Sodium ion battery negative electrode sheet and sodium ion battery
A sodium-ion battery and negative electrode technology, which can be applied to battery electrodes, secondary batteries, circuits, etc., can solve the problems that have not yet been found in the application of porous graphite membranes, and achieve good charge-discharge cycle stability, good conductivity, and stable performance Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Negative pole piece preparation:
[0022] Take a self-made polyimide graphite film with a size of 20cm×20cm, and the thickness of the graphite film is 20 μm. Place the film on the sample placement platform of the laser drilling machine, adjust the laser etching parameters: power 20W, marking speed 1500mm / s, laser focal length 160mm, laser wavelength 1064nm, frequency 20kHz, the diameter of the holes and the distance between the holes respectively By adjusting the cutting diameter and hole distance of the laser beam, and turning on the power supply, the diameter of the circular hole is 50 μm, the distance between the holes is 240 μm, and the mass ratio of carbon atoms is 99.5%. figure 1 Its scanning electron microscope image.
[0023] The polyimide porous graphite film obtained above was cut into 4cm×3cm pole pieces by a slitting machine, dried in a vacuum oven at 120°C, and then used to prepare aluminum-plastic flexible packaging batteries.
[0024] Positive sheet pr...
Embodiment 2
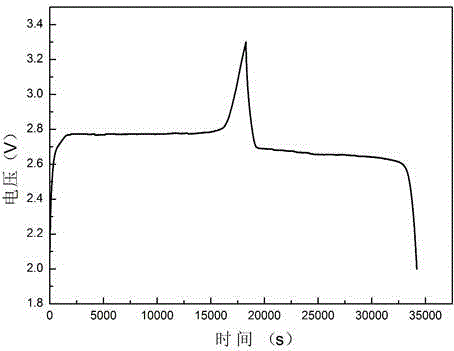
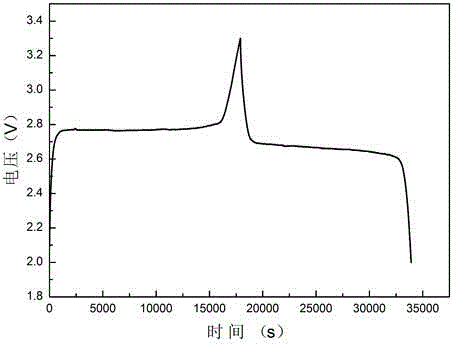
[0031] The polyimide graphite film negative electrode base material in embodiment 1 is changed into expanded graphite film, and thickness is 25 μ m, adjusts punching parameter, makes the pore spacing of expanded graphite porous film be 280 μ m, and electrolytic solution is changed into 1mol / L three Sodium fluoromethyl sulfonate / tetraethylene glycol dimethyl ether, all the other processes are the same as in Example 1. The prepared sodium-ion battery was charged and discharged at a rate of 0.1C, and the charge and discharge curves were as follows: image 3 As shown, after 100 charge-discharge cycles, as Figure 5 The indicated capacity retention was 97.8%.
Embodiment 3
[0033] The polyimide graphite film negative electrode substrate in Example 1 is replaced by a graphene composite film, the thickness is 20 μm, and the punching parameters are adjusted so that the hole spacing of the graphene porous composite film is 260 μm, and the positive electrode material is changed to NaNi 0.5 mn 0.5 o 2, and the rest of the process is the same as in Example 1. The prepared sodium-ion battery was charged and discharged at a rate of 0.1C, and the charge and discharge curves were as follows: image 3 As shown, after 100 charge-discharge cycles, as Figure 5 The indicated capacity retention was 98.4%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com