Process for producing nonwoven with improved surface properties
A surfactant-based, water-based technology for applications in nonwovens, surfactant addition, papermaking, etc., capable of solving even thin spots or holes, surface irregularities, interfering with hydroentanglement of nonwovens, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0066] Example 1 (comparative example)
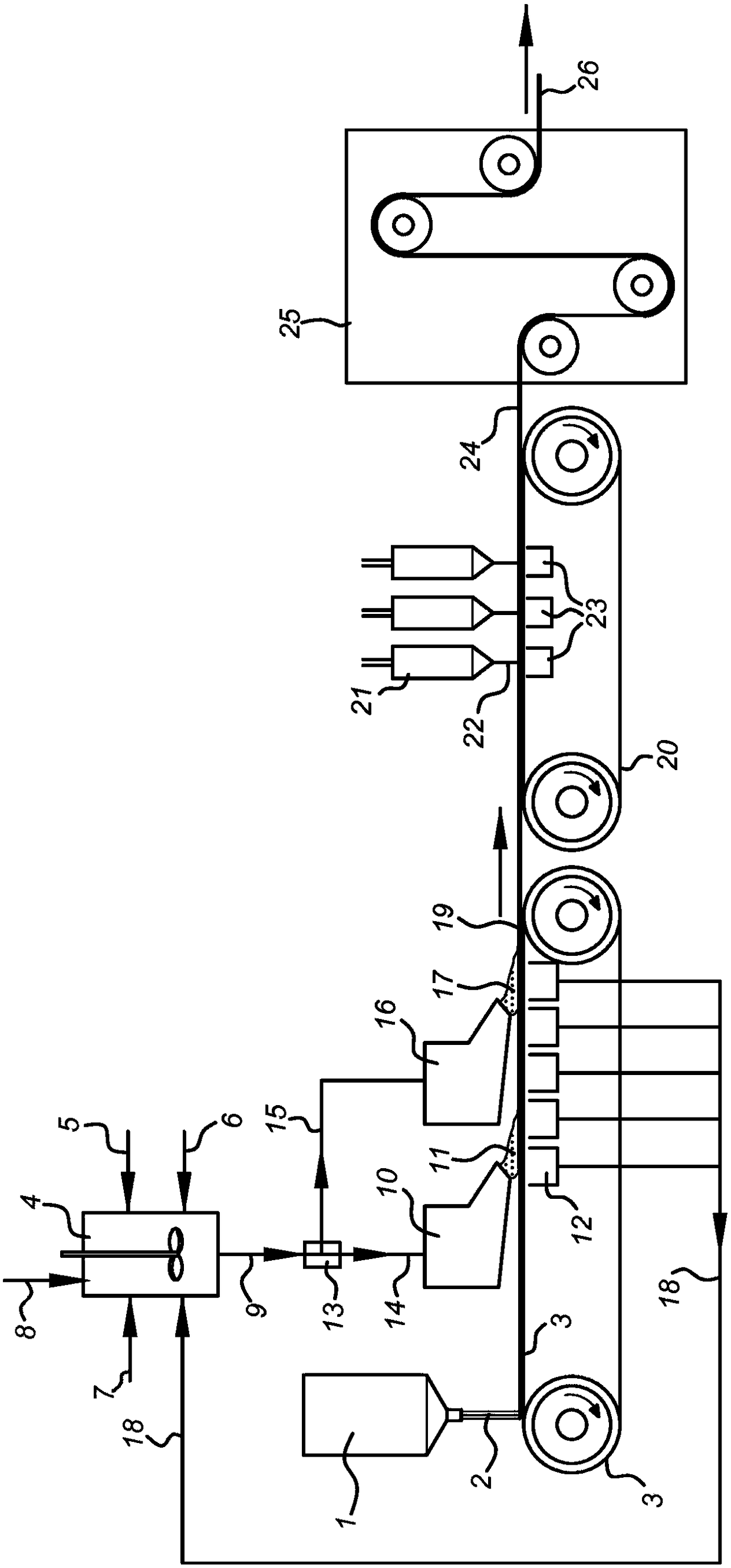
[0067] A nonwoven absorbent sheet material usable as a wipe (e.g. industrial cleaning cloth) was produced by laying down a web of polypropylene filaments on a running conveyor fabric, and then in a headbox Pulp containing wood pulp and polyester staple fibers in a weight ratio of 88:12 and 0.01-0.1 wt.% of nonionic surfactant (ethoxylated fatty alcohol) was applied on a polymer web in a foam forming process Dispersion, introducing a total of about 30 vol. % air (based on total foam volume). The proportion by weight of polypropylene filaments is 25 wt.% based on the dry weight of the final product. The amount is chosen to achieve 55g / m 2 basis weight of the final product. The combined fibrous web is then subjected to hydroentanglement using multiple water jets of increased pressure of 40-100 bar, providing a total energy supply of about 180 kWh / t in the hydroentanglement step, as in CA 841938, pp. 11-12 The description is measured an...
example 2
[0069] Example 2 (the present invention)
[0070] Example 1 was repeated with the only difference that the pulp dispersion was applied in two stages, using two headboxes placed approximately 2m apart from each other along the production line. Formation data and basis weight data for the five samples at the best and worst positions are presented in Tables 1 and 2, respectively, under the heading "Dual Headbox".
