Method for treating methylene blue dye wastewater
A methylene blue dye and wastewater technology, which is applied in the fields of energy wastewater treatment, chemical instruments and methods, biological water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of poor oxidation ability, selective oxidation, difficult treatment, large amount of adsorbent, etc. The effect of increasing the amount, improving the processing effect, and simple preparation method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
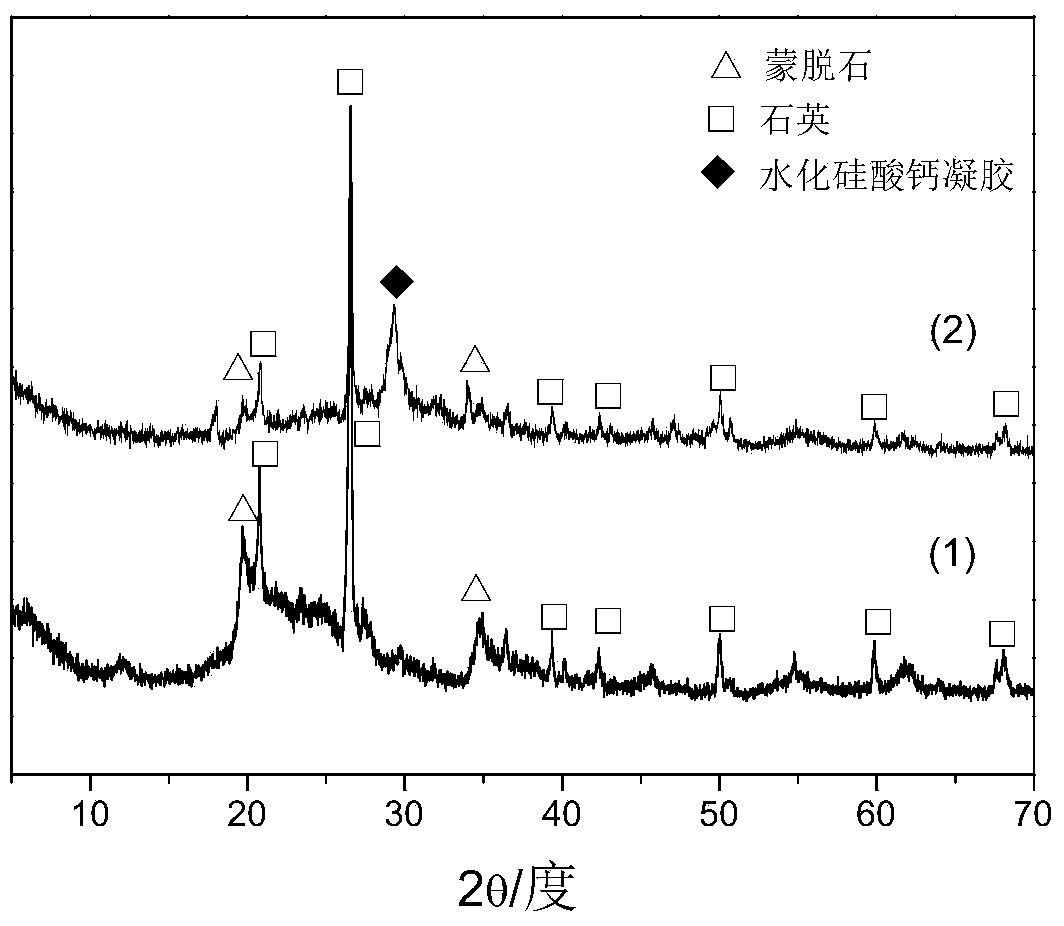
[0036] In the first step, mix 3g of diatomite dried and passed through a 80-mesh sieve, 1g of commercially available industrial grade calcium hydroxide, and 1ml of deionized water, and mix the mixture with a W270×D200 ×H450 specification tablet press, press molding at 20MPa, demould, obtain the sample after molding. Put the sample into a high-pressure hydrothermal kettle, control the reaction temperature to 200°C, and the reaction time to 24h. The sample obtained after the hydrothermal reaction is detected by X-ray diffraction analysis method as follows: figure 2Shown: figure 2 (1) is the XRD pattern of diatomite raw material, (2) is the XRD pattern of C-S-H after hydrothermal synthesis. It can be seen from the figure that the main components of diatomite raw material are quartz (Quartz) and montmorillonite (Montomorillonite), after hydrothermal synthesis, the composition of the obtained diatomite-based porous adsorbent retains the original diatomite (quartz), and generates...
