Composite material capable of adsorbing nucleic acid and preparation method thereof, and device capable of adsorbing nucleic acid
A composite material and nucleic acid technology, applied in the field of nucleic acid adsorption devices, can solve problems such as inability to fit tightly, lack of elasticity, and leakage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Thermoplastic polymer resin: UHMWPE, molecular weight 2 million, particle size 80-100 mesh.
[0056] Specific particles or fibrous materials that adsorb nucleic acids: silica gel powder, particle size 60-120 mesh, pore size
[0057] Experimental steps:
[0058] 1) Add 70% of UHMWPE and 30% of silica gel powder in sequence in a container, and mix well to obtain spare raw materials;
[0059] 2) Using an aluminum mold with several holes, the diameter of the hole is 4.0mm, and the height is 4.0mm. The spare raw materials are evenly added to the holes, and the compression is shaken;
[0060] 3) After sintering at 200°C for 20 minutes, cool down and take it out.
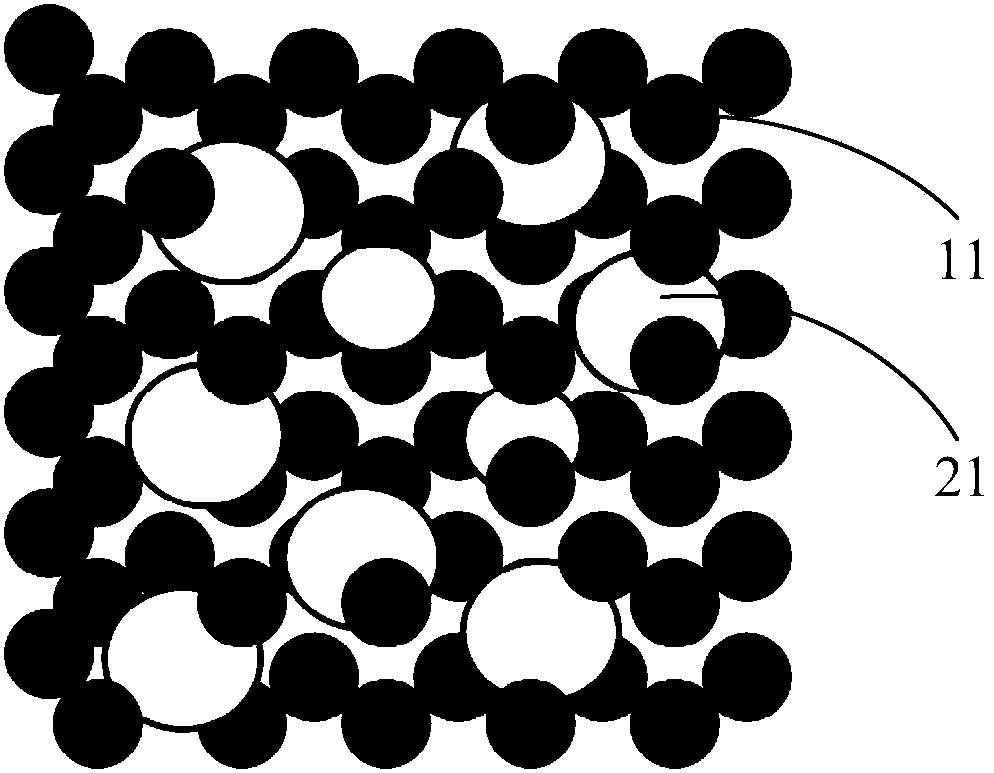
[0061] The composite material (such as figure 1 Shown) diameter 4.0mm, height 4.0mm, aperture 20-40μm.
Embodiment 2
[0063] Thermoplastic polymer resin: UHMWPE, molecular weight 4 million, particle size 60-80 mesh; HDPE, density 0.945, particle size 60-80 mesh.
[0064] Specific particles or fibrous materials that adsorb nucleic acids: silica gel powder, particle size 150-200 mesh, pore size
[0065] Experimental steps:
[0066] 1) Add 60% of UHMWPE, 20% of HDPE and 20% of silica gel powder in sequence in the mixing container, and mix well to obtain spare raw materials;
[0067] 2) Use an aluminum mold with a length of 297mm, a width of 210mm, and a height of 4.0mm. The spare raw materials are evenly added to the mold, and compressed and vibrated;
[0068] 3) After sintering at 160°C for 60 minutes, cool down and take it out.
