Method for establishing monoclonal mesenchymal stem cells and its application
A kind of stem cell and cell technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of no cell surface labeling, complicated operation, influence of cell activity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1 Cell Separation and Culture
[0036] Different tissues derived from animals were digested with collagenase, after centrifugation, and the supernatant was removed, the collected cells were washed twice with PBS and then cultured with complete medium. Change the medium and remove the rest of the suspended cells to obtain all the adherent cells. The complete medium includes α-MEM culture medium, 10% fetal bovine serum.
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2 Cell transfection
[0038] The newly isolated MSCs were adhered to the wall and cultured for 24 hours, and continued to culture after changing the medium. Before transfection, they were cultured in an antibiotic-free medium. After the cells were 70%-80% confluent, the plasmid containing the Nanog promoter and the control plasmid were dissolved separately. In 50 microliters of serum-free Opti-MEMI medium, mix well. Dissolve an appropriate amount of liposomes in 50 microliters of serum-free Opti-MEM Ⅰ culture medium, and mix well. Incubate for 5 min at room temperature. The above two solution mixtures were then mixed (total volume 100 µl). Mix gently and incubate at room temperature for 25 minutes, add 100 microliters of the complex and appropriate amount of medium to each well of a 24-well plate. After adding the complex for 4-6 hours, replace the medium with complete medium, and keep the cells at 37 degrees 5% CO 2 After culturing in the incubator for 48 h...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3 Cell Sorting
[0041] After digestion and centrifugation with trypsin, the adherent cells after successful transfection were transferred from the culture dish with PBS, and after washing, they were detected by a FACS flow cytometer under an argon laser at 488 nm. 10,000 cells in the sample were analyzed using Cell-Quest software (Weasel V2.3.1).
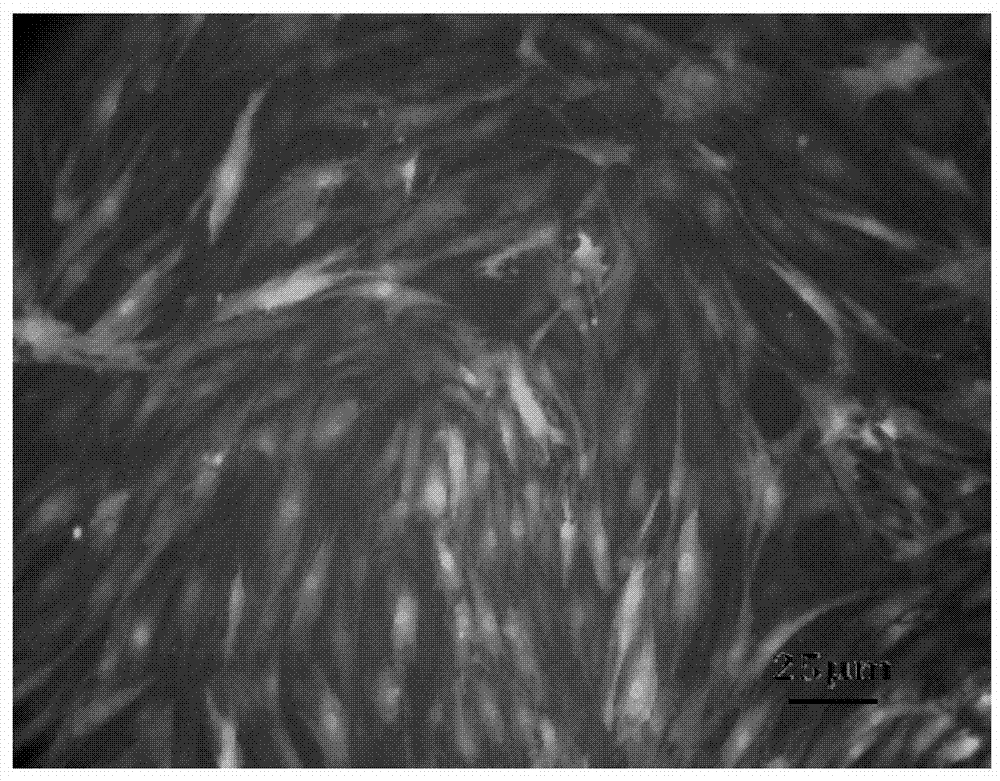
[0042] The sorted single cells were cultured in a 96-well plate at 37°C and 5% CO using the above-mentioned complete medium. 2 Cultivate under the same conditions and change the medium every 3 to 5 days. It can be seen from the observation that the growth of individual cloned cells is relatively slow in the early stage, but after a week, the cells grow rapidly after forming a colony group, showing a typical mesenchymal stem cell-like growth, showing a spindle shape , swirl-like, radial growth, the results are shown in image 3 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com