Zirconia ceramic and preparation method thereof
A technology of zirconia ceramics and zirconia, which is applied in the field of ceramic materials to achieve the effect of increasing the dielectric constant
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
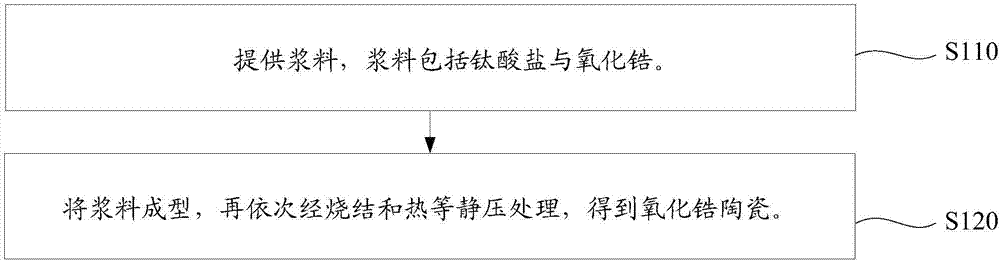
[0025] Such as figure 1 Shown, the preparation method of the zirconia ceramics of an embodiment, comprises the steps:
[0026] Step S110: providing a slurry, the slurry includes titanate and zirconia.
[0027] Among them, the zirconia includes 97%-99.5% of zirconia powder with a particle size of 0.5-0.8 micron and 0.5%-3% of zirconia powder with a particle size of 20-50 nm according to mass percentage. Due to fine-grain strengthening will occur when subjected to hot isostatic pressing at high temperatures, by using 97% to 99.5% of zirconia powder with a particle size of 0.5 micron to 0.8 micron and 0.5% to 3% of zirconia powder with a particle size of 20 nanometers ~50nm zirconia powder can improve strength and dielectric properties.
[0028] Wherein, the particle size of the titanate is 0.1 micron to 0.5 micron. Particles with a particle size of less than 1 micron are ultrafine powders. Due to their small particle size, correspondingly, their specific surface area is large...
Embodiment 1
[0057] The preparation process of the zirconia ceramics of the present embodiment is as follows:
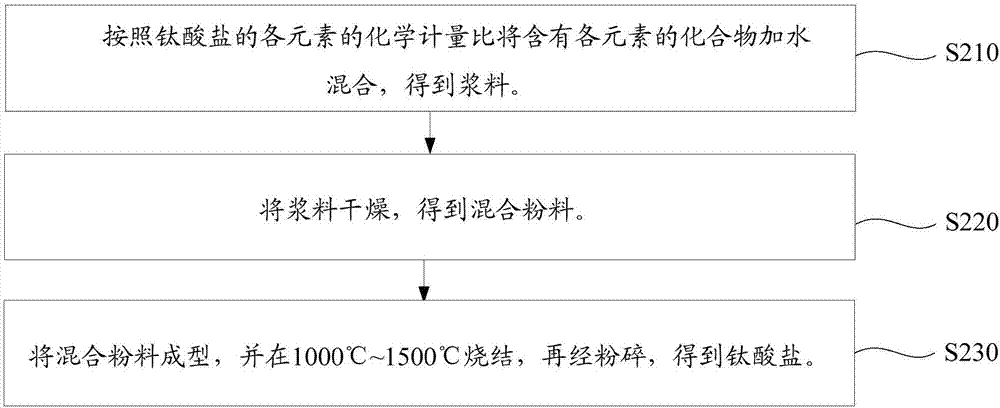
[0058] (1) Weigh zirconia and titania according to the stoichiometric ratio of each element of zirconium titanate, mix zirconia and titania, add in the ball mill jar, and add 0.5% of the total mass of zirconia and titania Dispersant, using deionized water as the ball milling medium, ball milling and mixing in a planetary ball mill at a speed of 300 rpm for 4 hours to obtain a slurry, wherein the dispersant is polyacrylic acid.
[0059] (2) Take out the slurry and bake it at 60°C for 18 hours, pass through a 100-mesh sieve after drying, and then press it into a block.
[0060] (3) Heating the block from room temperature to 1200°C at a heating rate of 2°C / min, and sintering at 1200°C for 2 hours, then cooling naturally to obtain a sintered body, breaking the sintered body to obtain a pulverized material, according to The mass ratio is 60:100:2 Put crushed material, water and polya...
Embodiment 2
[0065] The preparation process of the zirconia ceramics in this example is roughly the same as in Example 1, except that in step (4), the mass ratio of zirconium titanate to zirconia is 4:100.
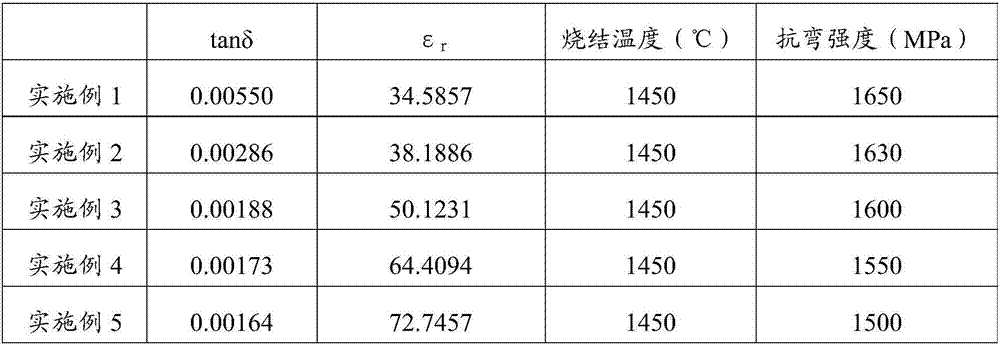
[0066] According to the test method of Example 1, the dielectric loss tangent, dielectric constant and bending strength of the zirconia ceramics of this example are shown in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com