Crosslinking hyaluronic acid gel, micro-needle film and manufacturing method for micro-needle film
A technology of cross-linking hyaluronic acid and hyaluronic acid, which is applied in the fields of beauty or medical treatment and biomedical materials, can solve the problems of poor cosmetic effect of microneedle patches, incomplete elimination of pain, and inability of microneedles to penetrate the skin, etc. Beauty effect retention, good moisturizing effect, excellent swelling effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
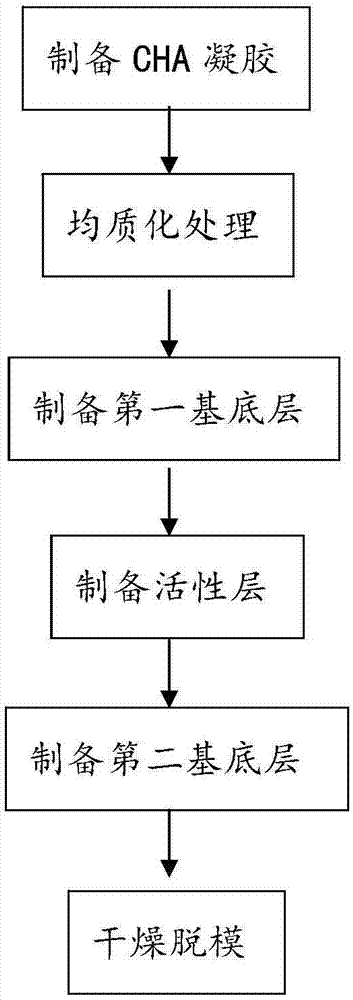
[0099] According to Table 1, HA is dissolved in the lye, and the concentration of HA in the lye is adjusted by adjusting the concentration of HA or the amount of addition to obtain a hyaluronate solution. joint agent. In this example the crosslinking agent is BDDE. After reacting for 20-35 hours at a temperature of 25-30° C., a CHA gel is generated, and finally the BDDE and NaOH remaining on the CHA gel are washed away with physiological saline to obtain a product CHA gel.
[0100] Homogenize the CHA gel for 10 min in a homogenizer with a rotational speed of 8000 rpm. The homogenized CHA gel was injected into the mold 200 under the condition of a pressure of 150 mmHg. After 160 minutes, the injection was completed, and the CHA gel was dried at 85° C. for 20 minutes. The dried CHA gel was centrifuged in a centrifuge with a centrifugal force of 650 g and a centrifugation time of 60 min. After centrifugation, the microneedle holes of the mold 200 are filled with CHA gel to for...
Embodiment 2
[0103] The difference between this example and Example 1 is that, in addition to the changes in the relevant raw material parameters for preparing CHA gel listed in Table 1, an active layer 102 is added on the basis of the first base layer 101 . specifically:
[0104] The active ingredient is added to the mold 200, in this embodiment the active ingredient is HA, which is added to the mold 200 as a single layer, and the concentration of HA is 30% (w / v). The mold 200 to which the active ingredient HA was added was centrifuged for 40 min under the condition of a centrifugal force of 800 g. After centrifugation, it was dried for 60 minutes at a temperature of 45° C. to obtain an active layer 102 . The thickness of the active layer 102 is determined by its added amount, and those skilled in the art can make corresponding adjustments according to actual conditions.
[0105] In this embodiment, the microneedle patch includes a first base layer 101 made of CHA gel and an active laye...
Embodiment 3
[0107] The difference between this example and Example 2 is that, in addition to the changes in the relevant raw material parameters for preparing CHA gel listed in Table 1, a second base layer 103 is added on the basis of the active layer 102 . Specifically: after forming the first base layer and the active layer 102, inject the CHA gel and the auxiliary agent of the embodiment of the present invention into the microstructure mold 200, thereby adding the second base layer 103 with a certain thickness to the microneedle patch middle.
[0108] In this embodiment, the auxiliary agent is a mixture of CHA gel and HA in a weight ratio of 100:20. After mixing the CHA gel and HA at a ratio of 100:20, inject it into the mold 200 at a pressure of 200 mmHg, and remove air bubbles in the mixture by a vacuum pump at a pressure of 300 mmHg. After drying at 45° C. for 8 hours, centrifuge again with a centrifugal force of 800 g and a centrifugation time of 30 minutes. Finally, dry at a tem...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com