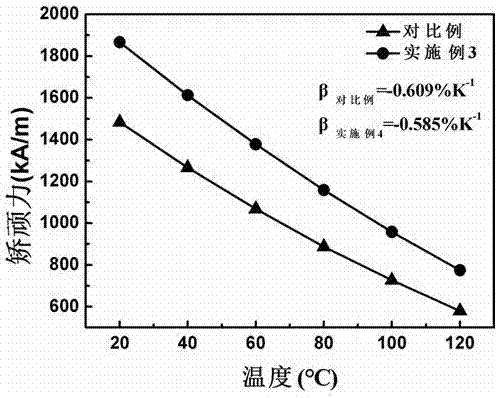
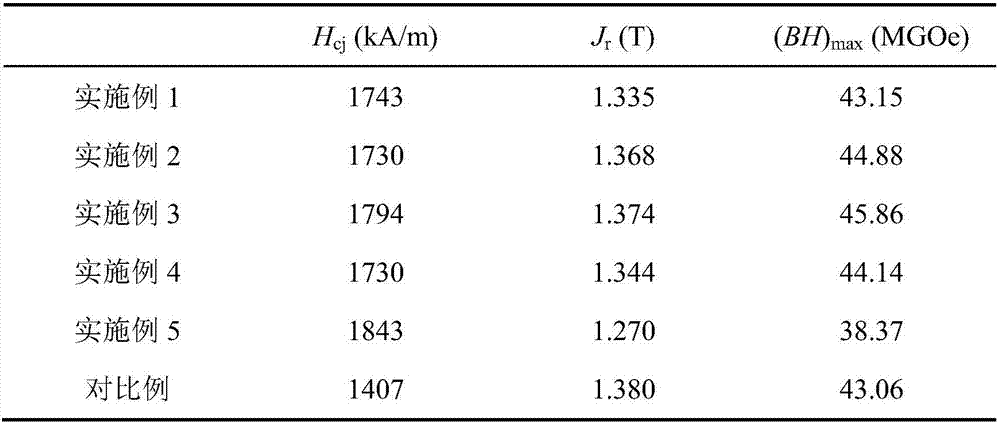
Crystal boundary diffusion method for improving coercive force and thermal stability of neodymium-iron-boron magnet
A technology of thermal stability and grain boundary diffusion. It is used in the manufacture of inductors/transformers/magnets, electrical components, circuits, etc. It can solve the problems of insufficient compactness and firmness of attachments, difficulty in mass production, and low production efficiency, and save energy. , The effect of low diffusion energy consumption and low diffusion temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] (1) Polish the sintered NdFeB magnet with a size of φ3×6mm to remove the surface scale with sandpaper, and clean it ultrasonically with alcohol;
[0041] (2) Mix the sample of step (1) with Dy 60 Ni 10 Cu 20 Al 10 The diffusion source alloy material is put into the quartz tube to ensure that the magnet is wrapped by the diffusion source material, and the tube is sealed after two argon washes;
[0042] (3) Diffusion heat treatment of the sample in step (2) at 700°C for 5h, followed by tempering at 450°C for 1h.
Embodiment 2
[0044] (1) with embodiment 1 step (1);
[0045] (2) with embodiment 1 step (2);
[0046] (3) Diffusion heat treatment of the sample in step (2) at 710°C for 3h, followed by tempering at 500°C for 1h.
Embodiment 3
[0048] (1) with embodiment 1 step (1);
[0049] (2) with embodiment 1 step (2);
[0050] (3) Diffusion heat treatment of the sample in step (2) at 730°C for 4h, followed by tempering at 500°C for 1h.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com