High-iron zinc leaching residue clean utilization method
A high-iron zinc and leaching slag technology, which is applied in the field of dressing and smelting, can solve the problems of difficult recovery of valuable metals and high recovery costs, and achieve the effects of eliminating environmental pollution, improving comprehensive grade and recovery rate, and efficient recovery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
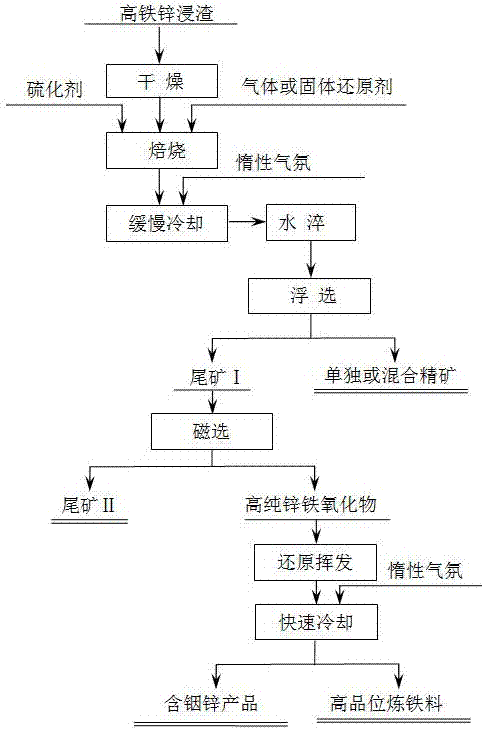
[0053] Such as figure 1 Shown, this high-iron zinc leaching slag cleaning utilization method, its specific steps are as follows:
[0054] (1) First, the high-iron zinc leaching slag (the content of copper and bismuth in the high-iron zinc leaching slag is very low, and its chemical composition is: Pb3.4%, Zn16.5%, Fe21.5%, Ag272.3g / t, In278.5g / t, the chemical phase of lead is PbSO 4 76%, PbS8%, other 16%, the chemical phase of zinc is: ZnSO 4 38.6%, ZnFe 2 o 4 58.3%, the other 3.1%, the chemical phase of silver is: Ag 2 O18.6%, AgS74.4%, other 7%) drying and dehydration, and then add reducing agent (carbon powder, the addition amount is 12% of the mass of high-iron zinc leaching slag) and vulcanizing agent (sodium sulfide, the addition amount is high-iron zinc leaching 1% of slag mass), roasted in a carbon-sulfur mixed atmosphere at a temperature of 750 °C for 1.5 h, after the roasting was completed, nitrogen or argon was introduced as a protective gas, and slowly cooled ...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Such as figure 1 Shown, this high-iron zinc leaching slag cleaning utilization method, its specific steps are as follows:
[0060] (1) First, the high-iron zinc leaching slag (its chemical composition is: Pb2.3%, Zn14.4%, Fe19.8%, Ag389.6g / t, Cu1.4%, In278.5g / t and Bi0.96 %, the chemical phase of lead is PbSO 4 68.9%, PbS12%, other 9.1%, the chemical phase of zinc is: ZnSO 4 42.5%, ZnFe 2 o 4 53.8%, the other 3.7%, the chemical phase of silver is: Ag 2 O13.8%, AgS71.2%, other 15%, copper chemical phase: CuO84.2%, CuS13.9%, other 1.9%, bismuth chemical phase: BiO76.2%, BiS21.3 %, other 2.5%) drying and dehydration, and then add reducing agent and vulcanizing agent at the same time (both reducing agent and vulcanizing agent are high-sulfur coal, the carbon content in high-sulfur coal is 80wt%, sulfur content is 5.5wt%, and the addition amount is high-iron-zinc The quality of leaching residue is 14.5%), roasting in a carbon-sulfur mixed atmosphere at a temperature of...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Such as figure 1 Shown, this high-iron zinc leaching slag cleaning utilization method, its specific steps are as follows:
[0066] (1) First, the high-iron zinc leaching slag (its chemical composition is: Pb3.4%, Zn10%, Fe25%, Ag350g / t, Cu2.4%, In450g / t and Bi1.8%, the chemical phase of lead is PbSO 4 72.5%, PbS2.5%, other 25%, the chemical phase of zinc is: ZnSO 4 38.5%, ZnFe 2 o 4 55.2%, the other 6.3%, the chemical phase of silver is: Ag 2 O21.5%, AgS74.5%, other 4%, copper chemical phase: CuO78.5%, CuS14.5%, other 7%, bismuth chemical phase: BiO68.4%, BiS19.6 %, other 12%) drying and dehydration, and then add a reducing agent at the same time (the reducing agent is a mixed gas reducing agent of carbon monoxide and producer gas with a volume ratio of 1:1, the amount of the reducing agent is 2L / min unit, the gas reducing agent Containing CO volume concentration 50%, H 2 The volume concentration is 12%, and the rest is N 2 ) and vulcanizing agent (the vulcanizi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com