Cultivation method capable of improving content of polysaccharides in shiitake mushroom hyphae
A technology of mycelium polysaccharides and cultivation methods, which is applied in the cultivation field of using ginkgo biloba residues to increase the content of mushroom mycelium polysaccharides, can solve the problems of low economic value, complicated cultivation methods, and low cultivation utilization rate, and achieve shortening The effect of cultivation time, high utilization rate and simple cultivation method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment 1 discloses a cultivation method for improving the polysaccharide content of shiitake mushroom mycelia, including base material treatment (gingko biloba residue treatment), base material preparation, bagging, high-temperature sterilization, inoculation, mycelium cultivation, and mycelium collection process steps,
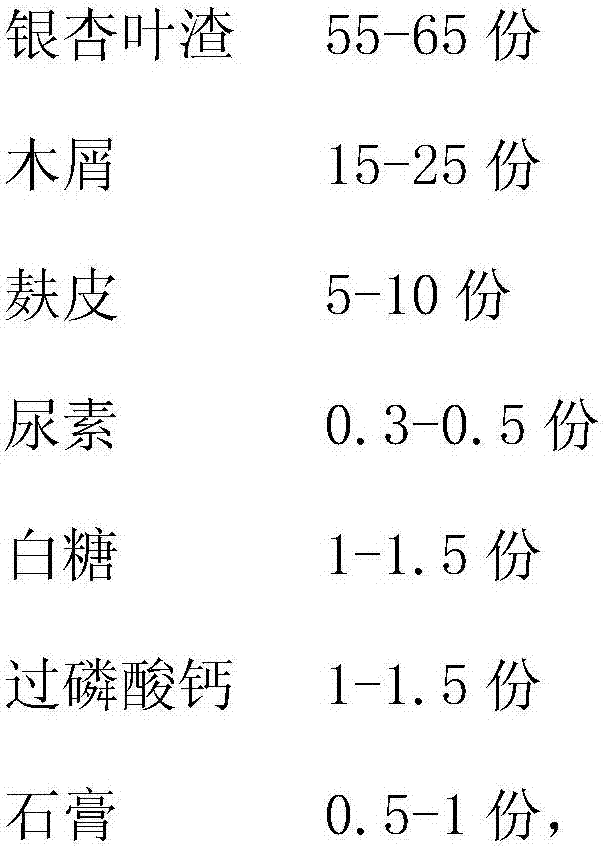
[0029] Base material treatment: first crush the ginkgo leaf residue weighed in step 1 into a size of 0.3-0.5 cm, add wood chips in proportion and add 1-2% cellulase by weight, and perform biodegradation treatment to prepare the base material;
[0030] Base material preparation: Weigh the main material and auxiliary materials according to the formula ratio, stir evenly, add water in an appropriate amount to achieve a suitable material-water ratio, and then carry out the bagging step; bagging: put the prepared cultivated mushroom base material into a special film In the tube, seal it to make cultivation sticks of mushroom mycelium; high temperature s...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2 has the same operation steps as in Example 1, the difference is that in Example 2, a biological growth regulator is added in the base material preparation and inoculation process, and the biological growth regulator is composed of oleic acid and α-naphthaleneacetic acid, and the base material In the preparation step, the components (weight) of the base material are: 65 parts of ginkgo biloba, 15 parts of sawdust, 10 parts of bran, 0.5 part of urea, 1.5 parts of white sugar, 1 part of superphosphate, and 0.8 part of gypsum; Add 0.3 parts of oleic acid to the mixture, stir evenly and then carry out the bagging step. Before the inoculation step begins after the high-temperature sterilization step ends, inject 0.03 parts of α-naphthalene acetic acid at the inoculation port, and then perform the inoculation step, wherein the depth of biological growth regulator injection is 2 / 3 of the thickness of the bacterial rod . The polysaccharide content in the mushroom m...
Embodiment 3
[0036]Embodiment 3 takes the same cultivation steps as in Example 1, the difference is that in the present embodiment, a biological growth regulator is added in the base material preparation and mycelia cultivation steps, and the biological growth regulator is composed of oleic acid and 3-indole Butyric acid; in the base material preparation step, the component (weight) of base material is: 60 parts of ginkgo biloba residues, 20 parts of sawdust, 5 parts of bran, 0.0 part of urea, 1.2 parts of white sugar, 1.2 parts of superphosphate, gypsum 1 part, and 0.4 part of oleic acid was added to the base material at the same time; after the main material and auxiliary materials were accurately weighed according to the formula ratio, they were repeatedly stirred evenly, and an appropriate amount of water was added to achieve a suitable material-water ratio, and then the bagging step was carried out; In the cultivation step, when the mycelium of the bacterium stick is overgrown and the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com