Injectable crosslinked hyaluronic acid gel and preparation method thereof
A technology for cross-linking hyaluronic acid and hyaluronic acid, which is applied in the fields of medical science and prostheses, can solve the problems of inability to effectively remove the cross-linking agent, different chemical environments, calcification of implants, etc., and achieve good cosmetic repair effect, Uniform gel morphology and the effect of controlling the degree of emulsification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
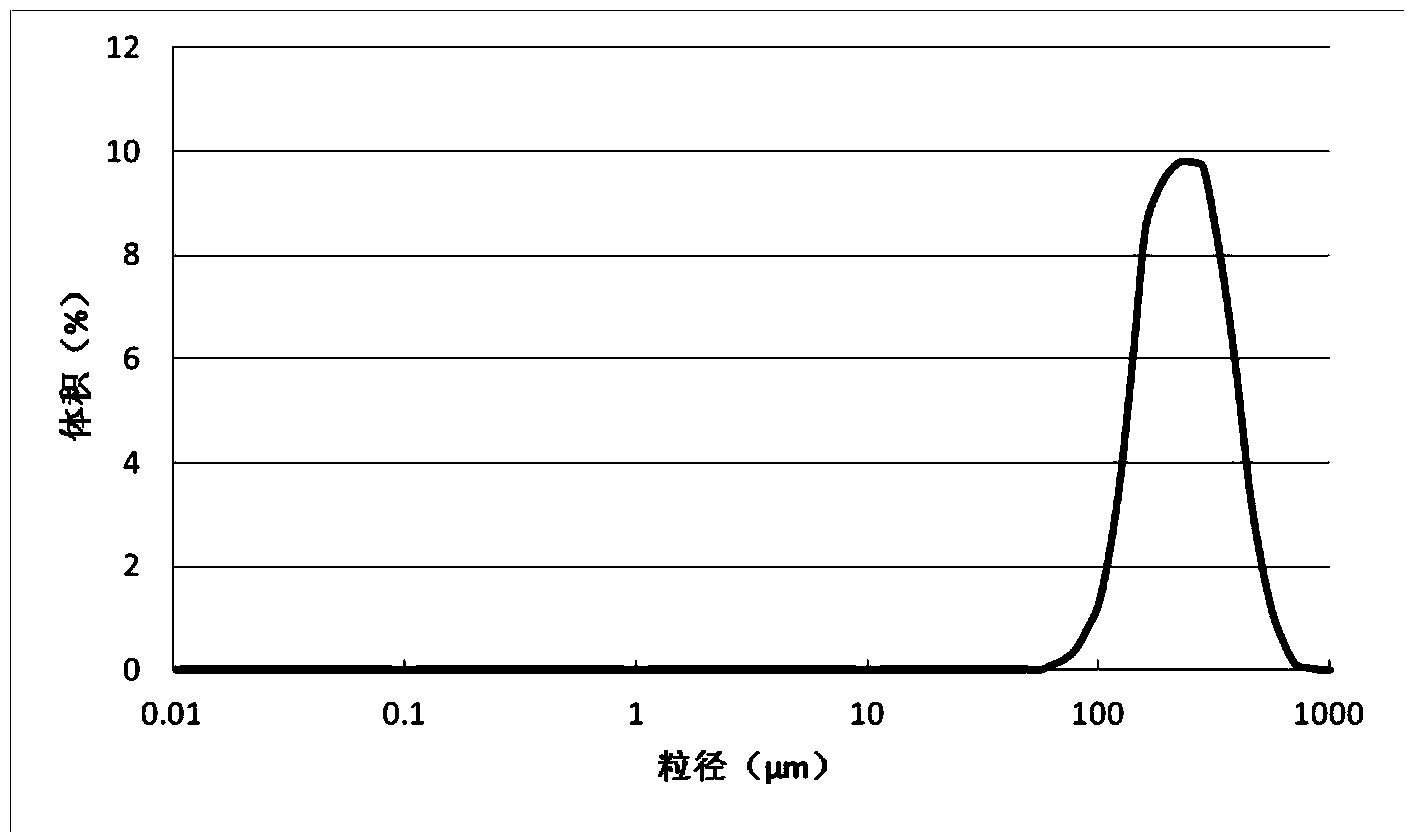
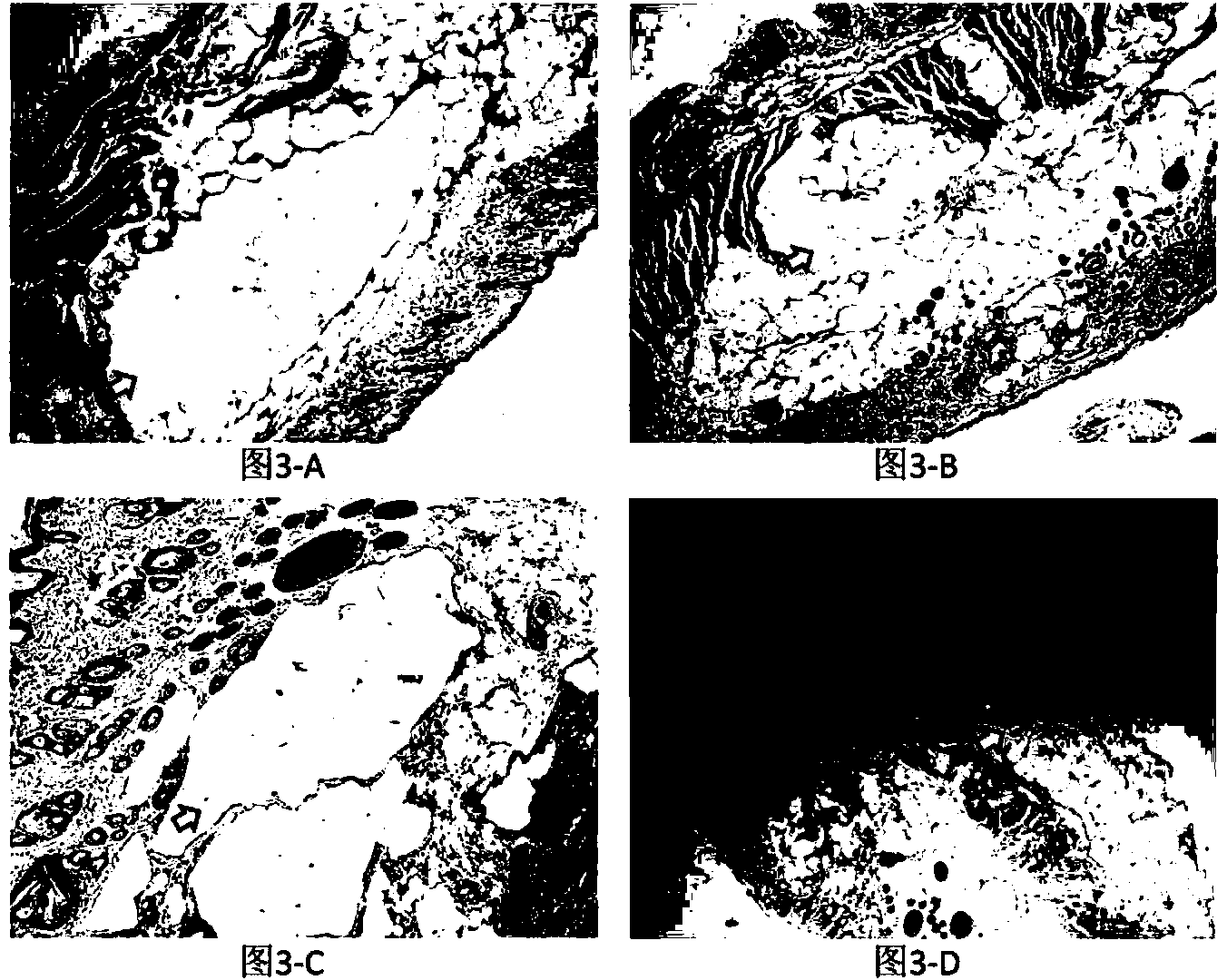
[0053] Step 1. Cross-linking treatment: Dissolve hyaluronic acid dry powder (molecular weight: 300,000 Da) in aqueous sodium hydroxide solution to form a hyaluronic acid solution with a concentration of 20g / L and a pH of 9, then add 1% hyaluronic acid mass The 1,6-hexanediol diglycidyl ether was cross-linked at 40°C for 2 hours to prepare a hyaluronic acid gel.
[0054] Step 2, emulsification and cross-linking granulation: heat and dry the hyaluronic acid gel obtained in step 1 at -0.08MPa, 40°C under vacuum, then add aqueous sodium hydroxide solution to re-dissolve, and then add the same hyaluronic acid gel as in step 1 1,6-Hexanediol diglycidyl ether is mixed evenly to form a mixed solution, and then the mixed solution is mixed with medical grade white oil at a ratio of 1:5, and 0.1g / L cetyl trimethazine is added to the medical grade white oil Ammonium nitrate and 0.2g / L polyethylene glycol, continuously stirred at 40°C for 2 hours, and the stirring rate was 10rpm, so that t...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Step 1. Cross-linking treatment: Dissolve hyaluronic acid dry powder (molecular weight 3 million Da) in potassium hydroxide aqueous solution to form a hyaluronic acid solution with a concentration of 200g / L and a pH of 13, and then add 10% hyaluronic acid mass Resorcinol diglycidyl ether was cross-linked at 60° C. for 10 hours to prepare a hyaluronic acid gel.
