Non-noble metal photocatalysis cocatalyst and preparation method thereof `
A co-catalyst and non-precious metal technology, applied in the field of materials science, can solve the problems of scarcity of raw materials and expensive catalysts, and achieve the effects of reducing production costs, improving electron transport efficiency, and mild synthesis conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] First prepare graphene oxide with Hummers, then prepare 50ml of 0.4~2mg / ml graphene oxide aqueous suspension by ultrasonication for 1~3h, and add 1ml of CoCL 2 aqueous solution, the CoCl 2 The concentration of the aqueous solution is 20-400 mg / ml, freeze-dried to form a brown powder, and then put it in a tube furnace for 1-2 hours under the atmosphere of argon and ammonia to form a black powder, which is the composite of cobalt nanoparticles and nitrogen-doped graphene non-noble metal photocatalytic cocatalysts.
Embodiment 2
[0017] The characterization of embodiment 2 catalyst
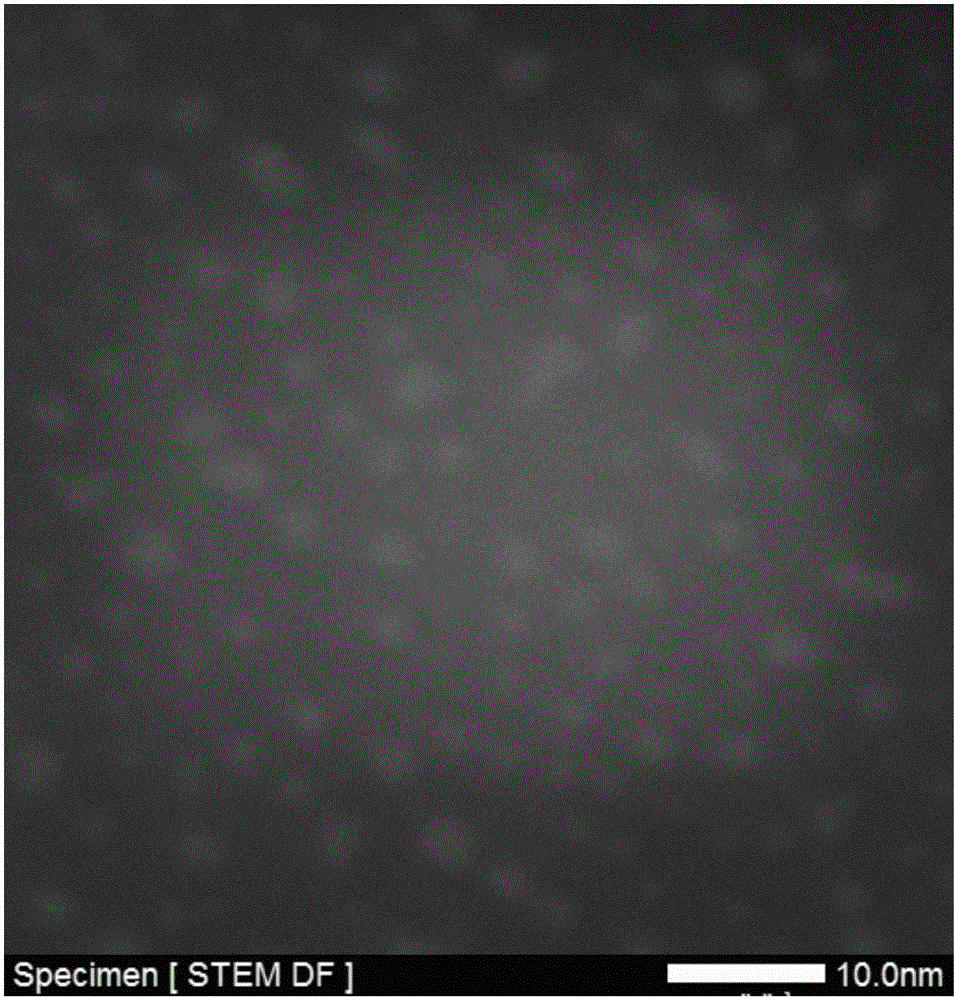
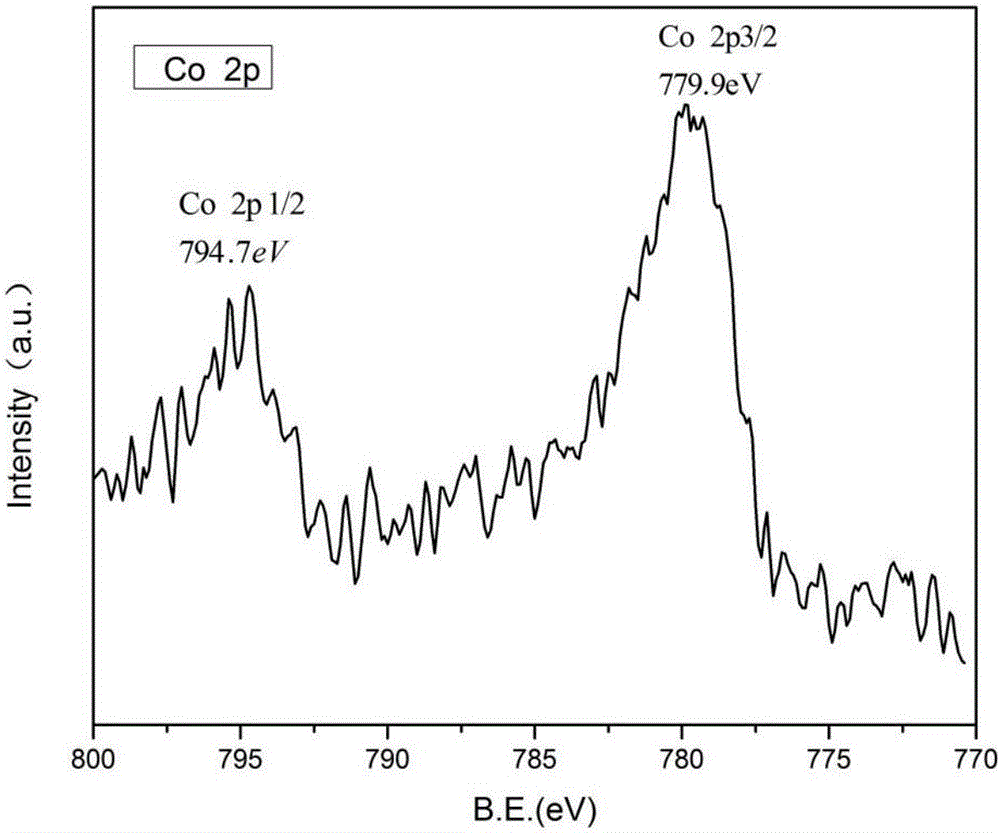
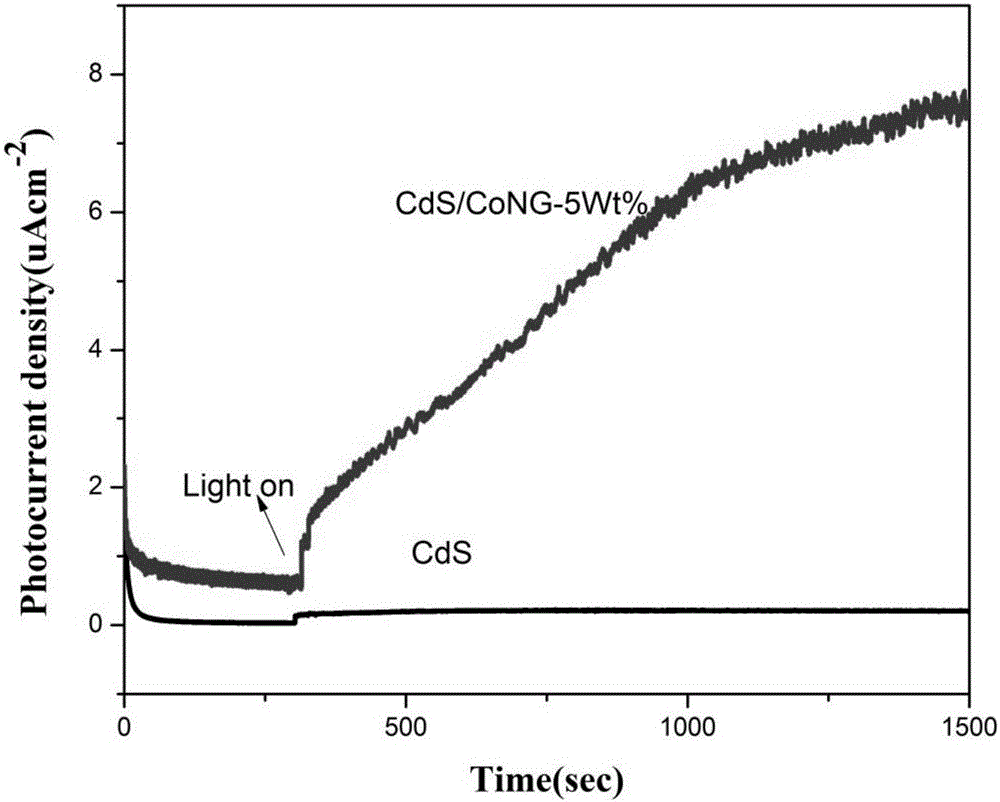
[0018] The microscopic morphology of the catalyst was detected by JEM-2100F transmission electron microscope. In the annular dark field image of the sample, we can see that there are many bright spots uniformly distributed in the carbon matrix, and the particle size is 1~2nm, corresponding to cobalt nanoparticles ( figure 1 ). X-ray electron