A method for electrolytic deplating of zinc layer and chromium passivation layer on the surface of iron parts
A technology of chromium passivation and iron parts, applied in the field of metal surface treatment and electrolytic stripping, can solve the problems of increasing the risk of hydrogen embrittlement, affecting the production environment, workpiece bubbling, etc., achieving high removal efficiency and reducing the effect of process flow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
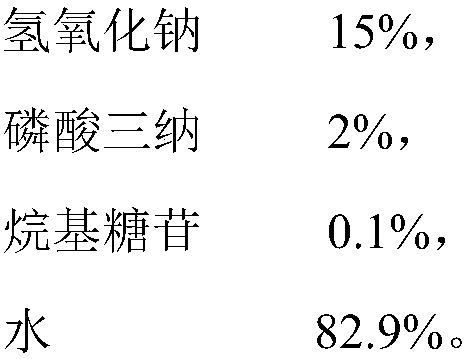
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] A method for electrolytic deplating of a zinc layer and a chromium passivation layer on the surface of an iron piece, comprising the following steps:
[0027] 1) Put the iron piece to be deplated into the deplating solution and connect it to the positive pole of the rectifier as the anode, put the stainless steel plate into the deplating solution and connect the negative pole of the rectifier as the cathode to form an electrolytic deplating system. The distance between the plated iron piece and the stainless steel plate in the deplating solution is 5cm;
[0028] 2) Turn on the rectifier, output 3V DC voltage to the electrolytic deplating system, start electrolytic deplating, the zinc layer and chromium passivation layer on the surface of the iron parts begin to dissolve, the zinc layer on the surface of the stainless steel plate continues to deposit, and the current of the electrolytic deplating system continues to drop ; The initial anode current density of the electro...
Embodiment 2
[0034] A method for electrolytic deplating of a zinc layer and a chromium passivation layer on the surface of an iron piece, comprising the following steps:
[0035] 1) Put the iron piece to be deplated into the deplating solution and connect it to the positive pole of the rectifier as the anode, put the stainless steel plate into the deplating solution and connect the negative pole of the rectifier as the cathode to form an electrolytic deplating system. The distance between the plated iron piece and the stainless steel plate in the deplating solution is 8cm;
[0036] 2) Turn on the rectifier, output 6V DC voltage to the electrolytic deplating system, start electrolytic deplating, the zinc layer and chromium passivation layer on the surface of the iron parts begin to dissolve, the zinc layer on the surface of the stainless steel plate continues to deposit, and the current of the electrolytic deplating system continues to drop ; The initial anode current density of the electro...
Embodiment 3
[0043] A method for electrolytic deplating of a zinc layer and a chromium passivation layer on the surface of an iron piece, comprising the following steps:
[0044] 1) Put the iron piece to be deplated into the deplating solution and connect it to the positive pole of the rectifier as the anode, put the stainless steel plate into the deplating solution and connect the negative pole of the rectifier as the cathode to form an electrolytic deplating system. The distance between the plated iron piece and the stainless steel plate in the deplating solution is 15cm;
[0045] 2) Turn on the rectifier, output 7V DC voltage to the electrolytic deplating system, start electrolytic deplating, the zinc layer and chromium passivation layer on the surface of iron parts begin to dissolve, the zinc layer or chromium layer on the surface of the stainless steel plate is continuously deposited, the electrolytic deplating system The current keeps decreasing; the initial anodic current density of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com