Conductive material for connection parts which has excellent minute slide wear resistance
A technology for conductive materials and connecting parts, applied in the field of conductive materials for connecting parts, can solve problems such as increased insertion force, achieve improved micro-sliding wear resistance, excellent micro-sliding wear resistance, and improve micro-sliding wear resistance characteristics. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
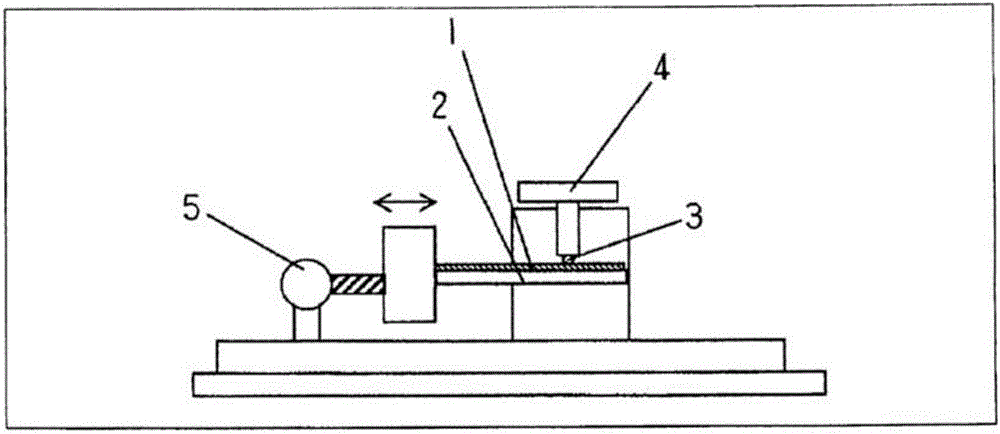
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach A
[0044] Hereinafter, an embodiment corresponding to claim 1 of the present invention will be described.
[0045] [Copper Alloy Base Material]
[0046] (1) Characteristics of copper alloy
[0047] The Cu-Ni-Si-based alloy widely used for mating-type terminals has a stress relaxation rate of 12-20% when maintained for 1000 hours under a bending stress of 80% of the 0.2% yield strength. . However, the stress relaxation rate increases with the increase in the holding temperature, and becomes 15 to 25% at 160°C, 25 to 30% at 180°C, and 30 to 40% at 200°C. In the case of a female terminal with strict requirements on the stress relaxation rate, as previously described, as the design basis, it is often required that the stress relaxation rate after being kept at the assumed use temperature for 1000 hours is 25% or less. Therefore, when the assumed use temperature exceeds 160°C, for example, it is difficult to use a Cu-Ni-Si-based alloy as a raw material for the female terminal.
[0048] In ...
Embodiment approach B
[0121] Hereinafter, an embodiment corresponding to claim 3 of the present invention will be described.
[0122] [Copper Alloy Base Material]
[0123] (1) Composition of Cu-Fe-P alloy
[0124] The copper alloy lath according to the present embodiment is a Cu-Fe-P alloy containing Fe: 0.01 to 2.6 mass%, P: 0.01 to 0.3 mass%, and the balance being Cu and unavoidable impurities.
[0125] Fe is the main element that precipitates in the form of Fe simple substance or Fe-based intermetallic compound and improves the strength and heat resistance of copper alloys. When the Fe content is less than 0.01% by mass, the amount of precipitates produced decreases, and although the increase in electrical conductivity is satisfied, the contribution to the increase in strength is insufficient, and the strength is insufficient. On the other hand, if the Fe content exceeds 2.6% by mass, the electrical conductivity is likely to decrease, and if it is desired to increase the amount of precipitation in orde...
Embodiment approach C
[0143] Hereinafter, an embodiment corresponding to claim 5 of the present invention will be described.
[0144] [Copper Alloy Base Material]
[0145] (1) Composition of Cu-Zn alloy
[0146] The Cu-Zn alloy lath according to the present embodiment contains 10-40% by mass of Zn, and the balance is composed of Cu and inevitable impurities. This Cu-Zn alloy is called copper and brass, and includes C2200, C2300, C2400, C2600, C2700, and C2801 specified in JIS H 3100.
[0147] If the content of Zn is less than 10% by mass, the strength required as a fitting terminal is insufficient. On the other hand, if the content of Zn exceeds 40% by mass, the elongation decreases, and the bending workability deteriorates. Therefore, the content of Zn is set to 10-40% by mass. The lower limit of the Zn content is preferably 12% by mass, more preferably 15% by mass, and the upper limit is preferably 38% by mass, and more preferably 35% by mass.
[0148] In order to improve the strength, stress relaxatio...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com