Flowability testing method and device for zirconium base block amorphous alloy melt
A technology of amorphous alloy and testing device, applied in the field of zirconium-based bulk amorphous alloy melt fluidity testing and device field
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
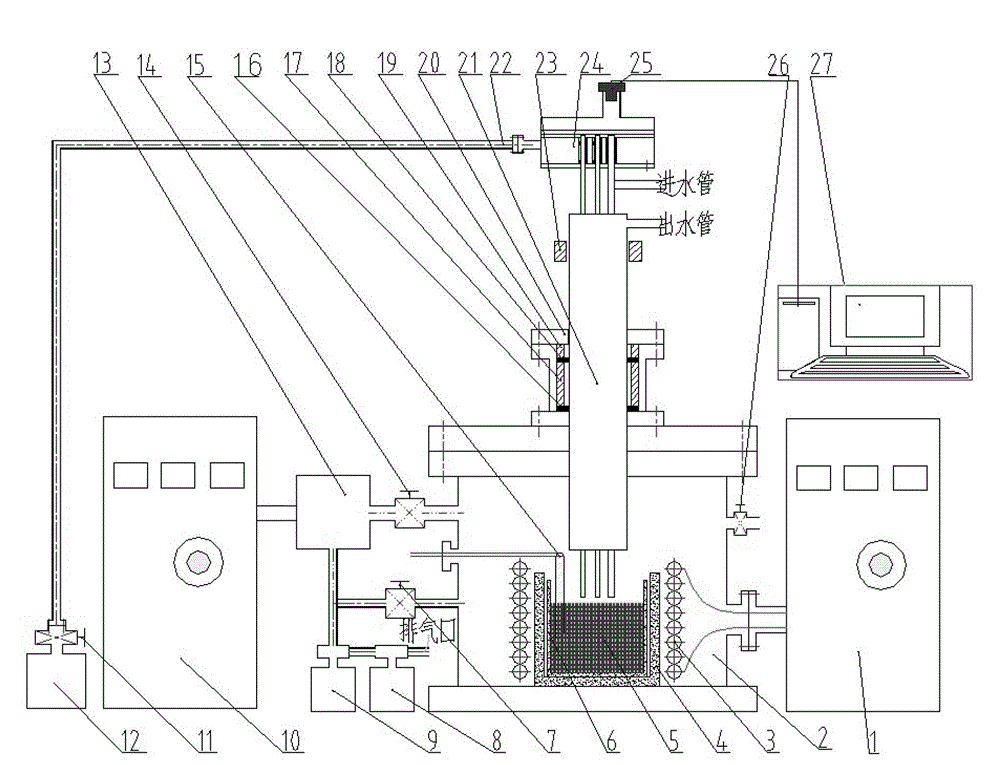
[0030] 500 grams of Zr to be melted in a non-consumable arc melting furnace 55 Ti 11 Cu 8 Ni 8 be 18 Put the bulk amorphous alloy ingot into the alumina ceramic crucible (manufacturer: Haili, Kaiping District, Tangshan City) of an intermediate frequency induction vacuum melting furnace (model: YZZ-multifunctional melting furnace, manufacturer: Shenyang Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd., Chinese Academy of Sciences) De pottery factory), close the furnace lid. Adjust the height of the stainless steel suction casting tube in the fluidity testing device through the lifting and locking mechanism and lock it. Then connect the intermediate frequency induction vacuum melting furnace and the cooling circulating water channel of the stainless steel suction casting pipe in the fluidity testing device, close all valves, switch on the main power supply of the vacuum mechanism, and turn on the mechanical pump to connect the melting furnace body and the fluidity testing device When the va...
Embodiment 2
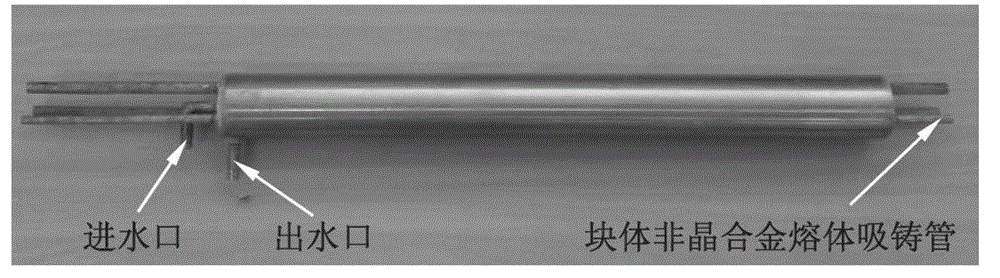
[0036] Take 500 grams of Zr melted in a non-consumable arc melting furnace 42 Ti 13 Cu 12.5 Ni 10 be 22.5 Bulk amorphous alloy ingot, repeat the operation of example 1, respectively obtain the bulk amorphous alloy cast bar that different lengths are coated with stainless steel tube, as image 3 As shown, the stainless steel tube that removes the outer layer of the bulk amorphous alloy cast rod by turning is used to test the amorphous structure, which is the flow length of the zirconium-based bulk amorphous alloy melt tested under different process parameters, The specific values are as follows:
[0037] Melt temperature 800°C, argon pressure 0.02MPa:
[0038] Melt temperature 850°C, argon pressure 0.025MPa:
[0039] Melt temperature 900°C, argon pressure 0.03MPa:
[0040] Through X-ray diffraction analysis and differential scanning calorimetry analysis (DSC analysis), the microstructure of the obtained zirconium-based bulk amorphous alloy is an amorphous structu...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Take 500 grams of Zr melted in a non-consumable arc melting furnace 38 Ti 14 Cu 13 Ni 11 be 24 Bulk amorphous alloy ingot, repeat the operation of example 1, respectively obtain the bulk amorphous alloy cast bar that different lengths are coated with stainless steel tube, as image 3 As shown, the stainless steel tube that removes the outer layer of the bulk amorphous alloy cast rod by turning is used to test the amorphous structure, which is the flow length of the zirconium-based bulk amorphous alloy melt tested under different process parameters, The specific values are as follows:
[0043] Melt temperature 800°C, argon pressure 0.02MPa:
[0044] Melt temperature 850°C, argon pressure 0.025MPa:
[0045] Melt temperature 900°C, argon pressure 0.03MPa:
[0046] Through X-ray diffraction analysis and differential scanning calorimetry analysis (DSC analysis), the microstructure of the obtained zirconium-based bulk amorphous alloy is an amorphous structure, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com