spectroscopy (XPS) test is carried out on the ESCALAB 250 type X-ray diffractometer. figure 2 Two peaks are shown with binding energies of 779.9 eV and 794.7 eV, respectively. It can be seen in the photocurrent intensity test, after turning on the light source. The photocurrent intensity of the cobalt nanoparticles / nitrogen-doped graphene composite cocatalyst sample increases rapidly and gradually stabilizes after reaching a certain value, while that of pure CdS increases slowly ( image 3 ).
Embodiment 3
[0019] Example 3 Photocatalytic hydrogen production under visible light
[0020] The light source of the photocatalytic activity test reaction is a 300W Xe lamp, and the infrared light part is removed by the cooling circulating water above the reactor, and the ultraviolet light part is removed by a 420nm filter. At room temperature, add a certain amount of deionized water, sacrificial agent ammonium sulfite, and 0.05 g of CdS photocatalyst loaded with 0.5 wt% (Co-NG) into the reactor. The hydrogen reaction system is connected to pump out the air in the system. Using visible light with a wavelength greater than 420nm as the light source, the hydrogen production was measured at regular intervals to study its photocatalytic activity. Finally, the hydrogen production per hour was measured to be 150 mmol, 15 times that of pure CdS, and the photocatalytic activity was significantly improved ( Figure 4 ).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com