High heat-resistant and high-strength polylactic acid fiber and preparation method thereof
A polylactic acid fiber, high-strength technology, applied in the field of polylactic acid fiber and its preparation, can solve the problems that the fabric cannot meet the high-temperature ironing and washing requirements of ordinary textiles, the PLA crystallization rate is slow, and the glass transition temperature is low. The effect of industrial scale production, reduced shrinkage in boiling water, and improved degree of orientation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
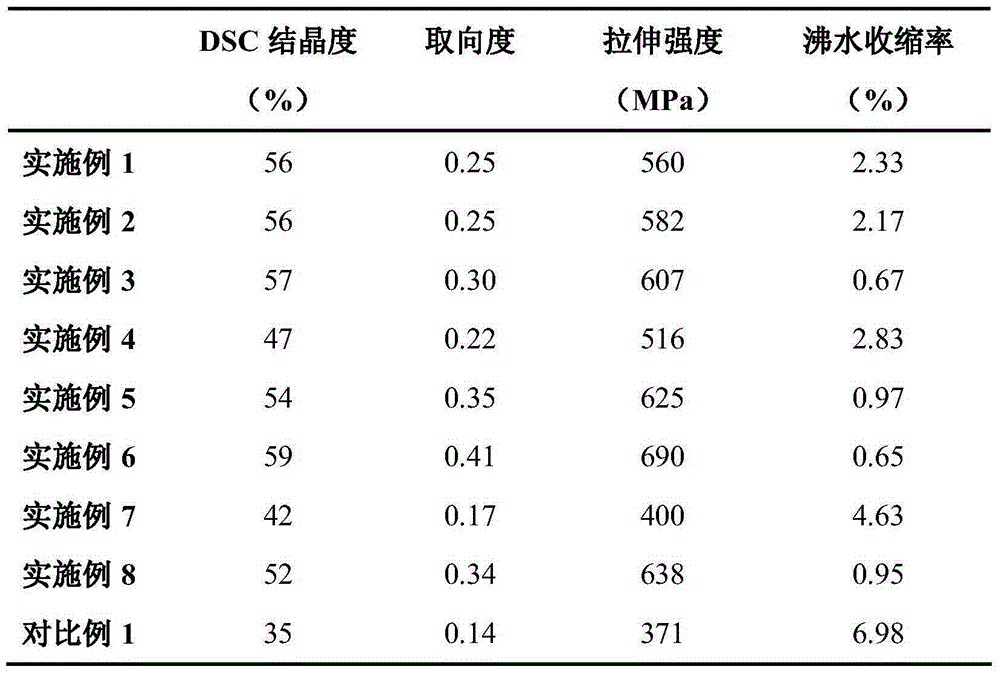
[0027] The weight average molecular weight is 1.41×10 4 g·mol, polylactic acid with an optical purity of 98.6% and tetramethylene-dibenzohydrazide are premixed evenly, and then the premixed material is added to a twin-screw extruder at 180°C to extrude and pelletize to obtain tetramethylene Methyl-dibenzohydrazide content is the masterbatch of 2wt%; The gained masterbatch and weight average molecular weight are 1.41 * 10 5 g·mol, polylactic acid with an optical purity of 98.6% is premixed uniformly according to the content of organic small molecule nucleating agent in the fiber at 0.2wt%, and melted and mixed at 180°C and then granulated; Melt spinning is carried out in a conventional way. After passing through a hot roller at 75°C, the obtained raw yarn is thermally stretched at 90°C with a draw ratio of 1.67, and heat-set and wound at 80°C to obtain a high heat-resistant high-strength fiber. Strength polylactic acid fiber.
Embodiment 2
[0029] The weight average molecular weight is 2.05×10 4 g·mol, polylactic acid with an optical purity of 98.0% and tetramethylene-dibenzohydrazide are premixed uniformly, and then the premixed material is added to a twin-screw extruder at 190°C to extrude and granulate to obtain tetramethylene Methyl-dibenzohydrazide content is the masterbatch of 5wt%; Gained masterbatch and weight-average molecular weight are 2.05 * 10 5 g·mol, polylactic acid with an optical purity of 98.0% is premixed uniformly according to the content of organic small molecule nucleating agent in the fiber at 0.5wt%, and melted and mixed at 190°C before granulation; Melt spinning is carried out in a conventional way. After passing through a hot roller at 75°C, the obtained raw yarn is thermally stretched at 100°C with a draw ratio of 1.67, and heat-set at 90°C and wound to obtain a high heat-resistant high-strength fiber. Strength polylactic acid fiber.
Embodiment 3
[0031] The weight average molecular weight is 2.80×10 4g·mol, polylactic acid with an optical purity of 98.9% and N,N',N"-tricyclohexyl-1,3,5-benzenetricarboxamide are premixed evenly, and then the premixed material is fed into a twin-screw extruder Extrude and granulate at 180°C to obtain a masterbatch with a N,N',N"-tricyclohexyl-1,3,5-benzenetricarboxamide content of 10wt%; combine the obtained masterbatch with a weight average molecular weight of 2.80 ×10 5 g·mol, polylactic acid with an optical purity of 98.9% is premixed uniformly according to the content of organic small molecule nucleating agent in the fiber at 0.3wt%, and is melted and mixed at 180°C and then granulated; Melt spinning is carried out in a conventional way. After passing through a hot roller at 75°C, the obtained raw yarn is thermally stretched at 100°C with a draw ratio of 1.67, and heat-set at 90°C and wound to obtain a high heat-resistant high-strength fiber. Strength polylactic acid fiber.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Weight average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Weight average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Weight average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com