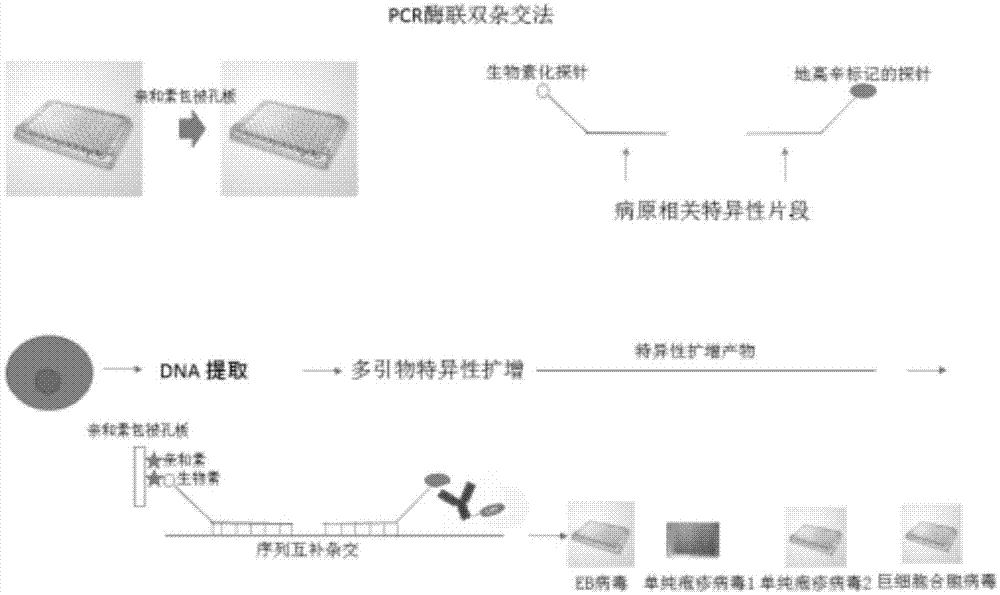
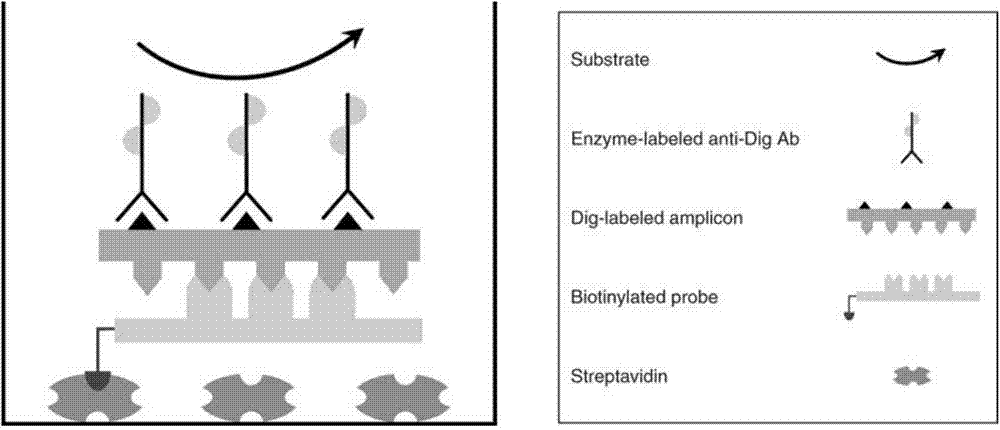
Method for detecting pathogenic microorganisms by using PCR (polymerase chain reaction) enzyme-linked double-cross method
A technology of pathogenic microorganisms and detection methods, applied in the direction of determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of limited clinical pathogenic microorganism detection and identification by gene chips, high price of gene chip technology, and low degree of automation, etc. Achieve the effect of low reagent cost, saving labor and reagent cost, convenient and flexible use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] Embodiment 1. Epstein-Barr virus rapid detection method
[0076] Epstein-Barr virus can be infected early in life, and generally 70-80% of children around the age of 10 are infected by this virus. HIV-infected people and organ transplant patients who require immunosuppressants are very susceptible to infection. Post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD) is a rare but fatal complication after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and solid organ transplantation, with a mortality rate as high as 40% to 70%. The PTLD induction rate is 1% in kidney transplantation, 9% in heart / lung transplantation, and 12% in pancreas transplantation. Most of PTLD is related to Epstein-Barr virus infection. Due to various reasons after transplantation, the function of effector T cells is inhibited, and B cells infected by Epstein-Barr virus grow uncontrollably, thus forming abnormal lymphocyte hyperproliferative diseases or monoclonal malignant tumors.
[0077] Epstein-Bar...
Embodiment 2
[0088] Example 2. Rapid detection method for human cytomegalovirus
[0089] Cytomegalovirus (Cytomegaoviyns, CMV) is a herpesvirus group DNA virus, which exists widely in nature and has a very high infection rate in the human population. The virus can invade the lungs, liver, kidneys, salivary glands, other mammary glands, and multinucleated leukocytes and lymphocytes, and can excrete the virus from saliva, milk, sweat, blood, urine, semen, and uterine secretions for a long time or intermittently. Usually oral, reproductive tract, placenta, blood transfusion or organ transplantation and other multi-way transmission. A disease resembling infectious mononucleosis is the most common presentation of CMV infection in immunocompromised patients. Clinical symptoms and phenotypes include: mononucleosis; CMV infection in the intestinal tract can cause diarrhea, fever and abdominal pain, colitis, and bloody stool; can cause liver function abnormalities and unexplained fever; Causes va...
Embodiment 3
[0100] Embodiment 3.HSV-1 / HSV-2 virus rapid detection method
[0101] Herpes simplex virus (HSV) can be divided into two subtypes, HSV-1 and HSV-2, which enter the human body mainly through the skin, mucous membranes or damaged places, and may cause oral or genital herpes. After the primary infection of HSV produces immunity, some viruses will be cleared, and some viruses can reach the trigeminal ganglion (HSV-1) and spinal ganglion (HSV-2) cells or surrounding astrocytes along the nerve myelin sheath, It persists in a latent state, is in relative balance with the body, and does not cause clinical symptoms. When the body has fever, cold, sun exposure, menstruation, emotional stress, use of pituitary or adrenal cortex hormones, or some bacterial virus infection, etc., the latent virus activates and proliferates, and travels down the nerve fiber cord to the sensory nerve endings and nearby epidermal cells Continue to proliferate, causing recurrent local herpes. Repeated infect...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com