Composite diamond-ene artificial joint and production method thereof
An artificial joint, diamond olefin technology, applied in pharmaceutical formulations, medical science, tissue regeneration, etc., can solve the problem of low hardness and wear resistance of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene, shortening the service life of artificial joint implants, and poor soft tissue organisms. Chemical reaction and other problems to achieve the effect of improving lubricity, improving biocompatibility, and avoiding loosening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
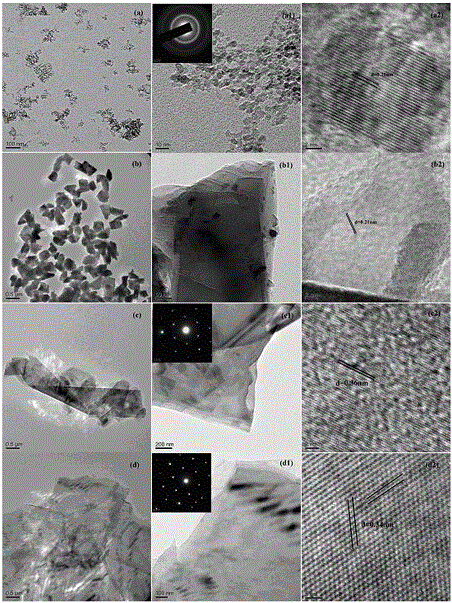
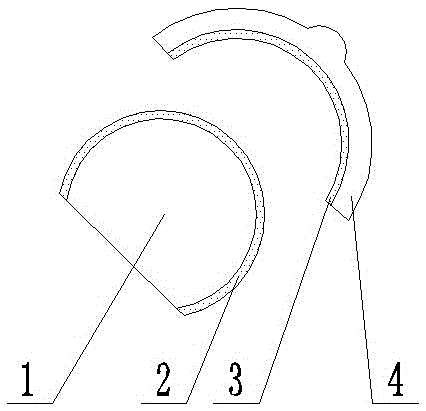
[0025] Composite diamondene artificial joints, such as figure 1 As shown, it includes the joint head and the joint socket that cooperate with each other. The joint head includes a metal base 1, and an ultrafine diamondene layer 2 is arranged on the outside of the metal base 1. The ultrafine diamondene layer 2 is composed of nanodiamondene; the joint socket includes polyethylene The substrate 4 is provided with a wear-resistant layer 3 on the side where the polyethylene substrate 4 matches the joint head, and the wear-resistant layer 3 is composed of nanodiamondene and polyethylene, wherein the volume ratio of nanodiamondene and polyethylene is 2:3 or 1:1; the surface roughness of the articular fossa is 0.09 microns; nanodiamantene is a lamellar single crystal structure, and the carbon atoms in the same sheet of nanodiamantene are sp3 orbital impurities between the carbon atoms in the same sheet The carbon atoms between the layers are connected by sp2 hybrid carbon bonds; the l...
Embodiment 2
[0030] The difference between this embodiment and Example 1 is that the volume ratio of nanodiamondene and polyethylene in the articular fossa is 2:3, the surface roughness of the articular fossa is 0.08 microns, and the thickness ratio of the polyethylene matrix to the wear-resistant layer is 3 : 2; the thickness of the ultrafine diamondene layer in the joint head is 2.5 microns, and the average particle diameter R of the nanodiamondene in the ultrafine diamondene layer is 40nm.
Embodiment 3
[0032] The difference between this embodiment and Example 1 is that the volume ratio of nanodiamondene and polyethylene in the articular fossa is 1:1, the surface roughness of the articular fossa is 0.06 microns, and the thickness ratio of the polyethylene matrix to the wear-resistant layer is 7 : 3; the thickness of the ultrafine diamondene layer in the joint head is 2 microns, and the average particle diameter R of the nanodiamondene in the ultrafine diamondene layer is 30nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com