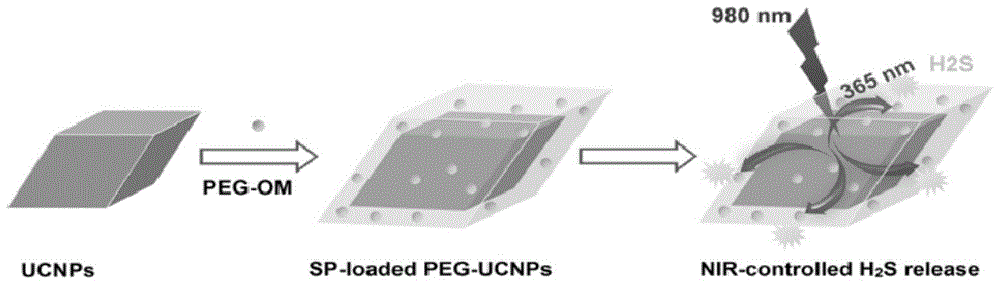
Composite nanoparticle for controlling H2S release by employing near-infrared light as well as preparation method and application of composite nanoparticle
A composite nanoparticle and near-infrared light technology, applied in the field of biochemistry, can solve the problems of large tissue and cell damage, hinder application, and weak tissue penetration, and achieve the effect of strong penetration and little damage to cells and tissues.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
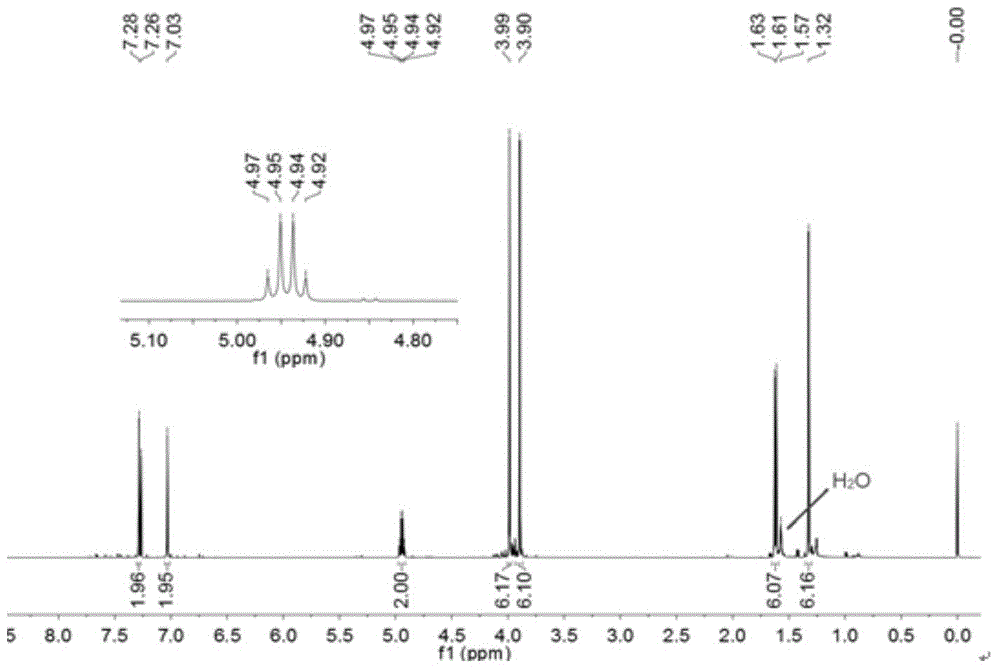
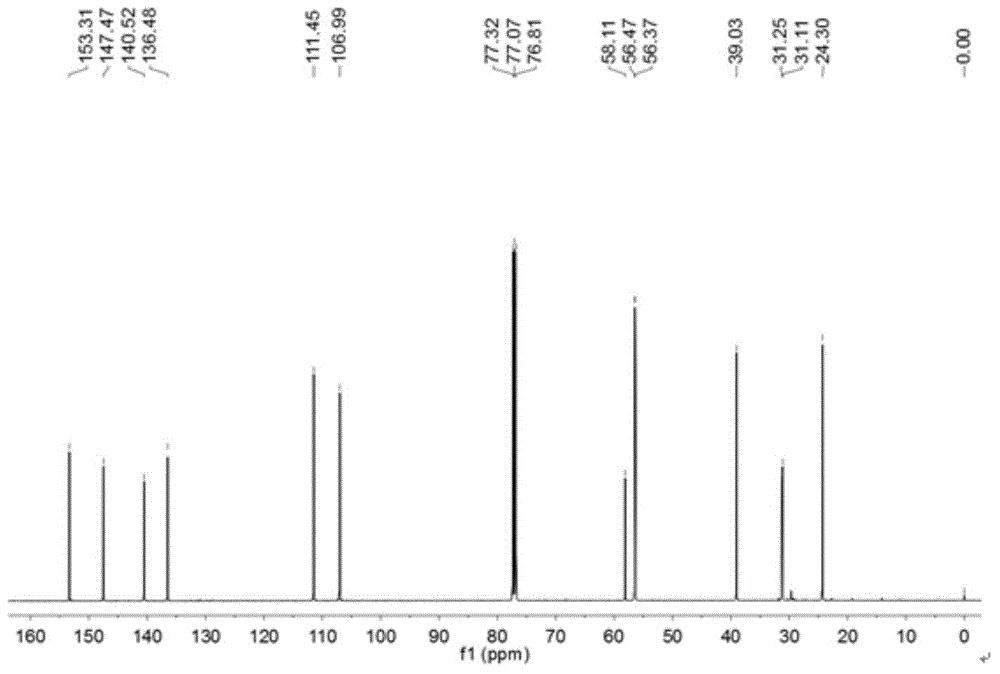
[0042] Organic H 2 Chemical synthesis of the S donor molecule:
[0043] The synthetic route is as follows:
[0044]
[0045] The specific steps are as follows:
[0046] (1) Weigh 3g (0.0142mol) of Compound I and dissolve it in 15mL of anhydrous dichloromethane, and slowly add 7mL of it dropwise under ice-cooling to a concentration of 2molL -1 trimethylaluminum, the color of the solution changed from yellow to orange, and after 2 hours of reaction, the reaction solution was poured into hydrochloric acid diluted with ice water. The crude product was obtained by filtration, and the crude product was separated by column chromatography to obtain compound II. The yield was 50.7%.
[0047] (2) Weigh 1.63g of compound II and dissolve it in 15mL of dichloromethane, and stir in an ice bath. Measure 1.367mL of phosphorus tribromide and slowly add to the above solution. After reacting for 1.5h in ice bath, transfer to room temperature and continue to react for 1.5h. After the re...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Up-conversion nanoparticles UCNPs (β-LiYF4:0.5%Er3 + ,25%Yb3 + ) preparation:
