Application of substances capable of inhibiting activity of Treg cells and promoting differentiation of Tfh cells in treating HBV infection
A technology of cell activity and cell differentiation, applied in the direction of medical raw materials derived from mammals, introduction of foreign genetic material using vectors, analysis of materials, etc., can solve the problems of lack of HBV infection models in small animals infected by hepatitis B virus
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
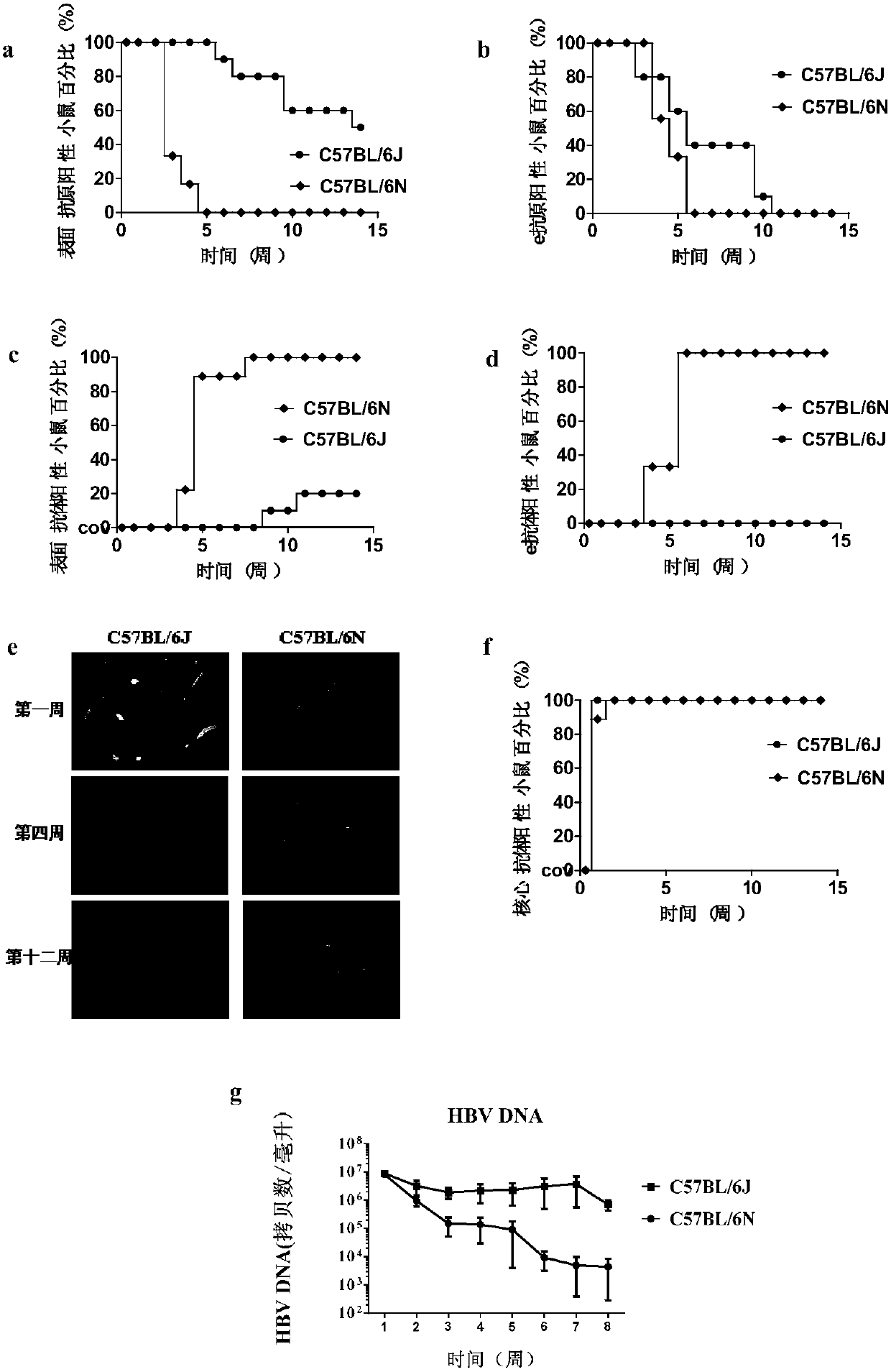
[0083] Embodiment 1, establishment of acute and chronic HBV mouse model
[0084] 1. Model building
[0085] The pAAV / HBV1.2 plasmid (diluted with normal saline) was injected into male C57BL / 6N mice aged 6-8 weeks by tail vein high pressure injection. The injection dose is 10 μg pAAV / HBV1.2 plasmid per mouse, the injection volume is 8%-12% of the mouse body weight, and all the injection volumes are pushed in at a uniform speed within 5-7 seconds, and a total of 9 pAAV / HBV1.2 plasmids are obtained Plasmid transfection mouse model (hereinafter referred to as acute HBV mouse model). To facilitate tail vein injection, the tip of the 2ml syringe can be replaced with the tip of the 1ml syringe.