[0061] Step 2, emulsification and cross-linking granulation: heat and dry the hyaluronic acid gel obtained in step 1 under the conditions of 0.1MPa and 60°C under vacuum, then add potassium hydroxide aqueous solution to redissolve, and then add the same sodium hydroxide as in step 1. Stir quinone diglycidyl ether evenly to form a mixed solution; then mix the mixed solution with medical grade simethicone at a ratio of 1:10, add 0.5g / L alkyl sulfate and 2g of medical grade simethicone / L polyglycerol ester, continuously stirred and reacted at 60°C for 4 hours, and the stirring rate was 100rpm, so that the hyaluron...
Embodiment 3
[0067] Step 1. Cross-linking treatment: Dissolve hyaluronic acid dry powder (molecular weight 1 million Da) in ammonia solution to form a hyaluronic acid solution with a concentration of 100g / L and a pH of 11, and then add 5% hyaluronic acid mass of 1 , 4-butanediol diglycidyl ether, cross-linking at 50° C. for 6 hours to prepare a hyaluronic acid gel.
[0068] Step 2, emulsification and cross-linking granulation: heat and dry the hyaluronic acid gel obtained in step 1 under the conditions of 0.01 MPa and 50°C under vacuum, then add ammonia solution to re-dissolve, and then add the same 1,4 -Butanediol diglycidyl ether is stirred evenly to form a mixed solution, and then the mixed solution is mixed with olive oil at a ratio of 1:8. 1g / L polyethylene glycol is added to the olive oil, and the reaction is continuously stirred at 50°C For 3 hours, the stirring rate was 55 rpm, so that the hyaluronic acid solution formed an emulsion in the organic phase, forming hyaluronic acid par...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com