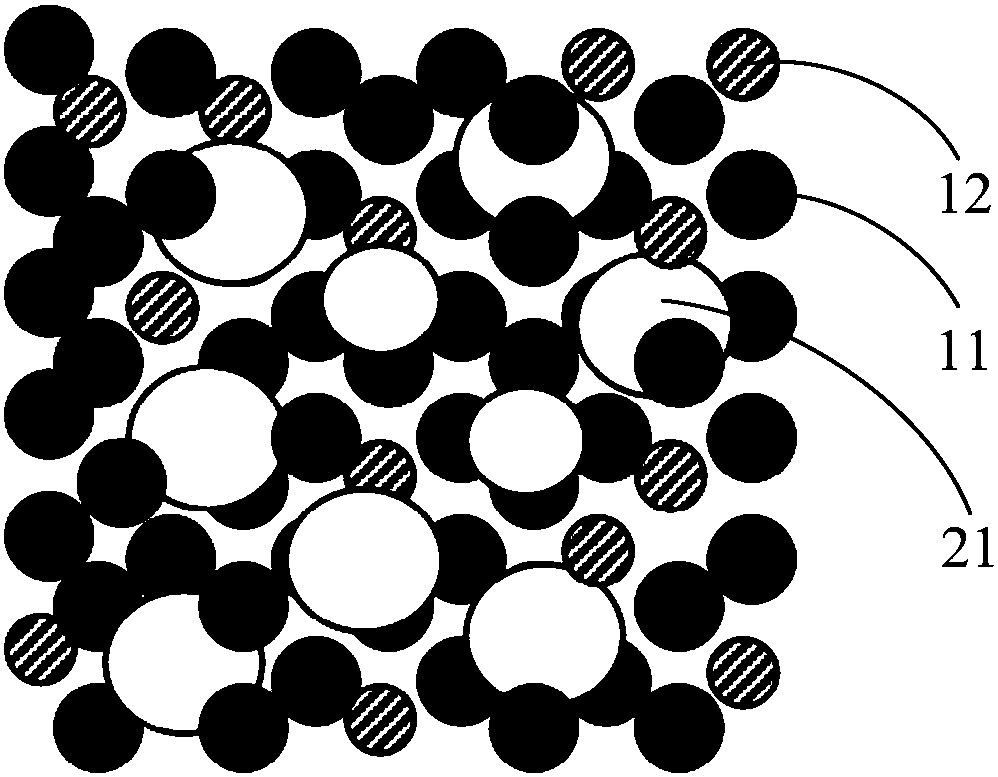
[0069] The composite material (such as figure 2 As shown), the length is 297mm, the width is 210mm, the height is 4.0mm, and the aperture is 50-80μm.
Embodiment 3
[0071] Thermoplastic polymer resin: HDPE, density 0.960, particle size 250-300 mesh.
[0072] Specific particulate or fibrous material for adsorbing nucleic acid: glass powder, particle size 300-500 mesh.
[0073] Experimental steps:
[0074] 1) Add HDPE 10% and glass powder 90% in sequence in the mixing container, and mix well to obtain spare raw materials;
[0075] 2) Adopt an aluminum mold with several holes, the diameter of the hole is 7.4mm, and the height is 2.0mm, and the spare raw materials are evenly added to the holes, and compressed and vibrated;
[0076] 3) After sintering at 180°C for 30 minutes, cool down and take it out.
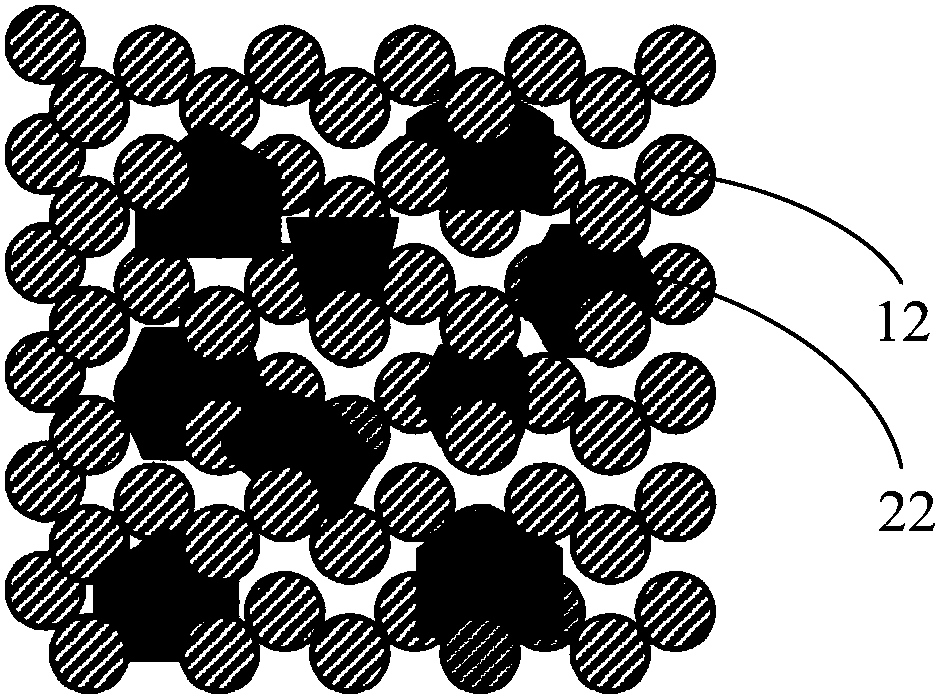
[0077] The composite material (such as image 3 As shown), the diameter is 7.4mm, the height is 2.0mm, and the aperture is 2-5μm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com