Grain boundary diffusion method of R-Fe-B rare-earth sintered magnet, HRE diffusion source and fabrication method thereof
A sintered magnet and grain boundary diffusion technology, applied in the field of magnet manufacturing, can solve the problems of inevitable loss of remanence, reduce the saturation magnetic polarization of compounds, etc., and achieve the effects of increased coercive force, efficient diffusion, and improved diffusion quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] Step a: Take TbF with an average particle size of 10 microns 3 Powder, add water to submerge TbF 3 The powder was put into a ball mill and ground for 5 hours to obtain ground powder.
[0062] Step b: adding cellulose to water to prepare an aqueous solution with a concentration of 1 wt% cellulose.
[0063] Step c: Press Cellulose and TbF 3 The weight ratio of the powder is 1:9, the grinding powder obtained in step a is added to the aqueous solution obtained in step b, and mixed evenly to obtain a mixed solution.
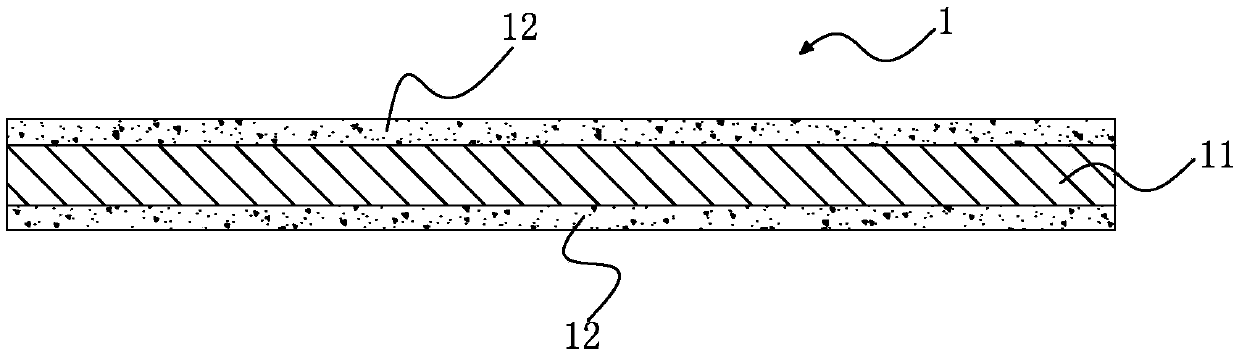
[0064] Step d: Select a W board 11 with a length and width of 10cm×10cm and a thickness of 0.5mm, put the W board 11 into an oven and heat it to 80°C, take it out, spray the above-mentioned mixture on the surface of the above-mentioned W board, and put it into the oven again to dry Dry to obtain a film-coated W plate with TbF attached to the film 3 powder.
[0065] Repeat the operation of step d on the other side of the film-coated W board to obtain a film...
Embodiment 11~ Embodiment 16
[0069] A rare earth magnet sintered body is prepared, the sintered body has the following atomic composition: Nd is 14.7, Co is 1, B is 6.5, Cu is 0.4, Mn is 0.1, Ga is 0.1, Zr is 0.1, Ti is 0.3, Fe is 0.1 quantity. It is produced according to the existing procedures of smelting, flake flakes, hydrogen crushing, jet milling, pressing, sintering and heat treatment of rare earth magnets.
[0070] The heat-treated sintered body is processed into a 15mm×15mm×30mm magnet, and the 30mm direction is the orientation direction of the magnetic field. The processed magnet is sandblasted and purged to clean the surface. The magnet uses the NIM-10000H large rare earth permanent magnet nondestructive testing system of the China Metrology Institute for magnetic performance testing. The measurement temperature is 20°C, and the measurement results are Br: 13.45kGs, Hcj: 19.00kOe, (BH)max: 42.41MGOe, SQ : 98.8%, the standard deviation value of Hcj is 0.1.
[0071] Such as figure 2 As shown ...
Embodiment 2
[0088] Step a: Take Dy with an average particle size of 20 microns 2 o 3 Powder, add absolute ethanol until Dy is submerged 2 o 3 powder, put into a ball mill and grind for 25 hours to obtain ground powder.
[0089] Step b: add resin in absolute ethanol, and configure an absolute ethanol solution with a concentration of 20 wt% resin;
[0090] Step c: Press Resin and Dy 2 o 3 The powder is in a weight ratio of 0.07:1. Add the grinding powder obtained in step a to the absolute ethanol solution obtained in step b, and mix evenly to obtain a mixed solution.
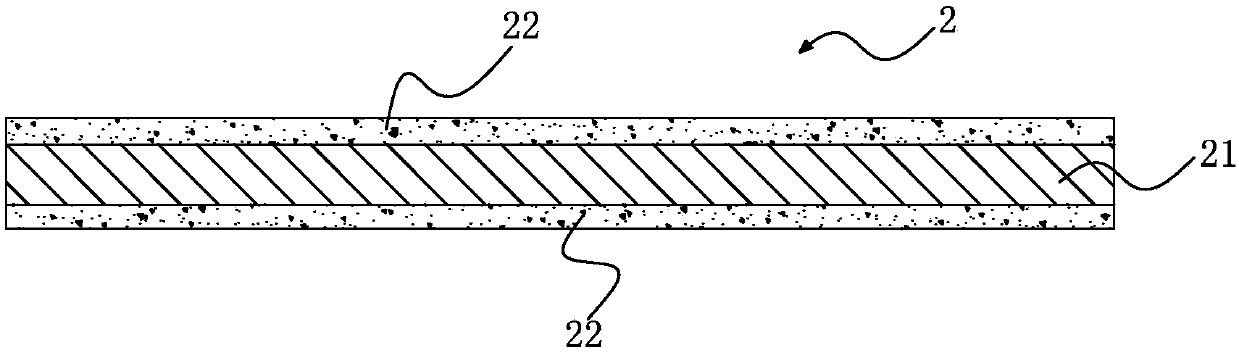
[0091] Step d: Select a zirconia plate 21 with a length and width of 10cm×10cm and a thickness of 0.5mm, put the zirconia plate 21 into an oven and heat it to 120°C, take it out, spray the above mixed solution evenly on the surface of the zirconia plate, and place it again Dry in an oven to obtain a film-coated zirconia plate, with Dy attached to the film 22 2 o 3 powder.
[0092] Repeat the operation of step d on the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com