[0053] The rare earth oxide (Y 2 o 3 :Yb 2 o 3 :Tm 2 o 3 =74.5%:25%:0.5%) was dissolved in an appropriate amount of trifluoroacetic acid, stirred and reacted at 80°C for 5h, and the trifluoroacetic acid was evaporated to obtain a white powder solid. This mixed powder was dissolved in a mixed solution of oleic acid and octadecene, and then 8 times the amount of lithium fluoride was added. Heated to 110° C. in a vacuum environment, and reacted for 1 h. Under nitrogen protection, raise the temperature to 320-330°C at 25°C / min, stir vigorously, react for 1 hour, and then cool to room temperature. An appropriate amount of acetone was added, and a white precipitate was obtained after centrifugation at 6000 rpm for 10 min. Dissolve in chloroform after washing twice with acetone and absolute ethanol. Centrifuge at 2000rpm for 1min to remove excess lithium fluoride, and finally obtain the ...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Determination of the number of SP molecules loaded on the surface of UCNPs:
[0067] (1) Drawing of UV standard curve: Prepare different concentrations of SP molecular solutions: 10μgmL -1 , 12.5 μg mL -1 , 16.5 μg mL -1 , 22.5 μg mL -1 , 28.5 μg mL -1 , 38.5 μg mL -1 , 50 μg mL -1 , measure the UV absorbance intensity, and draw the UV standard curve, see Figure 7 a.
[0068] (2) Take 0.25mL SP-PEG-UCNPs solution, mix it with 0.75mL acetonitrile solution, measure the UV absorbance intensity at 350nm, it is A 350nm = 0.093. Bring in the UV standard curve fitting function to get the concentration of SP molecules in this solution to be 7.71μgmL -1 . That is, there are 7.25×10 in 1mL SP-PEG-UCNPs solution 16 SP molecules.
[0069] (3) Take 1mL of pure UCNPs and dry and weigh it, which is 20mg. It is known that the volume of a UCNPs is 1.72×10 -16 cm 3 , the density of UCNPs is 4 gcm -1 , calculated to have 2.91×10 in 1mL solution 13 UCNPs.
[0070] (4) Th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com