Preparation method of master cell bank for umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells in perinatal period
A master cell bank and mesenchymal stem cell technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of perinatal umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell master cell bank, can solve the problem of inability to meet the demand for matching bank cell volume, low yield of primary cells, and inability to meet the needs of cells. Quantity requirements and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] Example 1: Isolation and culture of MSCs
[0057] S1. Aseptically collect the umbilical cord of a healthy newborn born by full-term cesarean section, the length of the collection is 20cm, both ends are ligated, and the parturient woman signs the informed consent.
[0058] S2. The parturient has been screened for pathogenic microorganisms and has no HIV, HBV, HCV, HTLV, EBV, CMV, or TP infection. The umbilical cord sample was soaked in normal saline, the residual blood sample was collected for sterility test, the result was negative, and the mycoplasma test was carried out, the result was negative.
[0059] S3. Wash the residual blood of the umbilical cord in normal saline, soak it in 75% disinfectant alcohol for about 30 seconds, take it out immediately, rinse it twice with normal saline, cut it off at the ligation site, and discard both ends.
[0060] S4. Perfuse the blood vessel with normal saline, squeeze out the residual blood, cut the umbilical cord sample into ti...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Example 2: Analysis of biological characteristics of P3 generation MSCs
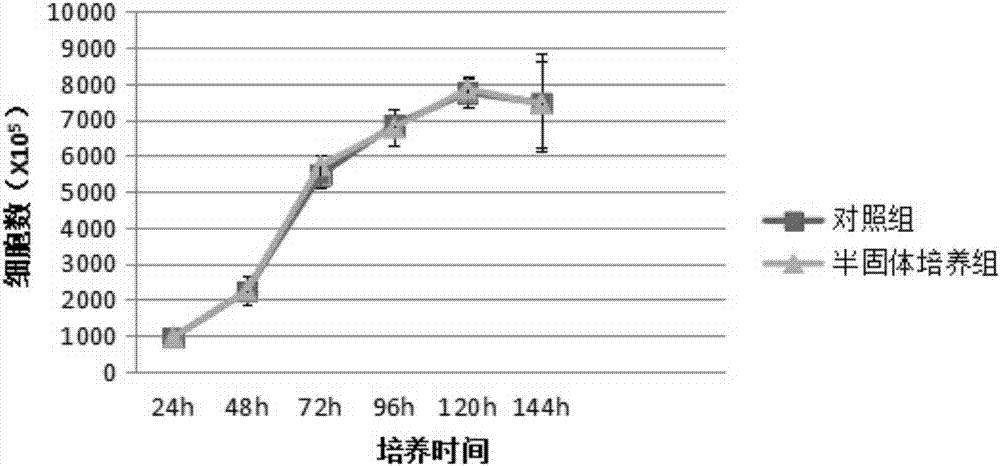
[0067] 2.1 Growth curve and population doubling time detection
[0068] Take the P2 generation cells, inoculate them into 24-well plates at 1000 / mL, and count 5 wells every 24 hours with a cell imaging system (Cytell CellImaging System, produced by GE Healthcare) for 6 consecutive days. Time is the abscissa, and the growth curve is drawn; the population doubling time is calculated with the formula TD=t×lg2 / lg(Nt / N0) (Nt is the number of cells at time t, and N0 is the number of initial cells).
[0069] 2.2 Cloning rate detection
[0070] Take the P2 cells, inoculate them into 24-well plates at 100 / mL, change the medium in half every other day, culture until the 12th day, discard the culture supernatant, perform HE staining, and count the number of CFU-F.
[0071] 2.3 Detection of differentiation potential in vitro
[0072] 2.3.1 Osteogenic differentiation function
[0073] Take the P2 generatio...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Embodiment three: detection result
[0081] 3.1 Results of yield of umbilical cord-derived MSCs
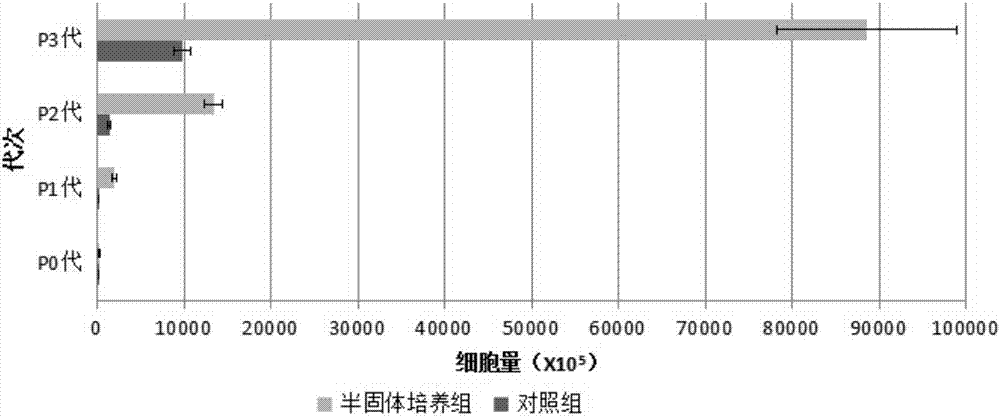
[0082] On the third day of culture in the 10cm umbilical cord semi-solid culture group, a small amount of cells could be seen crawling out under the microscope, and a large number of cells crawled out on the seventh day of culture, and it was close to 90% confluence on the 12th day of culture. The cell yield after harvesting (X10 5 ) was: 271.91±53.62; on the 12th day of culture in the 10cm umbilical cord control group, an average of 24.2 tissue pieces adhered to the wall, and cells crawled out around them. When harvested on the 14th day, it accounted for about 60% of the culture area, and the cell yield after harvest (X10 5 ) was: 28.91±4.81, significantly less than the semi-solid culture group.
[0083] Take 7.5X10 5 P0 cells at 6000 cells / cm 2 Inoculate to 25cm 2 The culture flask was cultured until harvested on the 4th day, which was recorded as P1 generation cells;...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com