[0086] According to the above method, the pAAV / HBV1.2 plasmid was replaced with the pAAV empty plasmid, and other steps remained unchanged, and a control mouse of the acute HBV mouse model was obtained, which was named control mouse N.
[0087] According to the above method, male C57BL / 6N...
Embodiment 2
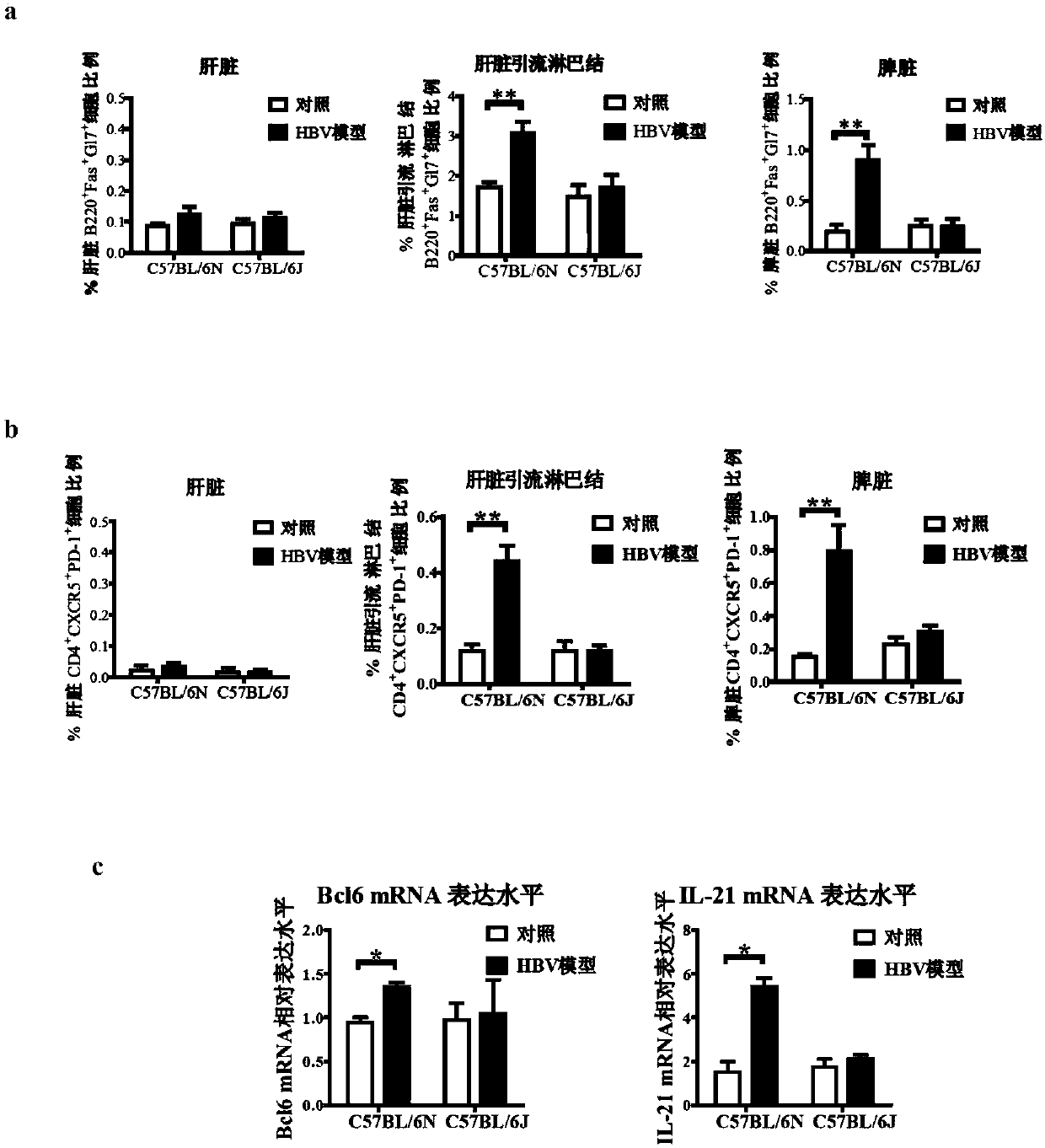
[0097] Example 2, Analysis of HBV-induced differentiation of germinal center B cells and Tfh cells in acute and chronic HBV mouse models
[0098] In the 3rd week of plasmid injection, according to the following steps 1-3, respectively isolate the liver lymphocytes and liver draining lymph nodes of the acute HBV mouse model and control mouse N and the chronic HBV mouse model and control mouse J in Example 1 For lymphocytes and splenic lymphocytes, the proportion of germinal center B cells and follicular helper T cells (Follicular helper CD4 + T cells, Tfh cells) ratio, according to the method of step 6, using Q-PCR to analyze CD4 + The mRNA expression levels of the mater transcription factor Bcl6 and the main effector cytokine IL-21 in T cells differentiated from Tfh cells. The experiment was repeated three times, and each experiment was set in triplicate.
[0099] 1. Liver Lymphocyte Isolation
[0100] (1) Dissection of mice: the mice were deeply anesthetized by intraperiton...
