Quasi-in-situ experimental method of dynamic compression deformation and failure behavior of metal material
A dynamic compression, metal material technology, used in the application of repetitive force/pulsation force to test the strength of materials, etc., can solve the problems of sample loading, material dynamic deformation and short failure process, unable to grasp the whole process of microstructure changes, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] A quasi-in-situ experimental analysis method for dynamic deformation and failure behavior of metal materials, the specific steps of the method are as follows:
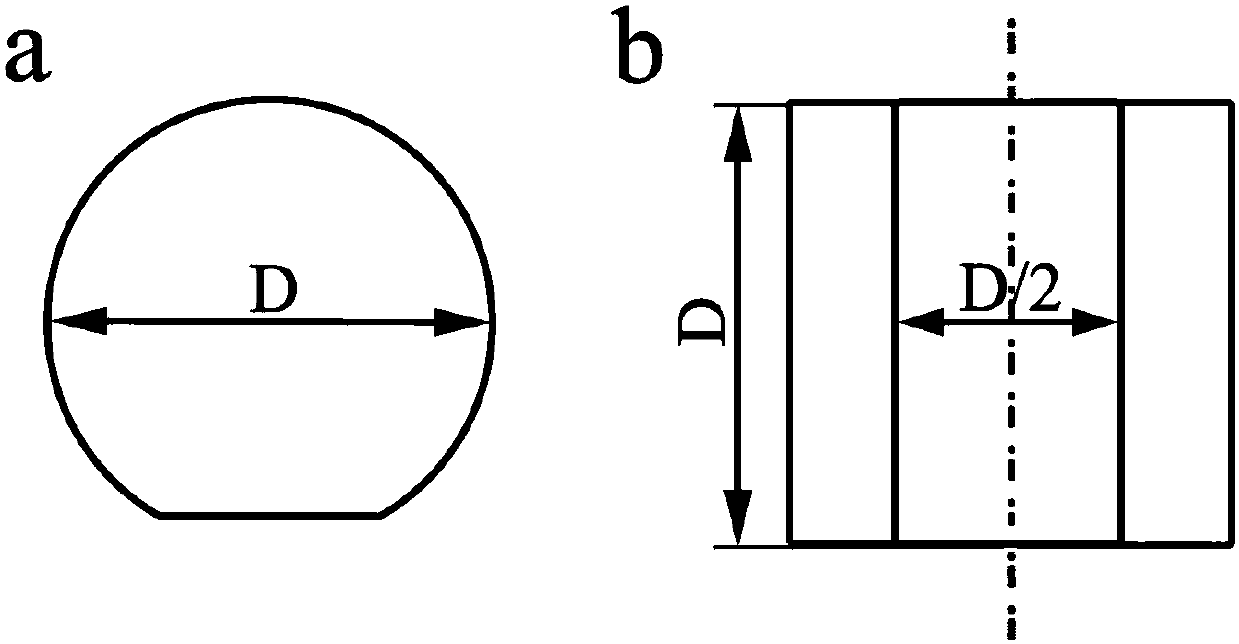
[0027] (1) Prepare pure titanium into The D-pillar sample, polished side, marked observation area, using scanning electron microscope imaging analysis and electron backscatter diffraction analysis method to observe the structure morphology and grain orientation in the marked area;
[0028] (2) to the sample that step (1) makes in A strain rate of 3000s was performed on the separated Hopkinson bar -1 , the strain amount is 0.03, and the deformation temperature is 200℃ under uniaxial dynamic compression loading;
[0029] (3) performing quasi-in-situ observation of microstructure and grain orientation on the marked area on the sample compressed in step (2);
[0030] (4) carry out the uniaxial dynamic compression that strain rate and deformation temperature are all consistent with step (2) after the observation...
Embodiment 2
[0034] A quasi-in-situ experimental analysis method for dynamic deformation and failure behavior of metal materials, the specific steps of the method are as follows:
[0035] (1) Prepare the aluminum alloy into The D-pillar sample, polished side, marked observation area, using scanning electron microscope imaging analysis and electron backscatter diffraction analysis method to observe the structure morphology and grain orientation in the marked area;
[0036] (2) to the sample that step (1) makes in A strain rate of 3000s was performed on the separated Hopkinson bar -1 , the strain amount is 0.05, and the deformation temperature is 100℃ under uniaxial dynamic compression loading;
[0037] (3) performing quasi-in-situ observation of microstructure and grain orientation on the marked area on the sample compressed in step (2);
[0038] (4) carry out the uniaxial dynamic compression that strain rate and deformation temperature are all consistent with step (2) after the observ...
Embodiment 3
[0042] A quasi-in-situ experimental analysis method for dynamic deformation and failure behavior of metal materials, the specific steps of the method are as follows:
[0043] (1) Prepare the steel into The D-pillar sample, polished side, marked observation area, using scanning electron microscope imaging analysis and electron backscatter diffraction analysis method to observe the structure morphology and grain orientation in the marked area;
[0044] (2) to the sample that step (1) makes in A strain rate of 5000s was performed on the split Hopkinson bar -1 , the strain amount is 0.05, and the deformation temperature is 20℃ under uniaxial dynamic compression loading;
[0045] (3) performing quasi-in-situ observation of microstructure and grain orientation on the marked area on the sample compressed in step (2);
[0046] (4) carry out the uniaxial dynamic compression that the strain rate and the deformation temperature are all consistent with the step (2) after the observat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com