Embodiment 2
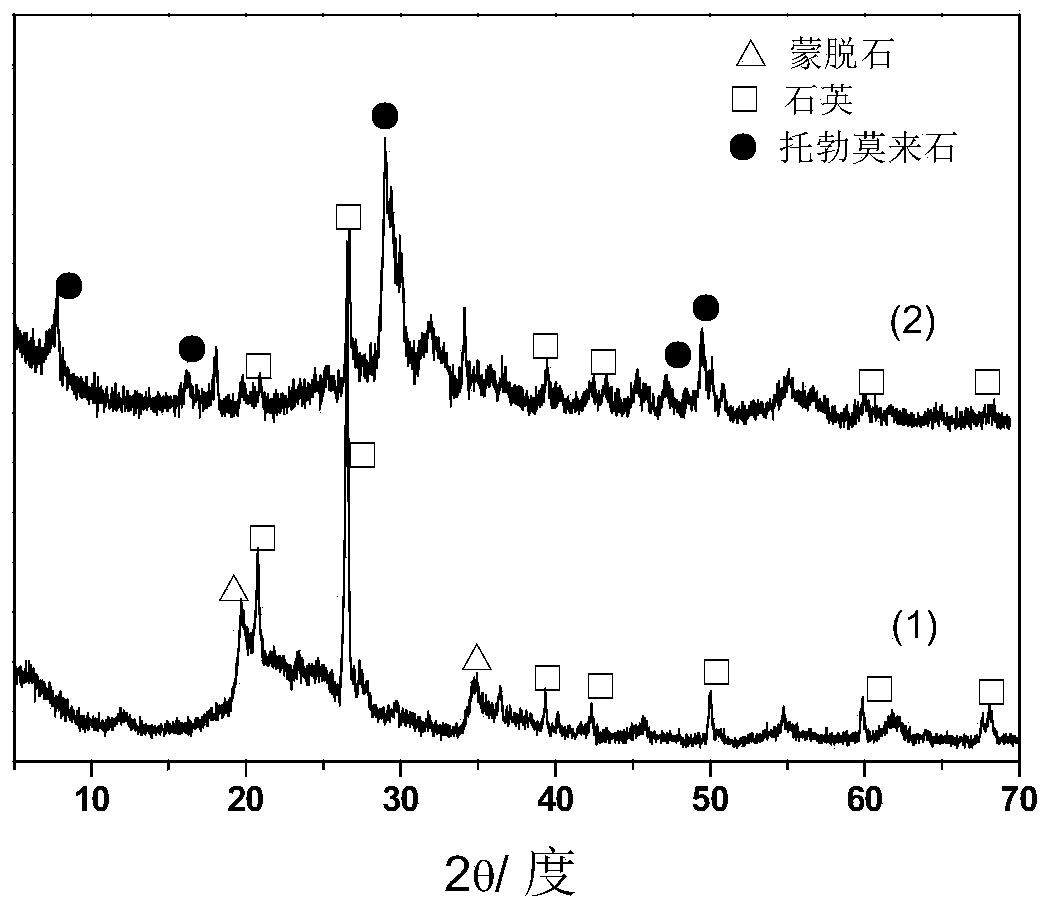
[0044] The first step, the diatomite of embodiment 1, 2.15g calcium hydroxide, 0.5g sodium hydroxide, 1.5ml deionized water are mixed evenly, and the mixture is compressed with 15MPa under the tablet press; The samples were placed in a high-pressure hydrothermal kettle for reaction. The reaction temperature is controlled at 175°C, and the reaction time is 12 hours. The samples obtained after the hydrothermal reaction are tested as follows: image 3 , where (1) is the XRD pattern of diatomite raw material, (2) is the XRD pattern of diatomite-based porous adsorbent after hydrothermal synthesis, from image 3 It can be seen that the main components of diatomite raw materials are quartz and montmorillonite. After hydrothermal synthesis, the diatomite-based adsorbent obtained has the original diatomite (quartz) in its composition. The optimized mineral tobermullite was generated. The structure seen by the scanning electron microscope is as follows Image 6 As shown, tobomullite ...
Embodiment 3
[0048] In the first step, 3 g of dried diatomite, 0.9 g of calcium hydroxide, 0.4 g of sodium hydroxide and 1.3 ml of deionized water are uniformly mixed, and the mixture is pressed into shape under a tablet machine at 30 MPa; The molded sample was placed in a high-pressure hydrothermal kettle, and 1 / 7 of the volume of deionized water was added to the reaction kettle, so that the sample did not directly contact with the water. The reaction temperature is controlled at 200°C, and the reaction time is 24 hours. The sample obtained after the hydrothermal reaction is detected as an analcite diatomite-based porous adsorbent, please see Figure 4 , Figure 4 The XRD pattern of diatomite-based adsorbent and diatomite optimized for hydrothermal synthesis of analcime, where (1) is the XRD pattern of diatomite raw material, (2) is the XRD pattern of diatomite-based adsorbent after hydrothermal synthesis From the XRD diagram, it can be seen from the figure that the main components of di...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Flexural strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Flexural strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com