Method for preparing porphyra anti-oxidation peptide and comprehensively utilizing byproducts
A technology of antioxidant peptides and by-products, which is applied in the field of extraction of active components of marine plants, preparation of laver antioxidant peptides and comprehensive utilization of by-products, can solve the problems of low price, less deep-processed products, and poor taste, and achieve economic value , small molecular weight, good thermal stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
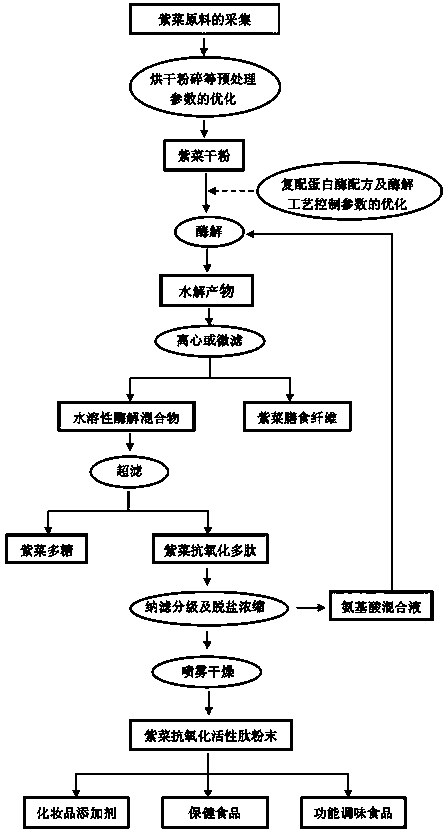
[0033] Example 1 Preparation of laver antioxidant peptide:
[0034] Crush and sieve Porphyra zebra and dry it for later use. Take 18g dried seaweed sample and dissolve it in 600mL Na with pH8.5 2 HPO 4 -KH 2 PO 4 In the buffer solution, in order to facilitate enzymatic hydrolysis of the laver by protease, the laver was treated in a boiling water bath for 15 minutes before the enzyme was added to destroy the protein structure of the laver and expose more enzyme cleavage sites. Add neutral enzyme 1.48×10 4 U / g, aminopeptidase 1.30×10 2 U / g, adjust the pH to keep 8.5 during the enzyme addition, boil the enzyme after 6 hours of enzymolysis, centrifuge at 8000r / min, 4°C for 15min, take the supernatant and dilute to 1.6 times, and pass the diluted enzymolysis solution to the molecular weight cut-off It is a 10kDa ultrafiltration membrane, which are ultrafiltration retentate and ultrafiltration permeate respectively. The ultrafiltration permeate is then passed through a nanofi...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Embodiment 2 Separation and performance measurement of laver polysaccharide:
[0039] Porphyra polysaccharides have a relatively large molecular weight and are trapped in the ultrafiltration retentate after being treated by a 10kDa ultrafiltration membrane. The polysaccharide concentration was determined by the phenol-sulfuric acid method and the salicylic acid method. The results showed that about 87% of polysaccharides were retained by ultrafiltration, and the extraction rate of polysaccharides in Porphyra zebra was about 55%;
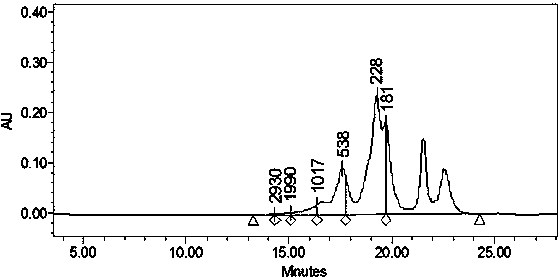
[0040] Determination of the molecular weight range of polysaccharides by high performance liquid chromatography: Glucose standards with different molecular weights were prepared into a standard solution with a concentration of 1 mg / mL, filtered through a 0.22 μm membrane, and loaded according to the following chromatographic conditions: Chromatographic column: Shodex Sugar KS 804, mobile phase: pure water, flow rate: 1mL / min, column temperatu...
Embodiment 3
[0042] The determination of the content of embodiment 3 dietary fiber:
[0043] According to the analysis method of AOAC 991.43-1994, the content of total dietary fiber, soluble and insoluble dietary fiber in laver residue is determined. The specific steps are as follows: the sample is subjected to enzymatic digestion with high-temperature amylase, protease, and glucosidase to remove protein, starch, and enzyme After solution, the sample solution is ethanol precipitated and filtered, and the residue is washed with ethanol and acetone, dried and weighed to obtain the total dietary fiber (TDF) content, which needs to be corrected by measuring the protein and ash content. Among them, the protein and ash content were measured by the national standard method. The determination of insoluble dietary fiber (IDF) and soluble dietary fiber (SDF) is to directly filter the sample after enzymatic hydrolysis, and weigh the residue after drying to obtain IDF; the filtrate is precipitated wit...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com