (600MHz, DMSO-d 6 )δ11.92 (s, 2H, anthraquinone-1, 8-2OH), 8.33 (s, 1H, imidazole-5-CH), 7.85 (s, 1H, imidazole-2-CH), 7.79 (t, J= 7.9Hz,1H,6-CH),7.71–7.65(m,2H,an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com