Method and device for utilizing microbial fuel cell-submerged plant to conduct situ-control on phosphorus release of sediment
A technology of submerged plants and fuel cells, which is applied in the fields of biological water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, electrochemical and biological combination treatment, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in planting and surviving submerged plants, large water level and stormy waves, etc., and achieve Promotes migration, improves oxidation-reduction potential, and reduces phosphorus content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] A method for controlling the release of phosphorus from eutrophic water body sediments in situ by utilizing microbial fuel cells and submerged plants, the steps of which are as follows:
[0046] A. Plant submerged plants in eutrophic water sediments; absorb part of phosphorus through the roots of submerged plants, and use the roots of submerged plants to release oxygen at the same time, which is conducive to the enrichment of iron-reducing bacteria around the rhizosphere.
[0047] B, bury the anode plate at 3cm or 5 or 7 or 9 or 10cm below the sediment-water interface, near the root system of submerged plants (5 or 7 or 8 or 10cm in diameter around the root); It is easy to release to the overlying water layer, and the root system length of submerged plants is generally 3-10cm (any distance is acceptable), and the anode plate is close to the root system, which can better enrich the electrogenic bacteria group and phosphorus removal bacteria with stable structure Groups, ...
Embodiment 2
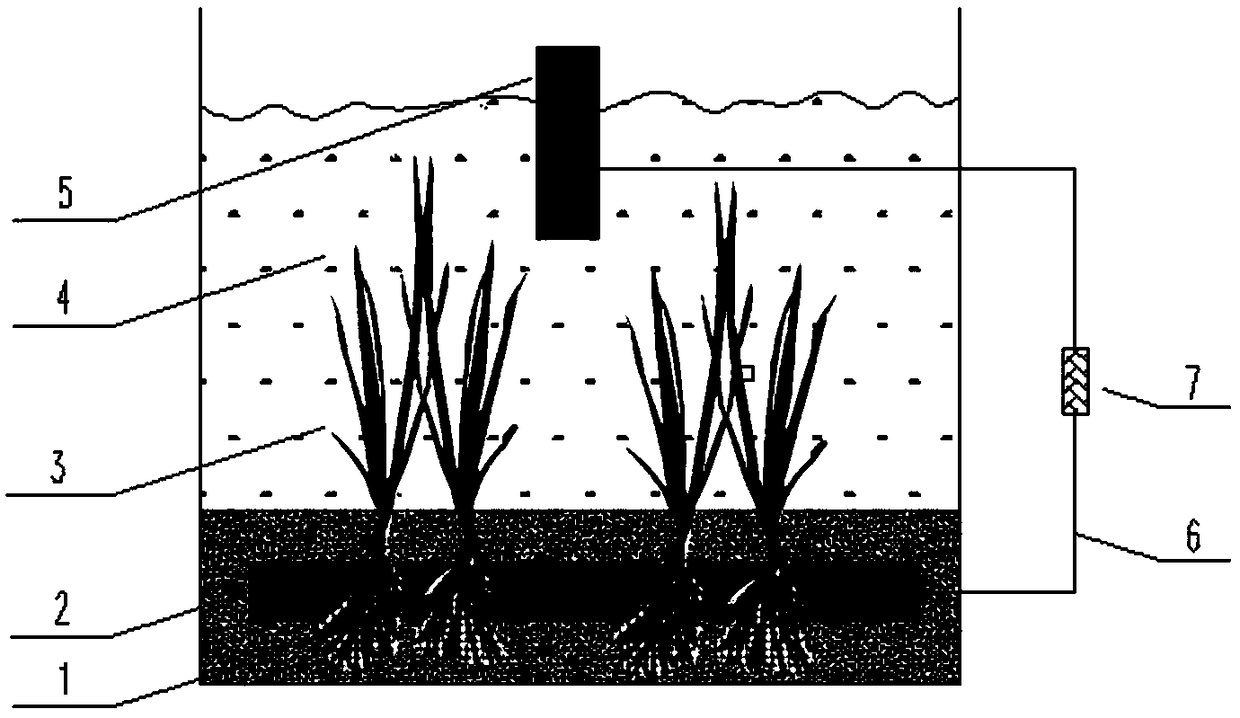
[0059] A device for controlling the release of phosphorus from sediments in situ using microbial fuel cells-submerged plants. Composed of wire 6 and external resistance 7, it is characterized in that: submerged plants 3 are rooted in the bottom sediment 1; the middle part of the anode plate 2 opens through the submerged plants 3, and the roots of the submerged plants 3 are located under the sediment-water interface 3 Or at 5 or 7 or 9 or 10cm, the upper water layer 4 is on the sediment-water interface, the cathode plate 5 is suspended at the upper water-air interface, and the cathode plate 1 / 2-2 / 3 (area in this range All can) must be exposed to the air; the anode plate 2 is connected to the cathode plate 5 through the wire 6, and the external resistor 7 is connected to the anode plate 2 and the cathode plate 5 through the wire 6 to form a current path.
[0060] The bottom sediment 1 has a thickness of 10 or 15 or 20 or 25 or 30 cm, which is the bottom mud in eutrophic lakes, r...
Embodiment 3
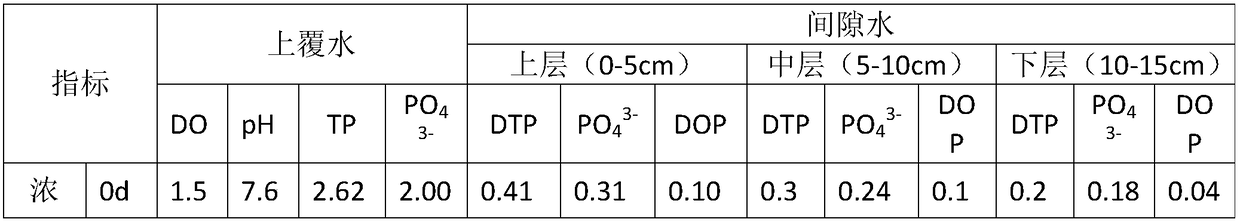
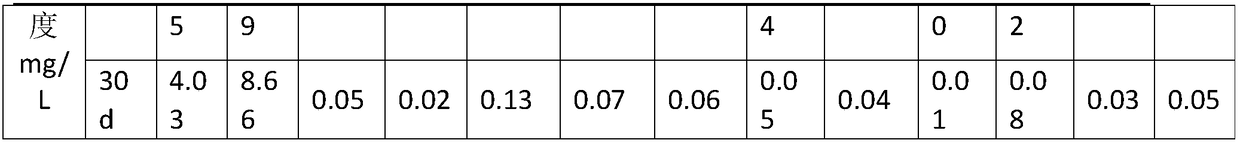
[0077] The experiments compared the bottom sediment 1-MFC-Literia galenica system and the bottom sediment 1-Littleweed system under the same conditions in the overlying water (upper, middle, lower) layer interstitial water, and the concentrations of different forms of phosphorus in the bottom sediment 1 The results showed that: 1) Eh in the bottom sediment 1-MFC-Littleweed system was higher than that in the bottom sediment 1-Littleweed system, and the corresponding calcium-phosphorus (HCl-P) and iron-phosphorus (BD -P) content was higher than 14.8% and 24.0% respectively, and the easily released aluminum phosphorus (NaOH-P) content was reduced by 9%. 2) The process of electricity production promotes the rapid growth of Erythrina fragrans on the PO in the overlying water layer and interstitial water. 4 3- The absorption of PO in the overlying water and interstitial water is promoted 4 3- 3) The process of electricity production effectively inhibits the accumulation of organo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com