Method for preparing Aurivillius-phase SrBiFeCoTiO material through microwave sintering and product prepared by method
A microwave sintering and colloid technology, applied in the field of functional materials, can solve the problems of easy occurrence of impurity ions, reduced material properties, long holding time, etc., and achieve the effect of shortening high temperature holding time, high energy utilization rate, and reducing sintering temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
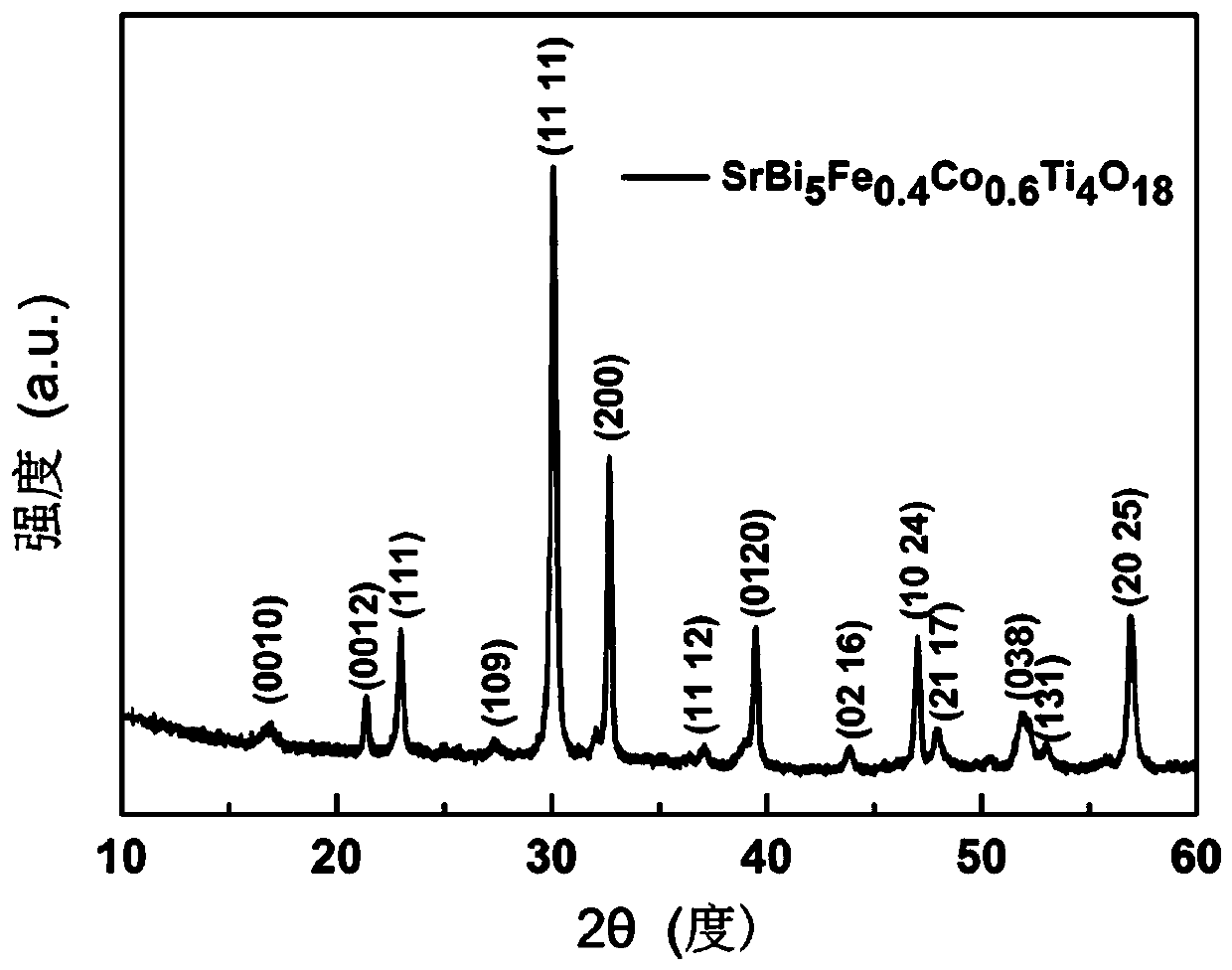
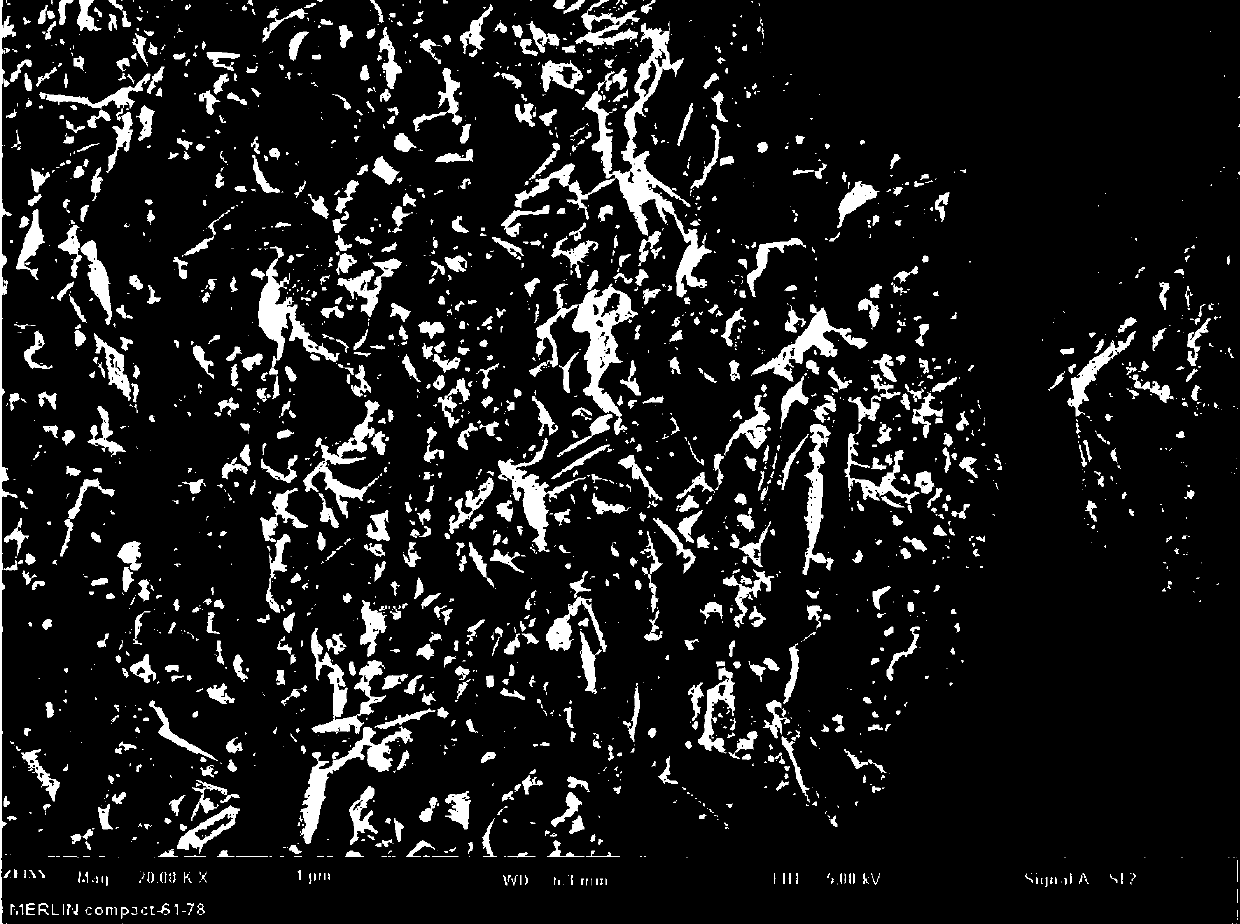
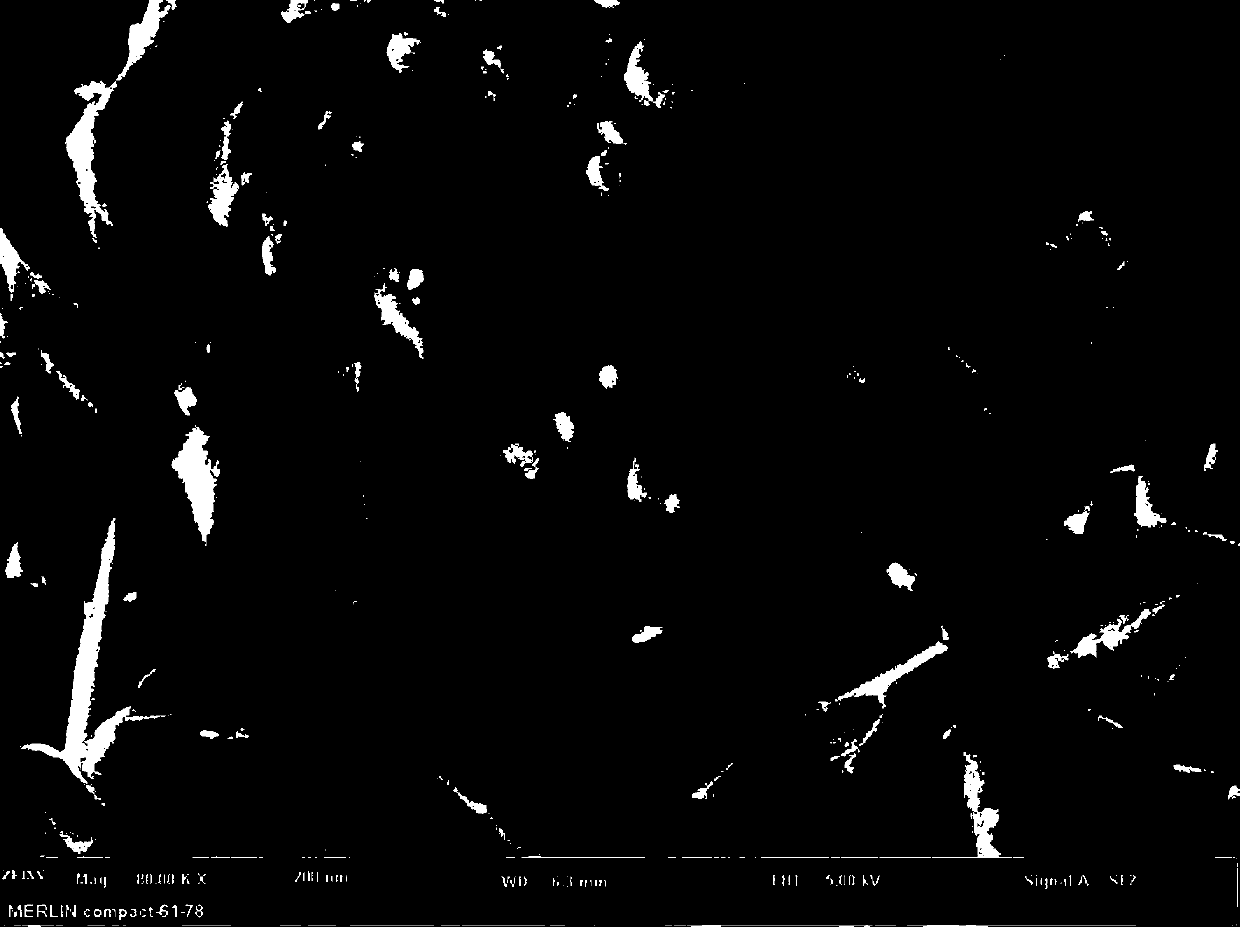
[0035] A method for preparing Aurivillius phase SrBiFeCoTiO material by microwave sintering, the specific material is SrBi 5 Fe 0.4 co 0.6 Ti 4 o 18 , the material has a layered perovskite-like structure, and its space group is orthorhombic B2cb , the preparation process includes the following steps:
[0036] 1) Mix 7.717 g of bismuth nitrate pentahydrate powder and 30 ml of glacial acetic acid solution, heat and stir at 60°C, after the bismuth nitrate powder is completely dissolved, add 0.451 g of cobalt acetate tetrahydrate powder, continue heating and stirring until the powder is completely dissolved to obtain Mixture A;
