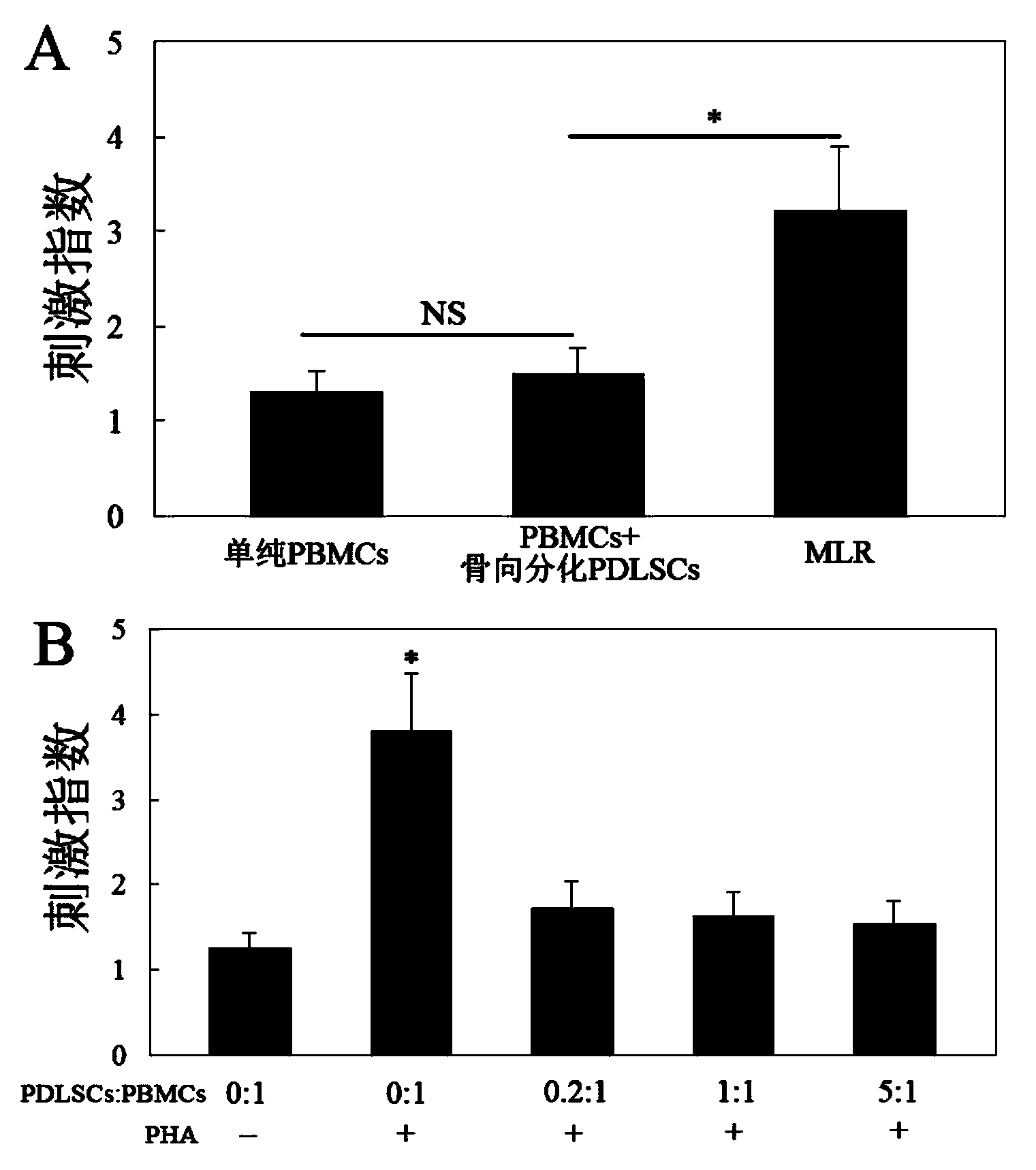
Osteogenic induction method of periodontal ligament stem cells (PDLSCs)
A technology of periodontal ligament stem cells and inducing differentiation, applied in the fields of medicine and cell biology, can solve problems such as inability to cure periodontitis, and achieve the effects of promoting development, realizing reuse, and expanding sources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Example 1: Isolation and cultivation of human PDLSCs:
[0021] Extracted normal third molars or premolars of healthy patients (provided by the Department of Stomatology, Yidu Central Hospital, Weifang City) were selected, and PDLSCs were isolated and cultured according to the methods reported in the literature. The brief description is as follows: immediately put the extracted teeth into a sterile centrifuge tube filled with pre-cooled PBS, transfer them into the cell chamber, and isolate and culture PDLSCs within 24 hours. Gently peel off the periodontal tissue around the teeth, take the periodontal tissue in the middle, wash it repeatedly with PBS, cut it into pieces, put it in the digestive solution containing type Ⅰ collagenase (3g / L) and neutral protease (4g / L), Digest at 37°C for 1 hour, collect cells through a 70 μm cell sieve, centrifuge at 1000 rpm for 10 minutes, and resuspend with culture medium to form a single cell suspension. Inoculate the single cell sus...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Example 2: Osteotropic differentiation of PDLSCs
[0023] The PDLSCs obtained in Example 1 were inoculated in the osteotropic differentiation medium, and the inoculum size was 2.0×10 4 / cm 2 , and then placed in a 37°C cell culture incubator for induction and differentiation for 2 weeks. –3 mol / L icariin, 10 -6 mol / L emodin, 10 -5 mol / L Puerarin, 10 -6 mol / L berberine, 10 -5 mol / L eucommia alcohol extract, 2mg / L drynaria total flavonoids, 4mg / mL psoralen, 4mg / mL oleanolic acid and 10 -6 mol / L Dipsacus saponin Ⅵ.
[0024] The formulation of the basal medium in the above osteotropic induction differentiation medium is α-MEM.
Embodiment 3
[0025] Example 3: Detection of osteogenic differentiation of PDLSCs
[0026] The following three methods were used to detect the osteotropic induced PDLSCs of Example 2:
[0027] 1. Detection of alkaline phosphatase activity:
[0028] The alkaline phosphatase activity kit was used to detect PDLSCs 1 day, 3 days, and 7 days after osteotropic induction. The specific operation was carried out according to the instructions of the kit.
[0029] Results: The alkaline phosphatase activity of PDLSCs was detected after 1 day, 3 days, and 7 days of osteotropic induction, and it was found that the alkaline phosphatase activity of PDLSCs and uninduced PDLSCs on the 1st day of osteotropic induction was similar, and there was no significant difference between the two, while The alkaline phosphatase activity of PDLSCs on the 3rd and 7th day of osteotropic induction was significantly higher than that of uninduced PDLSCs, indicating that PDLSCs had obvious osteogenic differentiation.
[0030]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com