Embodiment 3
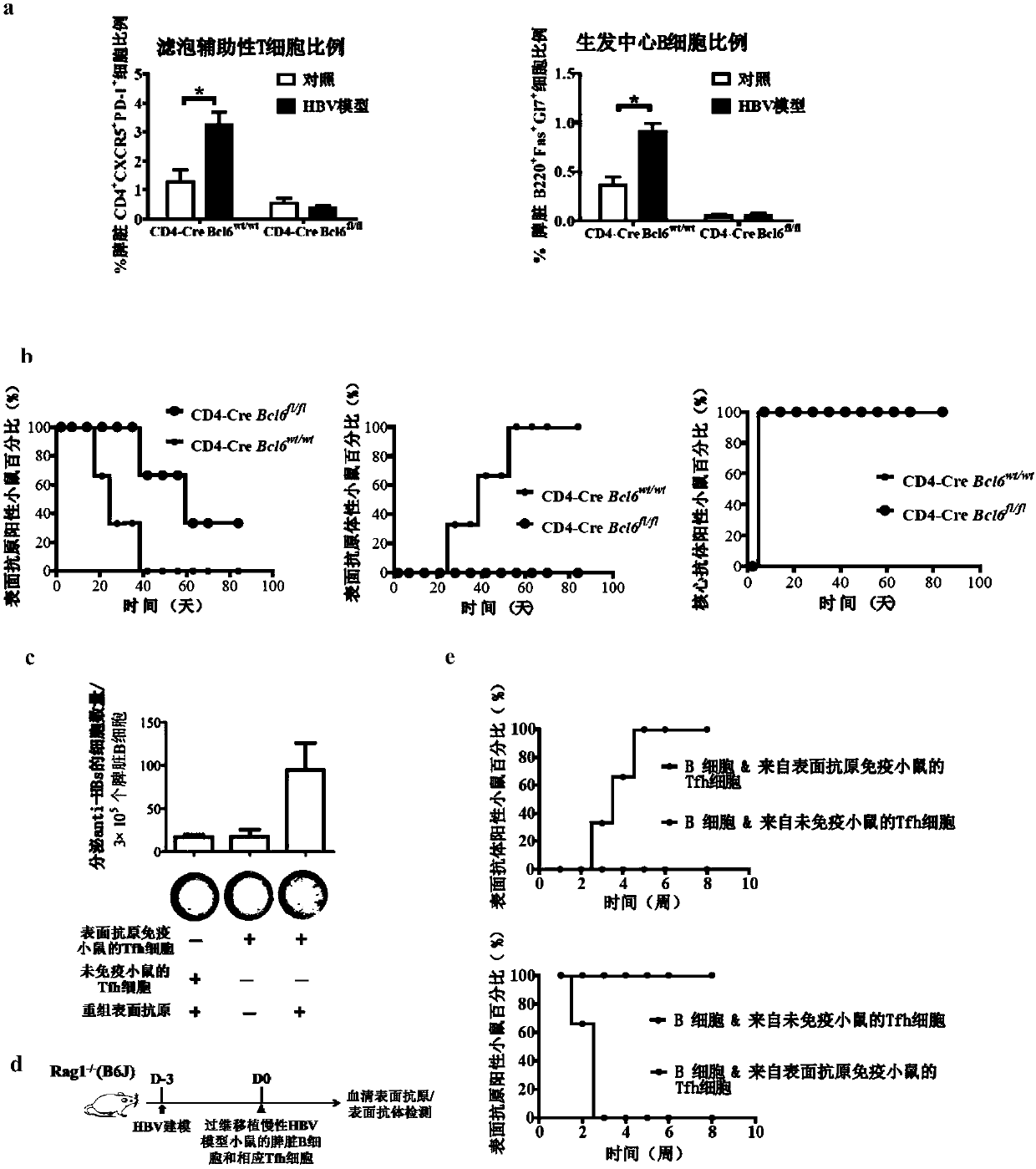
[0135] Example 3 Germinal center B cell differentiation and surface antibody response disappear in acute HBV model mice lacking Tfh cell differentiation
[0136] CD4-Cre Bcl6 fl / fl mouse CD4 + The transcription factor Bcl6 responsible for Tfh cell differentiation is specifically deleted in T cells, so the CD4 of this mouse + T cells cannot differentiate into Tfh cells after activation, while CD4 of other subsets + T cell effector differentiation was not affected. CD4-Cre Bcl6 of C57BL / 6 background fl / fl The mice were mated with C57BL / 6N mice to obtain CD4-Cre Bcl6 of the F1 generation wt / fl mice, and then the F1 generation of CD4-Cre Bcl6 wt / fl The mice were mated with C57BL / 6N mice to obtain CD4-Cre Bcl6 of the F2 generation wt / fl For mice, repeat this operation until the CD4-Cre Bcl6 of the F4 generation is obtained wt / fl Mice, which have acquired an acute HBV background (C57BL / 6N background). Then from the female CD4-Cre Bcl6 of the F4 generation wt / fl Mouse and ma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com