[0037] 2) Weigh 4.125 g of tetrabutyl titanate, add 20 ml of acetylacetone solution, heat and stir at 60°C until the two are evenly mixed to obtain a mixture B. Slowly pour the mixed solution A obtained in step 1) into the mixed solution B, continue heating and stirring, and obtain a clear and transparent mixed solution as mixed solution C;
[003...
Embodiment 2
[0043] A method for preparing Aurivillius phase SrBiFeCoTiO material by microwave sintering, the specific material is SrBi 5 Fe 0.4 co 0.6 Ti 4 o 18 , the material has a layered perovskite-like structure, and its space group is orthorhombic B2cb , the preparation process includes the following steps:
[0044]1) Mix 9.003 g of bismuth nitrate pentahydrate powder and 30 ml of glacial acetic acid solution, heat and stir at 60°C, after the bismuth nitrate powder is completely dissolved, add 0.523 g of cobalt acetate tetrahydrate powder, continue heating and stirring until the powder is completely dissolved to obtain Mixture A;
[0045] 2) Weigh 4.813 g of tetrabutyl titanate, add 20 ml of acetylacetone solution, heat and stir at 60°C until the two are evenly mixed to obtain a mixture B. Slowly pour the mixed solution A obtained in step 1) into the mixed solution B, continue heating and stirring, and obtain a clear and transparent mixed solution as mixed solution C;
[0046...
Embodiment 3
[0051] A method for preparing Aurivillius phase SrBiFeCoTiO material by microwave sintering, the specific material is SrBi 5 Fe 0.4 co 0.6 Ti 4 o 18 , the material has a layered perovskite-like structure, and its space group is orthorhombic B2cb , the preparation process includes the following steps:
[0052] 1) Mix 10.289 g of bismuth nitrate pentahydrate powder and 30 ml of glacial acetic acid solution, heat and stir at 70°C, after the bismuth nitrate powder is completely dissolved, add 0.601 g of cobalt acetate tetrahydrate powder, continue heating and stirring until the powder is completely dissolved to obtain Mixture A;
[0053] 2) Weigh 5.500 g of tetrabutyl titanate, add 20 ml of acetylacetone solution, heat and stir at 70°C until the two are evenly mixed to obtain a mixture B. Slowly pour the mixed solution A obtained in step 1) into the mixed solution B, continue heating and stirring, and obtain a clear and transparent mixed solution as mixed solution C;
[00...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com