Method for recovering metal resource from zinc calcine through reduction roasting-leaching-zinc sinking
A roasting and leaching technology, which is applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve problems such as difficult follow-up treatment, pollution, and high labor operation intensity, and achieve the effects of reducing iron leaching rate, shortening process flow, and improving leaching efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0036] In the present embodiment, the method of zinc calcined reduction roasting-alkali leaching-precipitating zinc comprises the following steps:
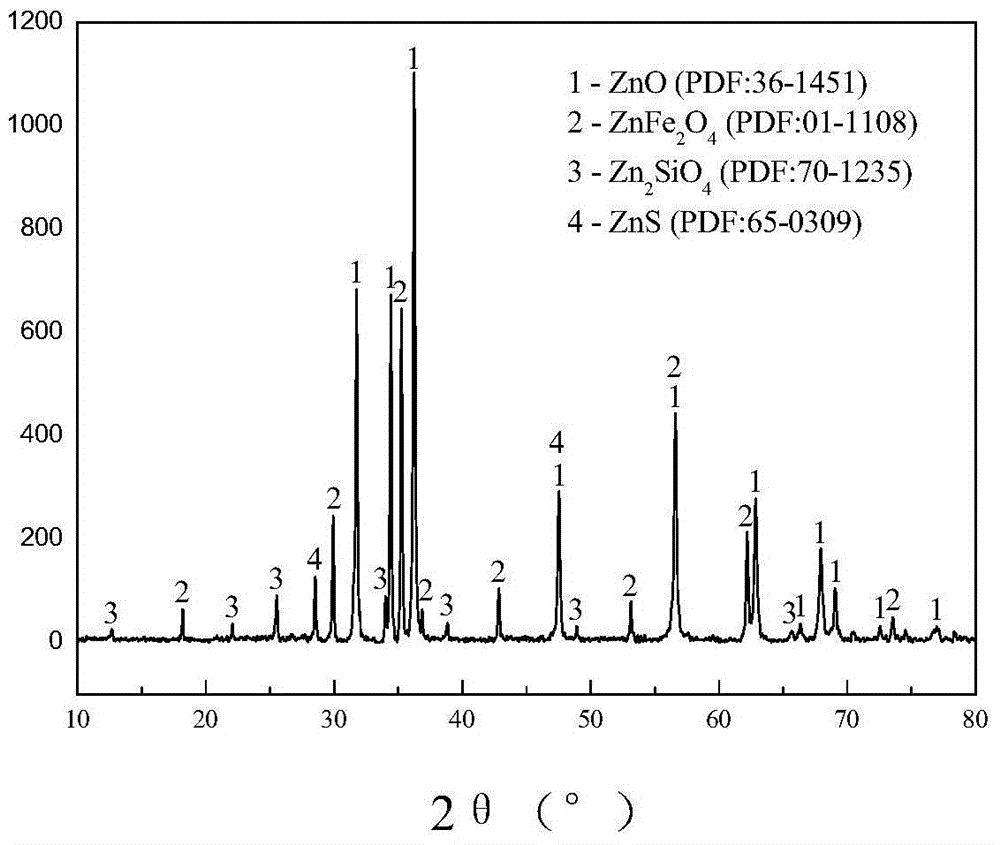
[0037] (1) Dry the zinc-zinc calcined sand of a lead-zinc smelter and grind it until it passes through a 100-200-mesh sieve. The chemical phase analysis and XRD analysis of all elements and zinc of zinc calcine are shown in Table 1, 2 and figure 1 . It can be seen from the analysis that the zinc calcine mainly contains 53.5% Zn and 12.1% Fe, and the Fe mainly exists in the form of ferrite. The recovery of zinc in zinc ferrite is the key to improving the overall zinc recovery rate.
[0038] Table 1 Elemental analysis results of zinc calcine, wt%
[0039]
[0040] Table 2 zinc phase analysis results, wt%
[0041]
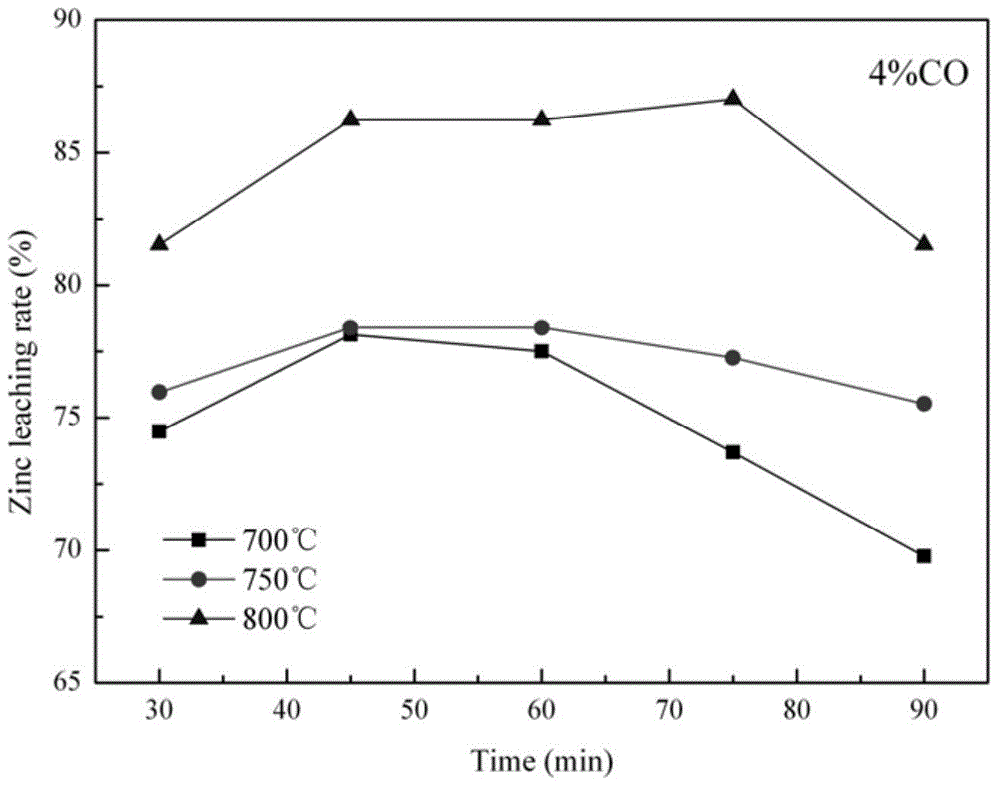
[0042] (2) Put the dry and fine zinc calcined sand into the reduction roasting furnace, use N 2 Purify the air in the furnace, raise the temperature of the reduction roasting furnace to 700-800°C, start to add C...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com