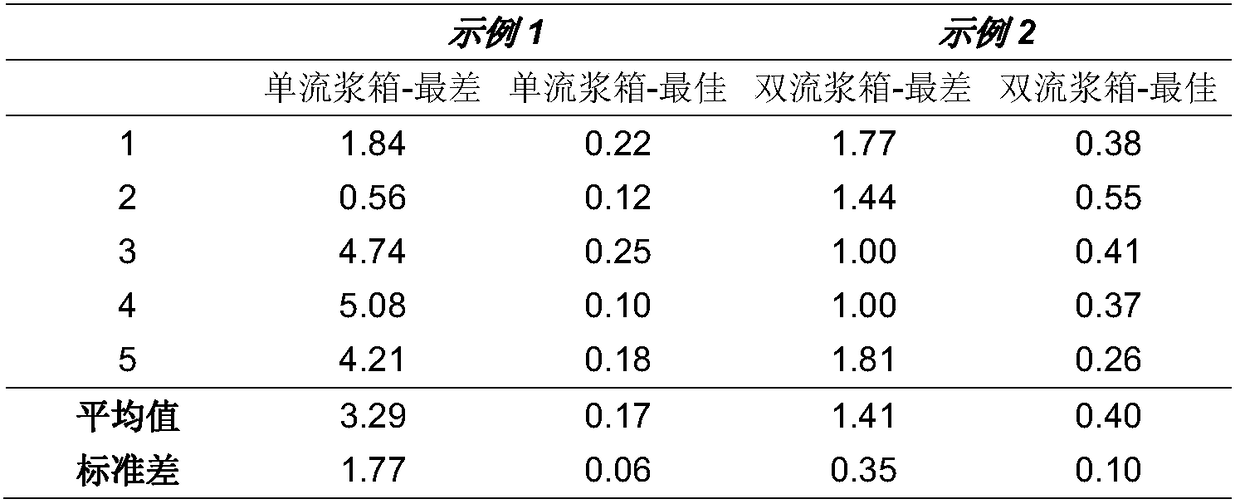
[0071] Table 1: Formation results (unit %)
[0072]
[0073] Table 1 shows that when using two headboxes compared to using a single headbox, the formation value of the worst point is significantly reduced (mean value from 3.29 to 1.41%) and the standard deviation is significantly reduced (for the worst point) . Also the difference between worst and best is drastically reduced when using two headboxes compared to one.
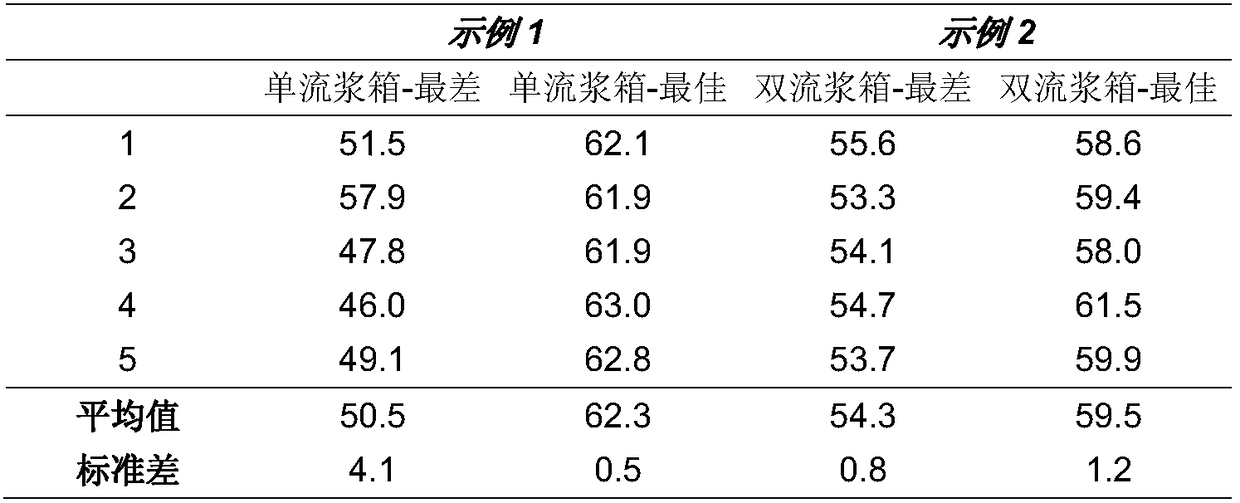
[0074] Table 2: Basis weight results (unit g / m 2 )
[0075]
[0076] Table 2 shows that for the worst point the basis weight increases signif...
example 3
[0077] Example 3 (comparative example)
[0078] Example 1 is repeated with the only difference that the amount is chosen so that the basis weight of the final product reaches 80 g / cm 2 . Formation data for 5 different samples of nonwoven fabric at the best and worst positions are presented in Table 3 below, under the heading "Single Headbox", with mean values and standard deviations. Basis weight data for the same samples are presented in Table 4 below, under the heading "Single Headbox", with mean and standard deviation.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Base weigh | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com