Immobilized 3-phenoxy benzoic acid degrading enzyme and its preparation method
A phenoxybenzoic acid, immobilized enzyme technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microorganism-based methods, immobilized on/in organic carriers, etc., can solve the problem of immobilization of 3-PBA degrading enzymes not seen Enzyme research and other issues, to achieve the effect of easy industrial production and preparation, good stability and high degradation rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1: Preparation of immobilized 3-phenoxybenzoic acid degrading enzyme beads and enzyme activity assay method.
[0023] A single colony of SC-1 was picked from the plate, streaked on the LB slant medium, and incubated at 30°C for 24 hours. Use sterile saline to elute the SC-1 bacterial lawn from the slant culture medium and mix it to make a bacterial suspension, inoculate 1.0mL of the SC-1 bacterial suspension (the bacterial concentration is about 10 8 cfu / mL) in 30 mL liquid fermentation medium, 30 ° C, 180 r / min constant temperature shaking culture for 24 h to obtain seed liquid. Inoculate the seed solution at 3% (v / v) into a 10L fermenter (fermentation medium: 1.5g ammonium sulfate; 0.5g magnesium sulfate; 0.5g sodium chloride; 0.5g potassium dihydrogen phosphate; 1.5g dipotassium hydrogen phosphate ; glucose 5.0g; yeast extract powder 5.0g; water 1000mL; adjust the pH value to 7.0; add 3-PBA to 100μg / mL, and sterilize at 121°C for 15min.), the filling coeffic...
Embodiment 2
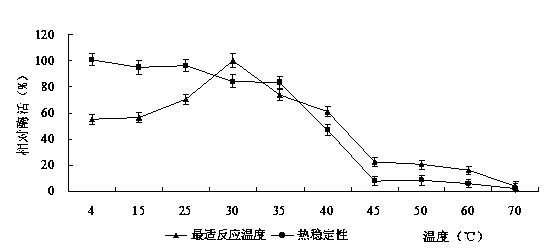
[0029] Example 2: Determination of the optimal reaction temperature and thermal stability of the immobilized enzyme degrading 3-phenoxybenzoic acid.
[0030] Weigh 0.5 g of immobilized enzyme beads, add 0.5 mL of substrate buffer containing 20 μg / mL 3-phenoxybenzoic acid, the buffer is 0.02 mol / LTris-HCl buffer at pH 7.0, and mix well. They were respectively placed at 4°C, 15°C, 25°C, 30°C, 35°C, 40°C, 45°C, 50°C, 60°C, and 70°C for 30 minutes with shaking. The reaction was terminated with acetonitrile, the residual amount of 3-phenoxybenzoic acid was detected, and the optimum reaction temperature of the immobilized enzyme beads was determined by the relative enzyme activity. After the immobilized enzyme beads were incubated in a water bath at different temperatures for 1 h, the substrate buffer was added and shaken at the optimum reaction temperature for 30 min to determine the residual enzyme activity and investigate the thermal stability of the immobilized enzyme beads.
...
Embodiment 3
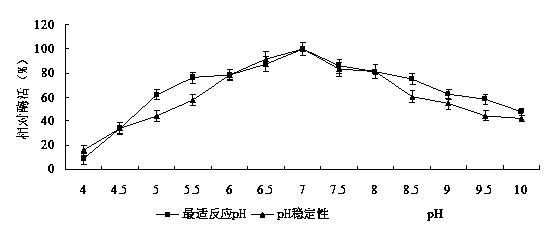
[0032] Example 3: Determination of the optimal reaction pH value and pH stability of immobilized enzyme degrading 3-phenoxybenzoic acid.
[0033] Weigh 0.5 g of immobilized enzyme beads and add 0.5 mL of 20 μg / mL 3 -Phenoxybenzoic acid substrate buffer solution, reacted at 30°C for 30 min, detected the residual amount of 3-phenoxybenzoic acid, and determined the optimal reaction pH of the immobilized enzyme beads from the relative enzyme activity. The immobilized enzyme beads were added to buffer solutions with different pH, and stood in a refrigerator at 4°C for 1 hour. Remove the buffer by filtration, wash and filter with normal saline, repeat once, blot the water on the surface of the immobilized enzyme, measure the residual enzyme activity at the optimum pH at 30°C, and investigate the pH stability of the immobilized enzyme beads.
[0034] The result is as image 3 The optimal reaction pH and pH stability curve of the immobilized 3-phenoxybenzoate degrading enzyme shown,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com