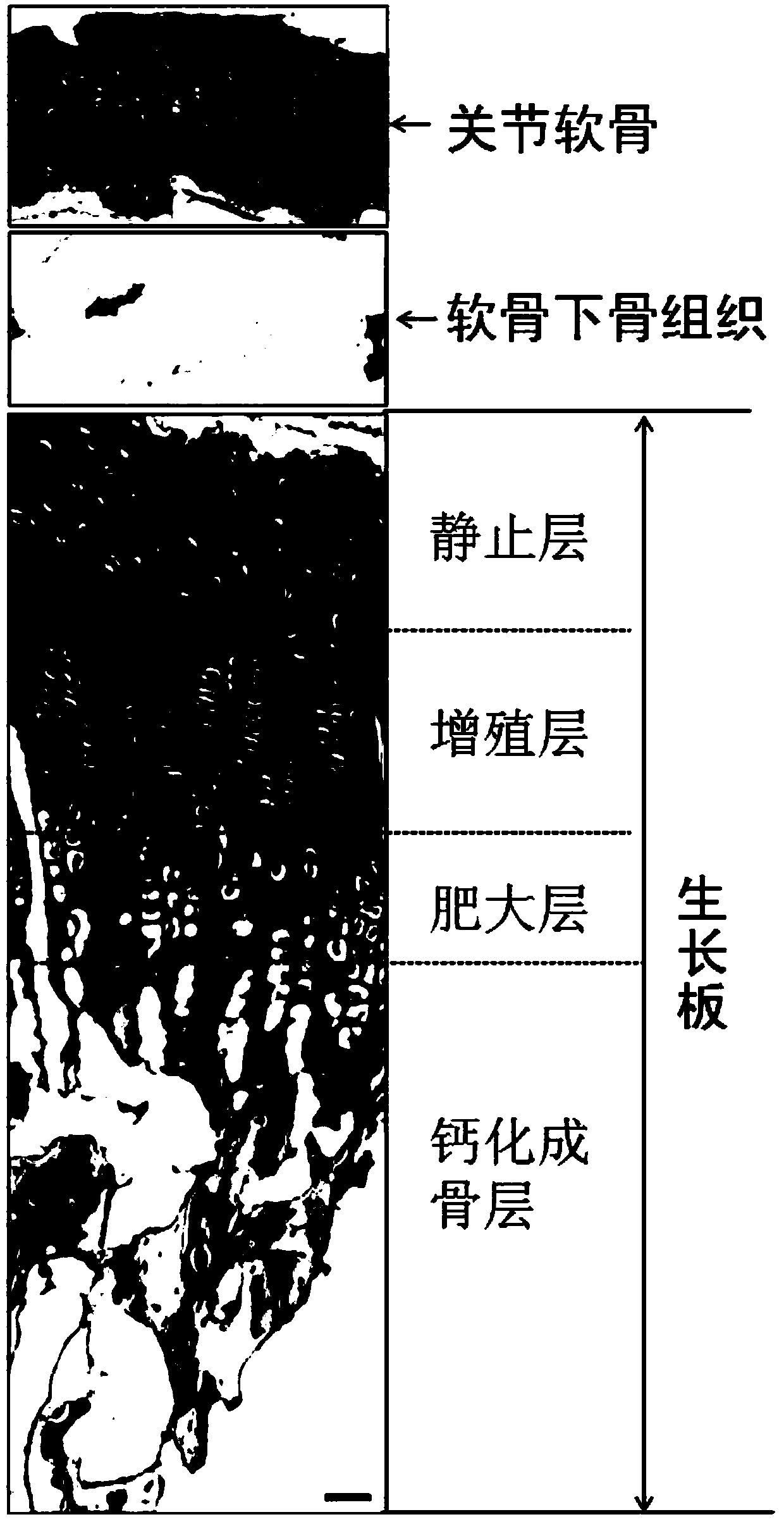
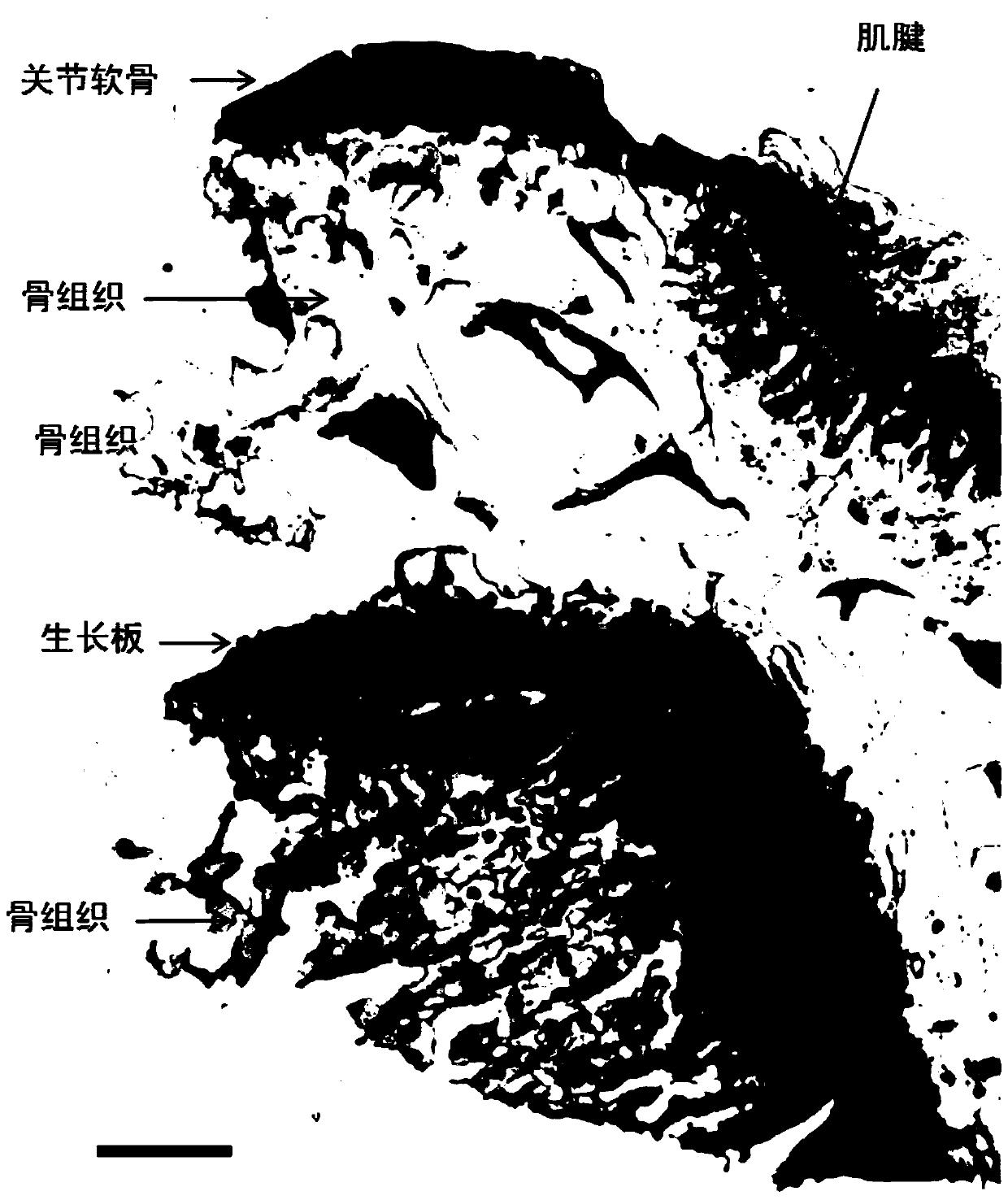
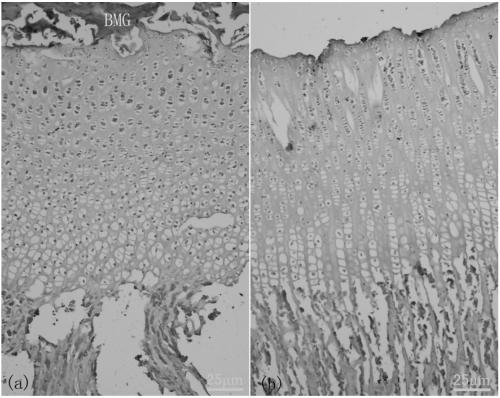
A method for constructing epiphyseal plate cartilage in vitro
A technology of cartilage and chondrocytes, applied in the direction of prosthesis, bone/connective tissue cells, tissue regeneration, etc., can solve the problems of restricting adult stem cells, high price, etc., and achieve the effect of easy acquisition and cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] A method for constructing epiphyseal cartilage in vitro, comprising:
[0054] S11. After culturing the human bone marrow stem cells to form a cell monolayer, digest with trypsin, wash, and resuspend to obtain a cell suspension, and count for later use;
[0055] S12. Cut the pre-treated bone matrix gelatin material into a cylinder smaller than the diameter of the culture hole, and drill a hole on the cylinder that runs through the two bottom surfaces of the cylinder, and sterilize it; the cut bone matrix gelatin material Suspended and fixed in the culture well;
[0056] S13. Implant the cell suspension obtained in step S11 under the bone matrix gelatin material through the channel, and make the liquid surface infiltrate the bone matrix gelatin material, and cultivate epiphyseal plate cartilage;
[0057] Wherein, step S11 and step S12 have no sequence.
Embodiment 2
[0059] A method for constructing epiphyseal cartilage in vitro, comprising:
[0060] S21. Human cartilage C28 / I2 cell line cells frozen in liquid nitrogen were resuscitated and inoculated in 75mL culture flasks with an inoculation amount of 350,000 for cultivation; the culture conditions were: add 3.5mL of 28% fetal bovine serum to each culture flask , 110U / mL penicillin and streptomycin in DMEM / F12 culture medium, 4.5% CO 2 , Cultivate at 38°C; change the medium at intervals of 68 hours for the first time, and change the medium at intervals of 44 hours thereafter.
