Low-melting-point lead-free solder alloy
A technology of lead-free solder alloy and low melting point, which is applied in welding/cutting medium/material, welding medium, welding equipment, etc. It can solve the problems of thermal fatigue resistance, poor ductility, insufficient welding reliability, limited promotion and application, etc. Achieve good wettability, good wetting performance and shear resistance, and improve the effect of shear resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
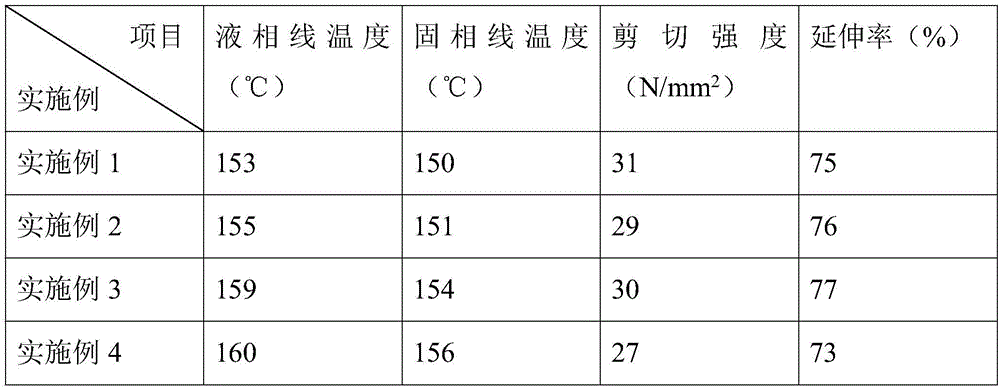
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] A lead-free solder alloy with a low melting point, calculated by weight percentage, comprising the following raw materials:
[0019] 20% of bismuth, 1.2% of silver, 0.6% of nanometer ferric oxide particles, 0.08% of vanadium, and the balance is tin.
[0020] Preparation:
[0021] According to Bi, Ag, nanometer Fe in the present embodiment 2 o 3 , weight percent of V and Sn Weigh the required raw materials, add them into the furnace, then heat up to 600°C to melt, start timing after complete melting, and keep warm for 120min. During this period, stir with a ceramic rod every 10 minutes to fully homogenize the alloy components. Two hours later, the hot crucible was taken out of the furnace, cooled to room temperature (20° C.) in the air, and then taken out from the crucible to obtain the low melting point lead-free solder alloy of the present invention.
Embodiment 2
[0023] A lead-free solder alloy with a low melting point, calculated by weight percentage, comprising the following raw materials:
[0024] 22% of bismuth, 1.2% of silver, 0.7% of nanometer ferric oxide particles, 0.0004% of Co and 0.08% of vanadium, and the balance is tin.
[0025] According to Bi, Ag, nanometer Fe in the present embodiment 2 o 3 , V, Co and Sn weight percentages Weigh the required raw materials, add them into the furnace, and then heat up to 600 ° C to melt, start timing after complete melting, and then keep warm for 120 minutes. During this period, stir with a ceramic rod every 10 minutes to fully homogenize the alloy components. Two hours later, the hot crucible was taken out of the furnace, cooled to room temperature (20° C.) in the air, and then taken out from the crucible to obtain the low melting point lead-free solder alloy of the present invention.
Embodiment 3
[0027] A lead-free solder alloy with a low melting point, calculated by weight percentage, comprising the following raw materials:
[0028] 10% of bismuth, 1.8% of silver, 0.8% of nanometer ferric oxide particles, 0.0005% of Co and 0.1% of vanadium, and the balance is tin.
[0029] The preparation method of the low melting point lead-free solder in this embodiment is the same as the method described in embodiment 2, the only difference is that the weight percentages of the components of the lead-free solder alloy are weighed according to the proportions in this embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com