Method and device for repairing black and smelly water body in situ by utilizing microbial fuel cell and aquatic plants
A technology for aquatic plants and black and odorous water bodies, applied in biological treatment devices, biological water/sewage treatment, biological sludge treatment, etc., can solve problems such as hard bottom, low water transparency, high nitrogen and phosphorus concentration, and achieve recovery , promote growth and reproduction, promote the effect of growth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] A kind of method utilizing microbial fuel cell-aquatic plant in situ repairing black and odorous water body, its steps are as follows:
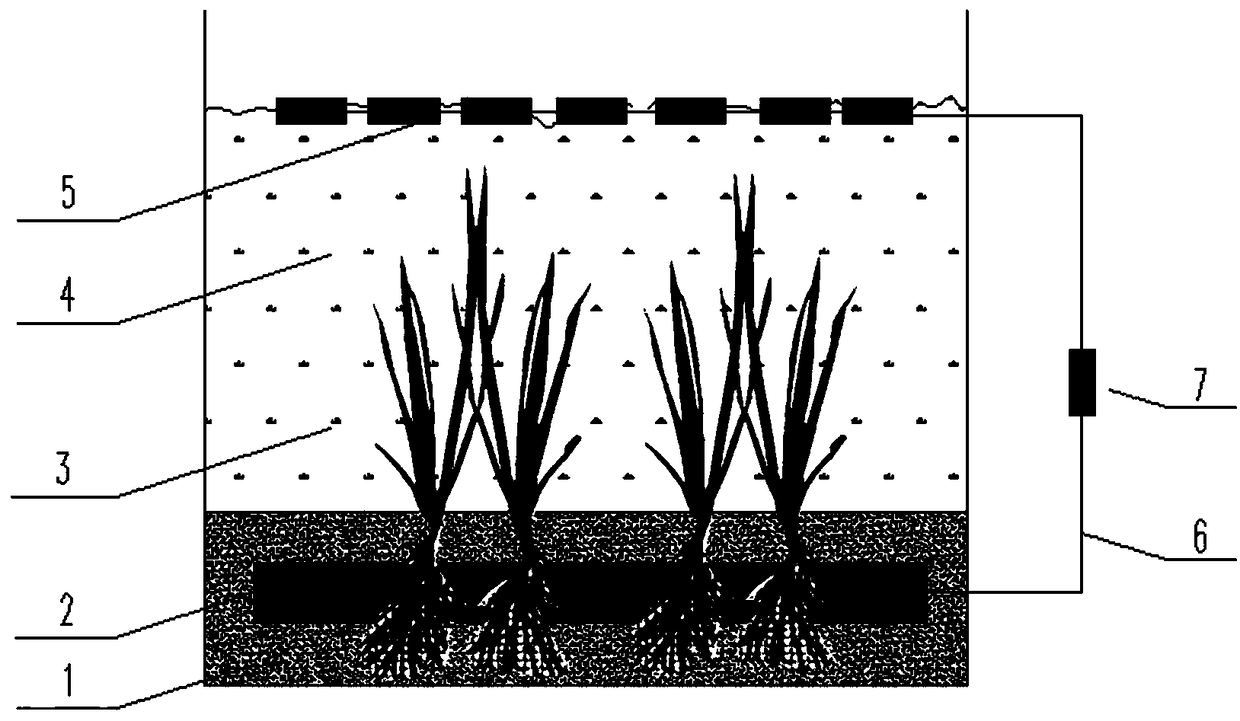
[0052] A. Buried the anode plate at 3 or 5 or 8 or 10 cm below the sediment-water interface of the black and odorous water body; this setting is because the black and odorous substances in the sediment generally gather in the middle and upper layers, and the oxidation-reduction potential of this part is relatively low. Low, the anode plate is set in this depth range, which is conducive to the improvement of redox conditions in this area. At the same time, this depth range is also the depth range of the root zone of aquatic plants, which is conducive to the synergy with the power generation and plant root zone.
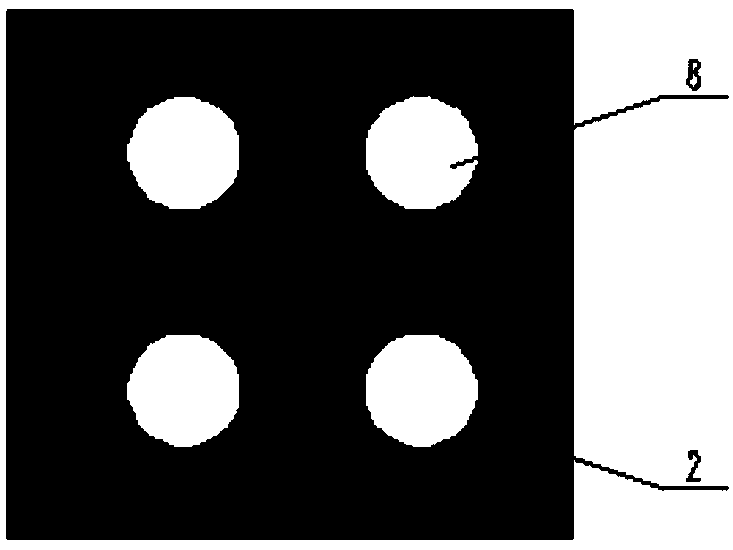
[0053] B. Put the root system of aquatic plants through the round hole on the anode plate and take root in the bottom mud, and use the synergistic effect of the plant root system and the anode electrogenic flora to promote the s...
Embodiment 2
[0064] A device for in-situ restoration of black and odorous water bodies using microbial fuel cells and aquatic plants. Wire 6, external resistance 7. It is characterized in that: the anode plate 2 is located under the surface layer of the bottom mud layer 1, the depth is 3 or 5 or 8 or 10 cm, the root system of the aquatic plant 3 passes through the opening 8 of the anode plate 2 and penetrates into the bottom mud layer 1, and the cathode The plate 5 is suspended in the upper water layer 4 and partially exposed (30%-70% of the area can be within this range) in the air, one end of the outer wire 6 is connected to the anode plate 2, and the other end of the outer wire 6 is connected to the external resistance 7 , The external resistor 7 is connected to the external wire 6 and the cathode plate 5 respectively to form a current path. Gradually enrich a large number of electrogenic bacteria and iron redox bacteria near the anode, which can promote the redox cycle process of iron...
Embodiment 3
[0077] The experiment compared the restoration effect of the MFC-Littleweed system and the single planting of Lilygrass system on black and odorous water bodies under the same environmental conditions, and the results showed that: the biomass of the coupled MFC system increased by 30-50%; there was an iron handle in the anode Iron bacteria such as Gallionella (abundance 0.2%), and iron-reducing bacteria such as Geobacter (abundance 10.4%) and Bacillus (abundance 4.4%) can promote iron production. The oxidation-reduction cycle process is conducive to the degradation of macromolecular organic matter in black and odorous sediment into small molecular organic acids, and the complete oxidation of small molecular organic acids without consuming more dissolved oxygen in the water body.
[0078] Its implementation steps, structure are identical with embodiment 1 and embodiment 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com