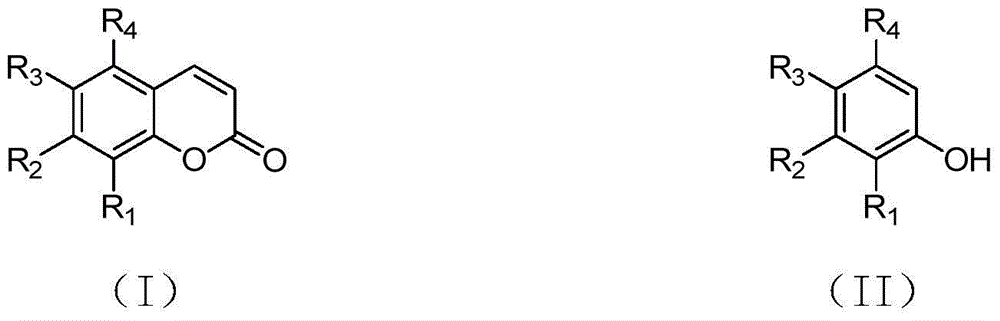Synthetizing method of coumarin compound
A technology for coumarins and synthesis methods, applied in the direction of organic chemistry and the like, can solve the problems of inapplicability of microwave method, unstable yield, troublesome synthesis operation, etc., and achieves simple and efficient product separation, green reaction conditions, and high conversion rate. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
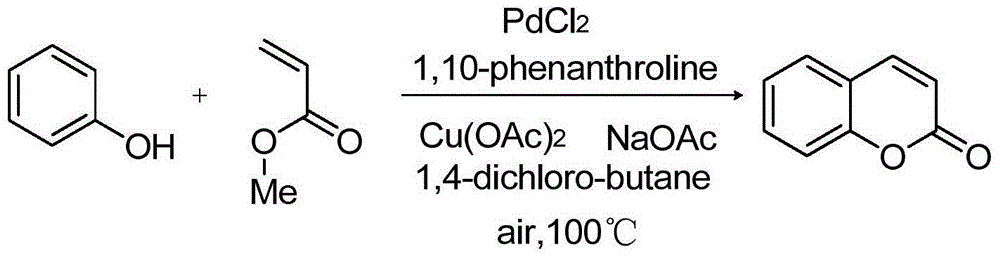
[0029] Embodiment 1: the preparation of coumarin
[0030]
[0031] Add palladium chloride (0.05mmol, 8.9mg), 1,10-phenanthroline (0.1mmol, 18mg), copper acetate (0.4mmol, 73mg), phenol (1mmol, 94.1mg), methyl acrylate (0.5mmol, 43.1mg), sodium acetate (1.5mmol, 123mg), 1,4-dichlorobutane (4mL), stirred at 100°C, and detected the reaction by thin-layer chromatography until the raw material The basic conversion is complete, and the 24 reaction ends. After completion of the reaction, add ethyl acetate (10 mL) to the reaction solution, then wash with 5% sodium bicarbonate solution to remove unreacted phenol, separate the organic phase, extract the aqueous phase with ethyl acetate (10 mL×3), combine the organic phases, It was dried with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filtered, and the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation to obtain coumarin (134.45 mg) with a yield of 92%.
[0032] 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ (ppm) 6.33 (d, J = 9.5Hz, 1H), 7.17–7.23 (td, J = 8.2, 7.4, 1.5Hz...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Embodiment 2: the preparation of coumarin
[0034] Add palladium chloride (5mmol, 89mg), 1,10-phenanthroline (10mmol, 180mg), copper acetate (20mmol, 4.7g), phenol (100mmol, 9.41g ), methyl acrylate (55mmol, 4.74g), sodium acetate (100mmol, 8.1g), 1,4-dichlorobutane (300mL), stirred and reacted at 110°C, condensed and refluxed for 20 hours, and the detection reaction was basically completed. After the reaction was completed, wash with 5% sodium bicarbonate solution to remove unreacted phenol, separate the organic phase, extract the aqueous phase with ethyl acetate (50mL×3), combine the organic phases, and dry with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filter, and remove by rotary evaporation. solvent to obtain coumarin (12.72g), yield 87%.
Embodiment 3
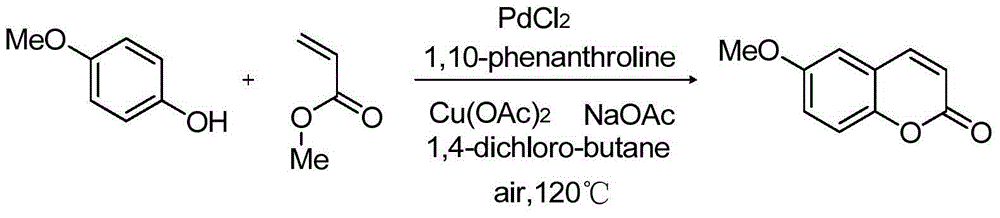
[0035] Embodiment 3: the preparation of 4-methoxycoumarin
[0036]
[0037] Add palladium chloride (0.05mmol, 8.9mg), 1,10-phenanthroline (0.1mmol, 18mg), copper acetate (0.5mmol, 91mg), 4-methoxy Phenylphenol (1mmol, 124.14mg), methyl acrylate (0.5mmol, 43.1mg), sodium acetate (1.5mmol, 123mg), 1,4-dichlorobutane (4mL), stirred at 120°C, and used TLC The reaction was detected by chromatography until the conversion of the starting material was basically complete, and the 18 reaction was completed. After completion of the reaction, add ethyl acetate (10 mL) to the reaction solution, then wash with 5% sodium bicarbonate solution to remove unreacted phenol, separate the organic phase, extract the aqueous phase with ethyl acetate (10 mL×3), combine the organic phases, It was dried with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filtered, and the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation to obtain coumarin (160.3 mg) with a yield of 91%.
[0038] 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ(ppm)2.39(s,3H),...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com