Application of bacillus amyloliquefaciens in preventing and controlling fungal disease of plants
A technology for plant fungal diseases and amylolytic spores, which is applied in the application field of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens in the prevention and treatment of plant fungal diseases, to achieve stable and safe biological control effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1 Isolation and identification of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain BSY3
[0034] 1. Isolate strains from marigold plants collected in Guangzhou Baiyun Nursery. The specific isolation method is as follows:
[0035] (1) Single colony isolation
[0036] 1) Clean the collected fresh marigold leaf material with tap water;
[0037] 2) After rinsing once with sterile water, soak in 75% alcohol for 5 minutes, soak in 2% sodium hypochlorite solution for 2 minutes, and then rinse with sterile water 4 times, and spread the sterile water after the last rinse as a blank control ;
[0038] 3) Put the sterilized fresh plant material in a sterilized mortar, add a small amount of sterile water to grind it into a homogenate, and then dilute it into different gradients of the grinding solution and spread it on a flat plate;
[0039] 4) Place the plate in a 30°C incubator for culture, observe the growth of the colonies, then pick colonies of different shapes, purify and cultiva...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Example 2 Optimum culture condition optimization of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain BSY3
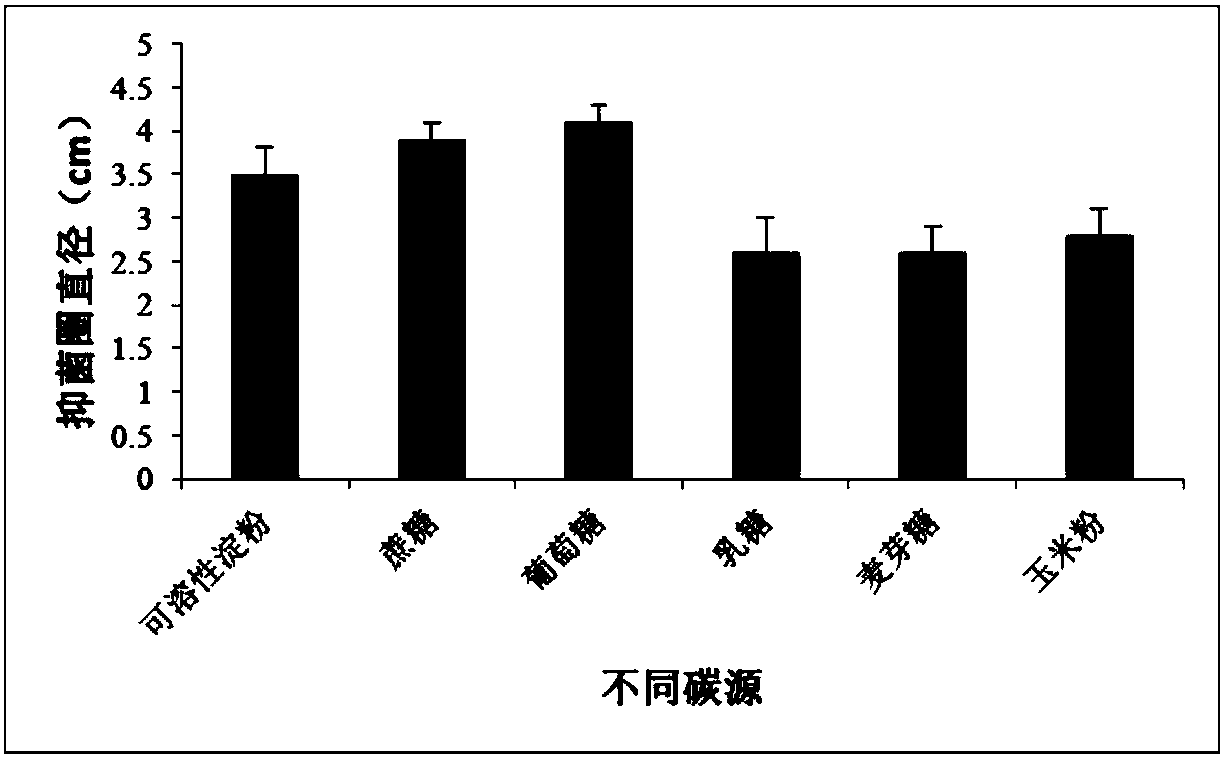
[0060] 1. The most suitable medium for strain growth
[0061] (1) Optimization method: Strain BSY3 was streaked and activated on LB medium (30°C), then inoculated into LB liquid medium, and activated at 280 rpm and 30°C. Inoculate the activated strain BSY3 with 0.5% inoculum in the shake flask fermentation basal medium YGN [yeast extract 10g (when different nitrogen sources), glucose 10 g (when different carbon sources), NaCl 5 g (when different inorganic salts ), dilute to 1 L, pH 7.0]. After inoculation, culture in a shaker at 30°C and 160 rpm for 2 to 5 days, and then centrifuge the fermentation broth of the above-mentioned different substances (carbon source, nitrogen source and inorganic salt) at 12,000 rpm for 15 min, and the supernatant was passed through a 0.22 μm micrometer. The original fermentation broth is obtained after filtering through a porous filter membrane. ...
Embodiment 3
[0075] Example 3 Detection of the antagonistic effect of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain BSY3 on common pathogenic fungi
[0076] 1. The BSY3 strain was co-cultured with several pathogenic fungi, and its antagonism to pathogenic fungi was detected.
[0077] Tested strains: Harmful Phylonotus xylinum ( P. noxius ), white butterfly anthracnose pathogen ( Colletotrichum sp.), canna blast pathogen ( Pyricularia cannaecola ), black pine leaf spot pathogen ( Pestalotiopsis sp.), the pathogen of banana wilt ( Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubes ) and Sclerotinia sclerotiorum pathogen ( Sclerotinia sclerotiorum ).
[0078] 2. Persistence culture detection method:
[0079] (1) Inoculate a 1% (v / v) ratio of the bacterial solution into a 150 mL Erlenmeyer flask filled with 40 mL LB medium, and incubate at 28°C and 200 rpm for 2.5 days;
[0080] (2) Centrifuge at 8000 rpm for 10 min to collect the supernatant, and then pass through a 0.22 μm filter membrane to obtain the cru...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com