[0061] After the cells are cultured to form a monolayer of cells, discard the culture medium, wash the cells once with 3mL D-Hanks solution for each bottle of cells, add 3mL of digestive enzyme solution of 0.25% trypsin and 0.02% EDTA, and digest at 36°C for 12min;
[0062] Collect the cells in the 7 bottles of culture flasks into a centrifuge tube, centrifuge to discard the supernatant, and resuspend the cells i...
Embodiment 3
[0067] A method for constructing epiphyseal cartilage in vitro, comprising:
[0068] S31. Cut the pretreated bone matrix gelatin material into a cylinder slightly smaller than the diameter of the culture hole, and drill a channel on the cylinder that runs through the two bottom surfaces of the cylinder. The diameter of the channel is 1.2-1.4 mm; cobalt- 60 radioactive sterilization treatment; suspending and fixing the cut bone matrix gelatin material in the culture hole; sealing the gap between the bone matrix gelatin material and the edge of the culture hole with sterile agarose gel.
[0069] S32. The human cartilage C28 / I2 cell line cells frozen in liquid nitrogen were resuscitated and inoculated in a 75mL culture bottle with an inoculation amount of 450,000 for culture; the culture conditions were: add 4.5mL of 32% fetal bovine serum to each culture bottle , 90U / mL penicillin and streptomycin in DMEM / F12 culture medium, 5.5% CO 2 , Cultivate at 36°C; change the medium at i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com